MT & ihMT
1CRMBM - CNRS, Aix Marseille University, UMR 7339, France
Synopsis
Keywords: Neuro: White matter, Contrast mechanisms: Microstructure, Contrast mechanisms: CEST & MT
This course provides an outline of the potential of magnetization transfer techniques for myelin imaging. In particular, this presentation will show how inhomogeneous magnetization transfer (ihMT) can overcome limitations of the basic MT contrasts (MTR, MPF) to provide more specific information related to myelin. The potential and scientific/technical challenges of these approaches for clinical applications are discussed.Course Summary
Microstructure is composed of (macro)molecules other than water that support tissue structure and function. These macromolecules contain an abundance of protons, but their restricted motion makes their T2’s too short for direct detection with conventional MRI imaging. Much of this invisible macromolecular proton pool can be however detected indirectly because it exchanges magnetization with mobile water protons 1. This magnetization exchange occurs by spin diffusion along the molecule to sites exposed to water and then either actual chemical exchange of protons between the water pool and the macromolecular pool or just magnetization transfer through spin-spin interactions (Fig. 1a) 2. Due to their very short T2, the macromolecular protons have a very broad spectrum, which can be selectively saturated using an off-resonance RF irradiation (Fig. 1b). The exchange of magnetization transfers the saturation to the mobile water pool resulting in a net decrease of the free protons magnetization, and therefore in a net decrease of the MR signal. Imaging of this saturation transfer from macromolecules is referred to as Magnetization Transfer (MT) imaging.In practice, MT effects can be assessed by calculating a metric, MTR (Magnetization Transfer Ratio), defined as the relative variation between a reference image (M0 – image acquired with no MT saturation power applied) and a MT image (MTw – image acquired with MT saturation power applied): MTR=1-MTw/M0 (Fig. 1c). However, the MTR depends on many factors including power and frequency-offset of the MT saturation pulses, pulse sequence details, the tissue relaxation time T1, and B1 inhomogeneities, thus limiting its ability to quantify the MT effects. To overcome limitations of MTR, quantitative approaches of magnetization transfer (qMT) have been developed and solved using a binary spin-bath model, allowing the measurement of several parameters including, the macromolecular proton fraction (MPF), the exchange rate between macromolecular protons and water protons (R) and the transverse relaxation time (T2B) 3 (Figs. 2a-c).
MTR and MPF demonstrated good sensitivity to myelinated tissues and myelin content and provided precious knowledge regarding pathological myelin in both animal models 4,5 and clinical studies on Multiple Sclerosis (MS) (Figs. 2d,e). MS is characterized among other things, by the presence of focal demyelinating lesions in white matter (WM). Demyelination, which causes a breakdown of the macromolecular structure, results in a decreased MTR 6–9 and MPF 3,10–12. Although sensitive to myelin, MTR and MPF are not specific markers since all other macromolecules also contribute to MTR and MPF and pathological processes other than demyelination, such as inflammation, gliosis, also induce MTR or MPF variations 13,14.
RF saturation of the macromolecular pool is more appropriately described by a thermodynamic model 15 based on Provotorov’s theory 16 that has been useful in accounting for the saturation effects occurring in solid spin systems. In this model, the macromolecular pool is divided into a Zeeman order (MZb, relaxation time T1), and a dipolar order (β, relaxation time T1D) that are effectively coupled in the presence of RF irradiation (power, ω12; frequency, ω) (Fig. 3a). Dipolar order effectively distorts the effective instantaneous absorption spectrum, or lineshape, of the motion-restricted Zeeman line, which becomes asymmetric in frequency (as seen in the first line of eqs. 2, Fig. 3a): the lineshape is more saturated on the side where the RF is applied while the opposite side is less saturated. Of note, if power is applied equally at positive and negative frequency (i.e., dual-offset saturation, ±ω) so that their absorption contributions add, the dipolar order effects cancel to the extent that the equilibrium line is symmetric17, usually a good first approximation. Without dipolar order effect, saturation of the Zeeman line is more efficient (eqs. 3, Fig. 3a). Dipolar order effects can thus be highlighted by subtracting an image acquired with dual-offset saturation from a single-offset saturated image (Fig. 3b), an experiment defined as inhomogeneous MT (ihMT) imaging18. IhMT is thus a refinement of MT that provides different contrast between tissues by isolating dipolar order effects within motion-restricted molecules that are weighted by the corresponding dipolar relaxation time, T1D19. Because dipolar order relaxation is slower in myelinated tissues than any other tissue observed, ihMT is highly sensitive to myelin (Fig. 3c).
