Nuclei & Magnetization: From Classical Physics to Quantum Mechanics
David E. J. Waddington1
1Image X Institute, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
1Image X Institute, Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Synopsis
Keywords: Physics & Engineering: Physics
MRI is often described as the most complicated medical imaging modality. Largely, this complexity arises from the quantum mechanical principles that underpin the interactions between nuclear spins and their environment. In this course, we will examine the classical response of single magnetic moments and spins in the presence of a magnetic field. We will then show how the Zeeman effect gives rise to quantized energy differences between nuclei in different spin angular momentum states and explain why classical precession physics suffices as a description for proton spin motion.Target audience
This course is targeted at scientists and clinicians who want to understand the physical principles that give rise to nuclear magnetization.Objectives and outcomes
At the completion of this course, students will understand why quantum mechanics is required to fully explain the phenomena of nuclear magnetization and precession in MRI. Further, students will be presented with a range of quantum/classical approaches to explaining MRI physics and will develop an understanding of when they can be applied.Content
The following topics will be covered at an introductory level:- The classical behaviour of magnetic moments in a static magnetic field (torque, angular momentum and precession).
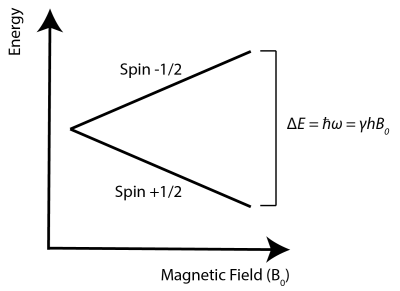
- The quantum mechanical origins of nuclear magnetization and Larmor precession (Zeeman splitting and energy level diagrams for spin-1/2 nuclei).
- Boltzmann distributions and the impact of temperature/magnetic fields on nuclear polarization.
- The ensemble interpretation of quantum mechanics and the emergence of classical behaviour.
- Rotating reference frames and spin nutation pulses.
Acknowledgements
D.E.J.W. is supported by a Cancer Institute NSW Early Career Fellowship 2019/ECF1015 and an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator Grant (2017140).References
[1] Brown, Robert W., Y-C. Norman Cheng, E. Mark Haacke, Michael R. Thompson, and Ramesh Venkatesan. Magnetic resonance imaging: physical principles and sequence design. John Wiley & Sons, (2014).
[2] Gerstein, Bernard C. "Rudimentary NMR: the classical picture." eMagRes (2007).