5397
Comparison of 3D VANE XD Technique in T1 weighted images of Liver MRI with free-breathing technique as the Radial percentage parameter changes1Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Synopsis
Liver examination with MRI has greater diagnostic value than other tests and is one of the more frequent examinations.[1,2] However, the ability to obtain images with good diagnostic value only when the patient breathes constantly.[3] A non-Cartesian Radial method for the collection of K-Space data enables examinations with free breathing differently. 3D VANE XD technique can be applied with mDIXON, a technique with high SNR and excellent fat suppression.[4] Therefore, the difference in Radial percentage, the parameter that most effects motion artifacts in T1 3D VANE XD and 3D-FFE techniques were compared and optimal time versus efficiency value were compared.
Materials and Methods
In the statistical analysis of the evaluation results, we used the intraclass correlation coefficient to examine the inter-rater reliability and agreement.Correlation analysis was used to change score with increasing Percentage in 3D VANE XD technique. The Wilcoxon test was used to compare 3D FFE free-breathing(FB), breath-hold(BH) and 3D VANE XD images 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 (%) images.In order to compare time and effects it has on motion artifacts and other assessments during the examination with FB, 3D FFE images were obtained with FB and the images obtained by changing the Radial percentage value of the 3D VANE XD parameters to 100%, 200%, 300%, 400%, 500%, and 500%, all of the remaining parameters were constant(Table 1). The equipment used was Ingenia CX 3.0T of the Philips medical system, and the signal collection coil used was a body coil. The evaluation items included five things: the vanguard diagram of blood vessels, the outline of the liver dome and lower margin, uniformity of signal strength, motion artifacts and the degree of streak artifact. Five professional radiographers with more than five years of MRI experience objectively evaluated 10 healthy volunteers on a scale of 1 to 5.
① Sharpness of blood vessel: very poor=1, poor=2, fair=3, good=4, excellent=5
② Contour of liver dome, lower margin: very poor=1, poor=2, fair=3, good=4, excellent=5
③ Motion artifact: very severe=1, severe=2, little=3, very little=4, no=5 (The higher the score, the less Artifact)
④ Homogeneity of signal intensity: very poor=1, poor=2, fair=3, good=4, excellent=5
⑤ Streak artifact: very severe=1, severe=2, little=3, very little=4, no=5 (The higher the score, the less Artifact)
Results
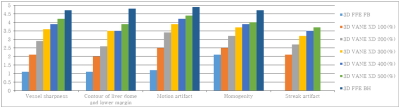
As a result of statistical analysis of the correlation coefficient within the hospital, a high degree of agreement of 0.956, 0.945, 0.953, 0.878, and 0.855 was shown in order of each evaluation item.With the 3D VANE XD technology, the correlation analysis of the evaluation score due to the increase in radial percentage showed a high degree of correlation of 0.8 or higher(Table 2). As a result of comparing 3D FFE BH, FB images and 3D VANE XD Percentage for each item and images, Vessel Sharpness items were all statistically significant (p<0.05). Contour of liver dome and lower margin showed no significant difference only in the 300% and 400% images (P = 0.317), and all the remaining comparative evaluations were statistically significant. (p<0.05) Motion artifact showed no significant difference only in 400% and 500% images (p=0.66), and there were statistically significant differences in all the remaining comparative evaluations.Homogeneity was not significantly different between 3D FFE FB images and 100% images (p=0.058), and there was no significant difference between 400% and 500% images (p=0.317). All remaining comparative evaluations were statistically significant (p<0.05). In the streak artifact, the 400% and 500% there were not significantly differences (p = 0.066), and all the remaining comparative evaluations were statistically significant(Table 3)(Figure 1).The higher the Radial percentage, the less motion artifacts appeared(Figure 2). Similarly, the Gradual percentage was reduced as the Radial percentage increased. The vessel sharpness assessment showed that the more Radial percentage, the better the shape of the blood vessels and the higher the resolution of the images(Figure 3). In addition, the image values proportionally higher than the rest. In the outline assessment of the liver dome and lower margin, there was no significant differences except for 300(%) with BH. Finally, with regards to the degree of homogeneity, satisfactory images were obtained as percentage increased, however there was no significant differences over 300-400(%).