Dual-offset saturation can be achieved by alternating the frequency of the saturation pulses on a timescale of τswitch 20,21. Varying τswitch allows deriving T1D-filtered ihMT signals with different dependence on T1D relaxation21. High-pass T1D-filtered ihMT signals, obtained by increase of τswitch, isolate long-T1D components (T1D>1ms) and provide very high specificity to myelination, unlike MTR 22 or MPF 23 for which, there is a significant contribution of short-T1D components (T1D<1ms) (Fig. 4a). IhMT is a relatively new technique whose physical concepts and contrast mechanisms were presented in a recent review 24. The very high specificity for myelin, combined with the ease of generating ihMT contrast have made ihMT an attractive method to assess myelin-related information in vivo (Fig. 4b,c), in the preclinical 25,26 and clinical contexts of demyelinating diseases 27–29, or in the context of aging studies 30,31.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Wolff SD, Balaban RS. Magnetization transfer contrast (MTC) and tissue water proton relaxationin vivo. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1989;10(1):135-144. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910100113
2. EDZES HT, SAMULSKI ET. Cross relaxation and spin diffusion in the proton NMR of hydrated collagen. Nature. 1977;265(5594):521-523. doi:10.1038/265521a0
3. Sled JG, Pike GB. Quantitative imaging of magnetization transfer exchange and relaxation properties in vivo using MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2001;46(5):923-931.
4. Dousset V, Grossman RI, Ramer KN, et al. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis: lesion characterization with magnetization transfer imaging. Radiology. 1992;182(2):483-491. doi:10.1148/radiology.182.2.1732968
5. Deloire-Grassin MS, Brochet B, Quesson B, et al. In vivo evaluation of remyelination in rat brain by magnetization transfer imaging. J Neurol Sci. 2000;178(1):10-16.
6. Gass A, Barker GJ, Kidd D, et al. Correlation of magnetization transfer ratio with clinical disability in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994;36(1):62-67. doi:10.1002/ana.410360113
7. Filippi M, Campi A, Dousset V, et al. A magnetization transfer imaging study of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1995;45(3 Pt 1):478-482.
8. Schmierer K, Scaravilli F, Altmann DR, Barker GJ, Miller DH. Magnetization transfer ratio and myelin in postmortem multiple sclerosis brain. Annals of Neurology. 2004;56(3):407-415. doi:10.1002/ana.20202
9. van Waesberghe JH, Barkhof F. Magnetization transfer imaging of the spinal cord and the optic nerve in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1999;53(5 Suppl 3):S46-48.
10. Tozer D, Ramani A, Barker GJ, Davies GR, Miller DH, Tofts PS. Quantitative magnetization transfer mapping of bound protons in multiple sclerosis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2003;50(1):83-91. doi:10.1002/mrm.10514
11. Davies GR, Tozer DJ, Cercignani M, et al. Estimation of the macromolecular proton fraction and bound pool T2; in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis. 2004;10(6):607-613. doi:10.1191/1352458504ms1105oa
12. Yarnykh VL, Bowen JD, Samsonov A, et al. Fast Whole-Brain Three-dimensional Macromolecular Proton Fraction Mapping in Multiple Sclerosis. Radiology. 2015;274(1):210-220. doi:10.1148/radiol.14140528
13. Vavasour IM, Laule C, Li DKB, Traboulsee AL, MacKay AL. Is the magnetization transfer ratio a marker for myelin in multiple sclerosis? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;33(3):713-718. doi:10.1002/jmri.22441
14. Newcombe J, Hawkins CP, Henderson CL, et al. Histopathology of multiple sclerosis lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging in unfixed postmortem central nervous system tissue. Brain. 1991;114 ( Pt 2):1013-1023.
15. Goldman M. Spin Temperature and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Solids. Oxford University Press.; 1970.
16. Provotorov B. Magnetic resonance saturation in crystals. Zh Exsp Teor Fiz. 1962;14:1126-1131.
17. Lee JS, Khitrin AK, Regatte RR, Jerschow A. Uniform saturation of a strongly coupled spin system by two-frequency irradiation. The Journal of chemical physics. 2011;134(23):234504.
