Biophysical Origins of the fMRI Signal
1Krembil Brain Institute, UHN, Canada, 2Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Synopsis
Keywords: Neuro: Brain function, Neuro: Brain connectivity, Contrast mechanisms: fMRI
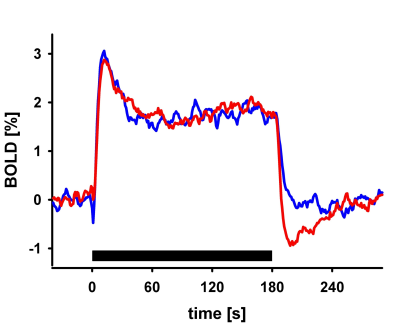
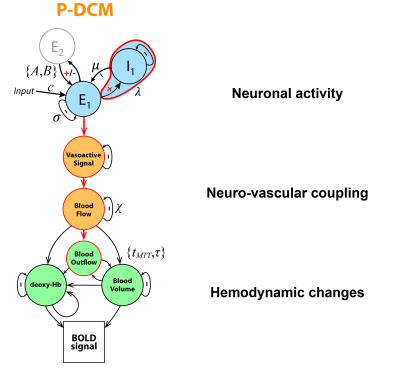
I will describe the physiological processes underlying BOLD signal and discuss the generative biophysical model and its time course properties: It primarily results from changes in oxygen metabolism, cerebral blood flow, and volume, which affect paramagnetic deoxygenated hemoglobin. The physiological origin of BOLD signal transients, such as the initial overshoot, steady-state activation, and post-stimulus undershoot, will be explored. Incorrect physiological assumptions in the generative model of the BOLD signal can lead to incorrect inferences about local neuronal activity and effective connectivity between brain regions. The author also introduces the recent laminar BOLD signal model.Abstract
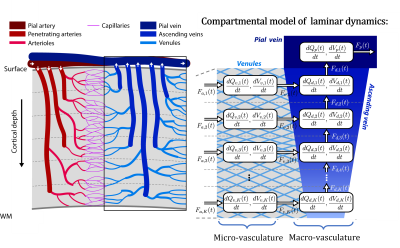
In this talk, I will provide an overview of the physiological processes that contribute to the observed BOLD signal (i.e., the generative biophysical model), including their time course properties. The BOLD signal is primarily determined by the change in paramagnetic deoxygenated hemoglobin, which results from combination of changes in oxygen metabolism, and cerebral blood flow and volume. Specifically, the physiological origin of the so-called BOLD signal “transients” will be discussed, including the initial overshoot, steady-state activation and the post-stimulus undershoot. I argue that incorrect physiological assumptions in the generative model of the BOLD signal can lead to incorrect inferences pertaining to both local neuronal activity and effective connectivity between brain regions. In addition, I introduce the recent laminar BOLD signal model, which extends the generative to cortical depths-resolved BOLD signals, allowing for laminar neuronal activity to be determined using high-resolution fMRI data.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Buxton, R.B., Uludağ, K., Dubowitz, D.J., Liu, T.T., 2004. Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation. Neuroimage 23 Suppl 1, S220-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.013
Buxton, R.B., 2021. The thermodynamics of thinking: connections between neural activity, energy metabolism and blood flow. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 376, 20190624. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0624
Friston, K.J., Harrison, L., Penny, W., 2003. Dynamic causal modelling. Neuroimage 19, 1273–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00202-7
Havlicek, M., Ivanov, D., Poser, B.A., Uludag, K., 2017a. Echo-time dependence of the BOLD response transients - A window into brain functional physiology. Neuroimage 159, 355–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.07.034
Havlicek, M., Ivanov, D., Roebroeck, A., Uludağ, K., 2017b. Determining Excitatory and Inhibitory Neuronal Activity from Multimodal fMRI Data Using a Generative Hemodynamic Model. Front Neurosci 11, 616. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00616
Havlicek, M., Roebroeck, A., Friston, K., Gardumi, A., Ivanov, D., Uludag, K., 2015. Physiologically informed dynamic causal modeling of fMRI data. Neuroimage 122, 355–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.07.078
Havlicek, M., Roebroeck, A., Friston, K.J., Gardumi, A., Ivanov, D., Uludag, K., 2017c. On the importance of modeling fMRI transients when estimating effective connectivity: A dynamic causal modeling study using ASL data. Neuroimage 155, 217–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.017
Havlicek, M., Uludağ, K., 2020. A dynamical model of the laminar BOLD response. Neuroimage 204, 116209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116209
Uludağ, K., Blinder, P., 2018. Linking brain vascular physiology to hemodynamic response in ultra-high field MRI. Neuroimage 168, 279–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.02.063
Uludag, K., Havlicek, M., 2021. Determining laminar neuronal activity from BOLD fMRI using a generative model. Prog Neurobiol 207, 102055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102055
Uludağ, K., Müller-Bierl, B., Uğurbil, K., 2009. An integrative model for neuronal activity-induced signal changes for gradient and spin echo functional imaging. Neuroimage 48, 150–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.051
Figures