Conclusion
This study shows that the appropriate Radial Percentage of 3D VANE XD technology is more than 300%. However, above a certain value, there was no significant difference in image quality compared to the image acquisition time, and it was not efficient. The higher the radial percentage (%), the better the quality of the image, but the longer the scan time, so 300 (%), which is about 3 minutes, is considered efficient and appropriate for clinical application. A previous related paper evaluated the diagnostic value of 3D Radial technique [5] but, this study presented an appropriate the Radial Percentage value. 3D VANE XD technique is used only for pediatric patients and patients who cannot cooperate breathing at all, and when all items are considered, it is most appropriate to use Radial Percentage 300 (%) as a base in clinical practice. In conclusion, if the results of the paper are applied according to the patient's condition and examination time, it is thought that efficient examination will be possible.Acknowledgements
I would like to thank my wife (ji-hye Ko) for love and continuous support.References
[1] Kenneth Coenegrachts, “Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver: New imaging strategies for evaluating focal liver lesions”, World J Radiol, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp.72-85, 2009
[2] Murakami T, Hori M, Kim T, Kawata S, Abe H, Nakamura H, “Multidetector row CT and MR imaging in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma”, Intervirology, Vol. 47, pp.209-226, 2004
[3] Yuusuke Hirokawa, Hiroyoshi Isoda, Yoji S. Maetani, Shigeki Arizono, Kotaro Shimada, Kaori Togashi, “Evaluation of motion correction effect and image quality with the periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction (PROPELLER) (BLADE) and parallel imaging acquisition technique in the upper abdomen”, JMRI, Vol. 28, No. 4, pp.957-962, 2008
[4] Bo-Woo Lee, Myung-Cheol Park, Jin-Hoi Lee, Ki-Jin Kim, Seok-Hwan Bae, “Evaluation of Usefulness of an m-DIXON Technique during an Abdomen MRI Examination : A Comparison with an e-THRIVE Technique” Journal of digital convergence, Vol. 12, No. 10, pp.385-39, 2014
[5] Chandarana H1, Block TK, Rosenkrantz AB, Lim RP, Kim D, Mossa DJ, Babb JS, Kiefer B, Lee VS, “Free-breathing radial 3D fat-suppressed T1-weighted gradient echo sequence: a viable alternative for contrast-enhanced liver imaging in patients unable to suspend respiration”, invest radiology, Vol. 46, No. 10, pp.648-653, 2011
Figures
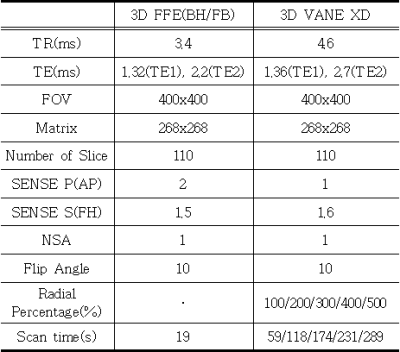
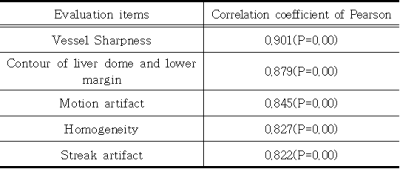
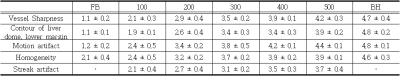
Table 3: Qualitative Assessment on 5-point scale
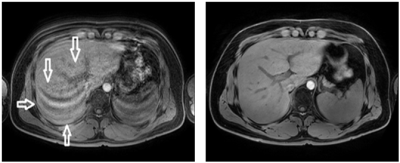
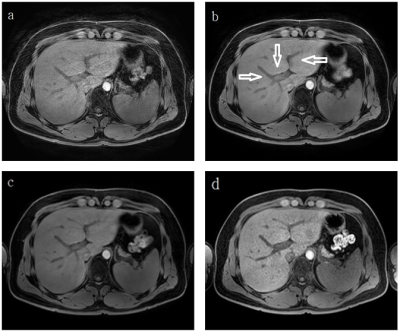
(a) : 3D VANE XD(100%), (b) : 3D VANE XD(300%), (c) : 3D VANE XD(500%), (d) : 3D FFE BH
Figure 3: It shows that the blood vessel's sharpness is gradually increasing with the increase in Radial Percentage.