18. Varma G, Duhamel G, de Bazelaire C, Alsop DC. Magnetization transfer from inhomogeneously broadened lines: A potential marker for myelin: Magnetization Transfer from Inhomogeneously Broadened Lines. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2015;73(2):614-622. doi:10.1002/mrm.25174
19. Varma G, Girard OM, Prevost VH, Grant A, Duhamel GD, Alsop DC. Interpretation of magnetization transfer from inhomogeneously broadened lines (ihMT) in tissues as a dipolar order effect within motion restricted molecules. Journal of Magnetic Resonance. 2015;260:67-76. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2015.08.024
20. Varma G, Girard OM, Prevost VH, Grant AK, Duhamel G, Alsop DC. In vivo measurement of a new source of contrast, the dipolar relaxation time, T1D , using a modified inhomogeneous magnetization transfer (ihMT) sequence. Magn Reson Med. 2017;78(4):1362-1372. doi:10.1002/mrm.26523
21. Hertanu A, Soustelle L, Le Troter A, et al. T 1D ‐weighted ihMT imaging – Part I. Isolation of long‐ and short‐T 1D components by T 1D ‐filtering. Magnetic Resonance in Med. 2022;87(5):2313-2328. doi:10.1002/mrm.29139
22. Duhamel G, Prevost VH, Cayre M, et al. Validating the sensitivity of inhomogeneous magnetization transfer (ihMT) MRI to myelin with fluorescence microscopy. NeuroImage. 2019;199:289-303. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.061
23. Hertanu A, Soustelle L, Buron J, et al. T 1D ‐weighted ihMT imaging – Part II. Investigating the long‐ and short‐T 1D components correlation with myelin content. Comparison with R 1 and the macromolecular proton fraction. Magnetic Resonance in Med. 2022;87(5):2329-2346. doi:10.1002/mrm.29140
24. Alsop DC, Ercan E, Girard OM, et al. Inhomogeneous magnetization transfer imaging: Concepts and directions for further development. NMR in Biomedicine. August 2022. doi:10.1002/nbm.4808
25. Hertanu A, Soustelle L, Buron J, et al. Inhomogeneous Magnetization Transfer (ihMT) imaging in the acute cuprizone mouse model of demyelination/remyelination. NeuroImage. 2023;265:119785. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119785
26. Lee CH, Walczak P, Zhang J. Inhomogeneous magnetization transfer MRI of white matter structures in the hypomyelinated shiverer mouse brain. Magnetic Resonance in Med. 2022;88(1):332-340. doi:10.1002/mrm.29207
27. Van Obberghen E, Mchinda S, le Troter A, et al. Evaluation of the Sensitivity of Inhomogeneous Magnetization Transfer (ihMT) MRI for Multiple Sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(4):634-641. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A5563
28. Rasoanandrianina H, Demortière S, Trabelsi A, et al. Sensitivity of the Inhomogeneous Magnetization Transfer Imaging Technique to Spinal Cord Damage in Multiple Sclerosis. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2020;41(5):929-937. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A6554
29. Zhang L, Wen B, Chen T, et al. A comparison study of inhomogeneous magnetization transfer (ihMT) and magnetization transfer (MT) in multiple sclerosis based on whole brain acquisition at 3.0 T. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2020;70:43-49. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2020.03.010
30. Geeraert BL, Lebel RM, Mah AC, et al. A comparison of inhomogeneous magnetization transfer, myelin volume fraction, and diffusion tensor imaging measures in healthy children. Neuroimage. September 2017. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.019
31. Taso M, Girard OM, Duhamel G, et al. Tract-specific and age-related variations of the spinal cord microstructure: a multi-parametric MRI study using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and inhomogeneous magnetization transfer (ihMT): Spinal Cord Microstructure Assessment Using DTI and ihMT. NMR in Biomedicine. 2016. doi:10.1002/nbm.3530
Figures
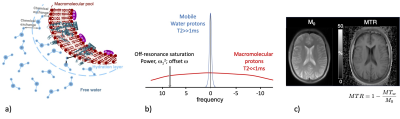
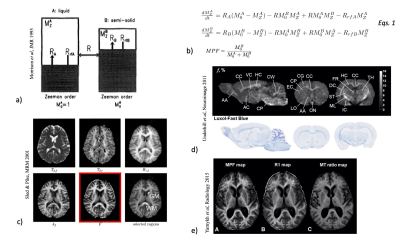
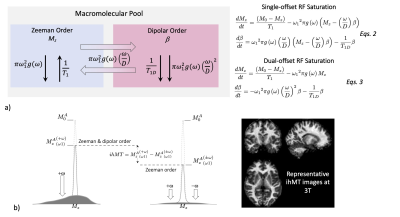
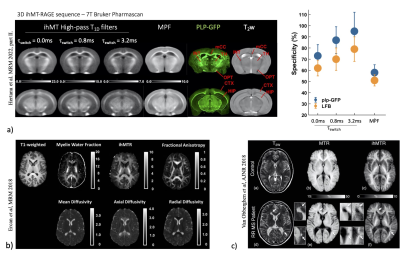
Fig.4: ihMT imaging. (a) Correlation of ihMT images obtained with different values of τswitch and MPF with myelin density obtained by Green Fluorescence microscopy and Luxol fast blue optical density. Specificity of ihMT T1D-filters and MPF for myelin. (b) Correlation of ihMT with other myelin-sensitive MRI techniques. (c) Application of ihMT on MS patients.