How to Efficiently Travel Through k-Space
1Centre for Advanced Imaging, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Synopsis
Keywords: Physics & Engineering: Physics, Image acquisition: Reconstruction
MRI scanners measure and store MRI signals in the form of a 2D/3D data matrix, called k-space. K-space contains spatial frequency information which is acquired through phase and frequency encoding. The k-space spatial frequency information can be used to reconstruct MR images using inverse Fourier transform. This lecture will introduce the basic concepts of k-space in MR image acquisition and reconstruction. It will give an overview of different k-space trajectories and the effect of MRI acquisition parameters on k-space data. Finally, we will learn about k-space under-sampling and how it can be used in fast MR imaging.
Target Audience
Beginner to intermediate scientists or clinician-scientists, including trainees (students and fellows). While no prior knowledge is required, a basic understanding of the concepts behind nuclear spin would be beneficial.Learning Objectives
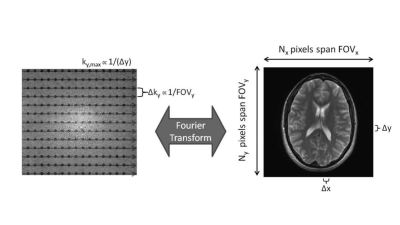
- Understand the basic concepts of k-space [1] and how to reconstruct MR images from k-space data using inverse Fourier Transform (see Figure 1)
- Understand how MR image acquisition parameters affect k-space and thereby the reconstructed images
- Learn about most common k-space trajectories [2]
- Learn about k-space under-sampling and how it can be used in fast MR imaging
- Learn about two main parallel imaging techniques (GRAPPA [3] & SENSE [4]) and how k-space data is acquired and processed in these techniques
Acknowledgements
I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose with regard to the subject matter of this presentation.References
[1] Mezrich R. A perspective on K-space. Radiology. 1995 May;195(2):297-315.
[2] Hennig J. K-space sampling strategies. European radiology. 1999 Jul 1;9(6):1020.
[3] Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002 Jun;47(6):1202-10.
[4] Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1999 Nov;42(5):952-62.
Figures