5415
Comparative evaluation of fiber number implementation of median nerve during wrist DTI technique : Neutral vs Superman position1radiology, Seoul National University Bundang hospital, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, Republic of
Synopsis
To find out whether this change in position affects the actual fiber tracking, we compared the number of fiber implementations in the median nerve in accordance to neutral and superman position. In 12 of the 14 cases, the superman position produced more fibers than in the neutral position. The reason for this thought is due to the fact that the wrist in the superman position is closer to the isocenter of the magnetic field. Other parameters may be important to optimize the images of wrist DTI, however positioning of the wrist should be considered first.
Purpose
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is useful for determining the intergrity and connectivity of nerve fibers. However, DTI technique must consider many effects such as magnetic field inhomogeneity, motion, incomplete fat suppression, aliasing and distortion. Especially in the case of wrist MRI, it is generally examined in neutral position (supine positioning with the arm alongside the torso), which may affect the fiber tracking accuracy as the wrist is positioned out of the isocenter. Due to this reason, wrist MRIs are often examined in superman position (prone positioning with the arm stretched over the head at the magnet's center)(Fig. 1). To find out whether this change in position affects the actual fiber tracking, we compared the number of fiber implementations in the median nerve in accordance to neutral and superman position.Methods
Both wrists of seven volunteers (7 males, mean age 30.5 years, age range 28-36 years) with normal wrists were included (14 cases in total). Philips Ingenia CX 3.0T MRI scanner was used with a ds Wrist 8channel coil. DTI was performed in the neutral position and the superman position, respectively and through tractography method, the number of fibers in the median nerve were quantitatively measured (Fig. 2). For neutral positioning, the wrist was placed in the coil so that it can be placed in a position that can fasten the wrist in place. For the superman positioning, the wrist coil was placed in the isocenter as much as position. Statistical analysis was performed to compare the number of fibers using the wilcoxon signed rank test. The parameters used for the DTI technique was Single-shot EPI, TR:4000ms, TE:79ms, FA:90°, NSA:5, FOV:100x100mm, Matrix:80x80, slice thickness:2mm, gap:0mm, number of slices:30, Fat suppression technique:SPIR, SENSE factor:2, b-value:0, 1000s/mm², number of directions:6, scan time:2minutes 42seconds. The purpose of this study is to compare the number of fibers according to the position change. In order to achieve a short scan time, the direction number is set to 6 directions, which is the minimum number of directions.Results
The average number of fibers in the neutral position was 171.86 ± 123.19 and 217.71 ± 139.44 at the superman position. In 12 out of 14 cases, the superman position produced more fibers and showed a statistically significant difference (p<0.05).Conclusions
In 12 of the 14 cases, the superman position produced more fibers than in the neutral position. The reason for this thought is due to the fact that the wrist in the superman position is closer to the isocenter of the magnetic field. DTI technique is based on the single-shot EPI method, which is more affected by magnetic field uniformity than other techniques. Even in the image, distortion and incomplete fat suppression occurred in the distal slice in the neutral position (Fig. 3). Other parameters may be important to optimize the images of wrist DTI, however positioning of the wrist should be considered first.Acknowledgements
I would like to thank you my famaily for love and continuous support.References
[1] A. Heckel, et al. PLOS ONE 2015 Jun 26;10(6):e0130833.
[2] Tina Jeon, et al. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 May;47(5):1171-1189.
[3] Jaana Hiltunen, et al. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005 Oct;116(10):2315-23.
[4] C. Khalil, et al. Eur Radiol. 2008 Oct;18(10):2283-91.
[5] Dan Stein, et al. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009 Mar;29(3):657-62.
Figures
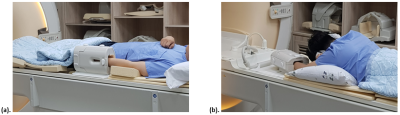
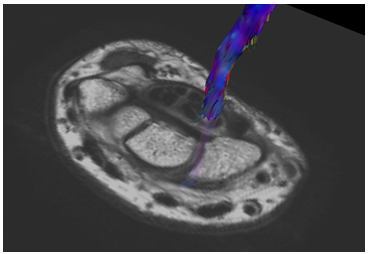
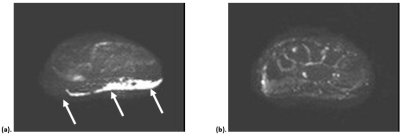
Fig. 3. (a): Image of the distal side of the wrist in the neutral position. Distortion and incomplete fat suppression have occurred compared to image of the superman position(b). (arrow)
(b): Image in the superman position of the same slice level.