5392
Diffusion imaging: multi-shell DTI on a whole-body 3T scanner versus a head-only MAGNUS 3T for traumatic brain injury evaluation1Radiology & Radiological Sciences, USUHS, Bethesda, MD, United States, 2Radiology, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, MD, United States, 3GE Research Center, Niskayuna, NY, United States
Synopsis
Diffusion imaging has progressed beyond standard DTI to mutli-shell and non-Gaussian techniques to improve upon the sensitivity of detecting multiple fiber angles in a voxel. Newer high-gradient scanners are able to further expand the capabilities of these advanced DTI sequences to help us improve upon the detection of complex fiber tracks in voxels, which is important in the evaluation and treatment of traumatic brain injury. These new technologies hold promise to improve our understanding of the movement of microcellular fluids.
Purpose:
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) can be classified as mild, moderate, or severe. This is based on the clinical presentation of a patient’s neurologic signs and symptoms (1). Research over the past 20 years has progressed to recognize TBI as a more complex disease process than previously thought. The advent of new scanners with high end gradients such as the Connectome (2), Compact (3) and MAGNUS MRI (4) scanners has been a mechanism to explore improvements in diffusion imaging made possible by the higher gradients systems. Once a human experiences a TBI, anatomical damage happens in the white matter tracks of the brain (5). The purpose of this project is to demonstrate the advantage of multi-shell diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) compared to single shell DTI, and how high gradient system scanners can improve the sensitivity of detecting damage from TBI compared to a standard clinical 3T MRI scanners.Teaching Points:
DTI is the application of motion encoding gradients to sensitize the signal response to the movement of water intra- and extra-cellularly (6). Diffusion-weighted imaging has been in clinical use for over 25 years (7), with most diagnostic 3T magnets in service using single shell (single b-value) DTI. To sensitize the signal response to more restricted diffusion in matter, multiple b-values shells are needed. Single-shell DTI gives us fractional anisotropy (FA), the main directional movement of water in a given voxel, mean diffusivity (MD), the average rate of diffusion across a voxel, axial diffusivity (AD), the diffusion along the main axis and radial diffusivity (RD), the diffusion along the 2 minor axes. These measurements help see the microstructure of white matter in each voxel. Both DWI and DTI are based on the Gaussian distribution of water diffusion in a biologic system (8), whereas techniques such as Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging (DKI) assume a non-Gaussian distribution of diffusion (9) that are more sensitive to the heterogeneity of microstructures as seen in brain injuries and is enabled by the multi-shell DTI.Single-shell diffusion imaging is limited in the brain because of the inability to resolve crossing fibers within a given voxel. Multi-shell DTI is needed to improve sensitivity to better discern orientation distribution function, especially in regions of fiber-crossings, and thus improve detection of multiple fiber orientations running through a voxel (Figure 1).
MAGNUS is a 3T MRI scanner with a gradient coil that delivers 200 mT/m at a maximum slew rate of 500 T/m/s. This allows for shorter TE times, shorter EPI echo spacing, reduced distortion and blurring while gaining higher SNR compared to a whole-body gradient system. This also allows for ultra-high b values (30,000 s/mm2). With the ultra-high b values, we can suppress the extra axonal water signal and can have a better estimate of intra axonal diffusivity (4,11). This is may be useful in assessing mild TBI, which has struggled to show changes on traditional 3T MRI scanners. Scanners with stronger gradients can deliver superior diffusion imaging as compared to conventional MRI scanners. With the ultra-high b-value diffusion, MAGNUS can offer a 50% increase in SNR (11). There are many potential applications for high gradient scanners that cannot be enabled in whole-body gradient systems, such as in visualizing flow interstitial fluid flow in the brain.
Summary
Diffusion imaging, namely DTI, has progressed beyond standard DTI to mutli-shell and non-Gaussian techniques to improve upon the sensitivity of detecting multiple fiber angles in a voxel. Newer high-gradient scanners are able to further expand the capabilities of these advanced DTI sequences to help us improve upon the detection of complex fiber tracks in voxels, which is important in the evaluation and treatment of traumatic brain injury. These new technologies hold promise to improve our understanding of the movement of microcellular fluids.Acknowledgements
Grant funding from NIH U01EB028976, NIH U01EB024450, CDMRP W81XWH-16-2-0054.
MAGNUS is not FDA approved, so all use of the MAGNUS MRI is considered research only. MAGNUS is an investigational product of GE Research Center.
Abstract Disclaimer
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the views of the authors and are not to be construed as the views of the U.S. Department of Defense, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, or the Uniformed Services University.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Author G.K. is an employee of the Geneva Foundation. Author T.K.F. is an employee of General Electric Research
References
1. Tenovuo O, Diaz-Arrastia R, Goldstein LE, Sharp DJ, van der Naalt J, Zasler ND. Assessing the Severity of Traumatic Brain Injury-Time for a Change? J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 4;10(1):148. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010148. PMID: 33406786; PMCID: PMC7795933.
2. Huang SY, Witzel T, Keil B, Scholz A, Davids M, Dietz P, Rummert E, Ramb R, Kirsch JE, Yendiki A, Fan Q, Tian Q, Ramos-Llordén G, Lee HH, Nummenmaa A, Bilgic B, Setsompop K, Wang F, Avram AV, Komlosh M, Benjamini D, Magdoom KN, Pathak S, Schneider W, Novikov DS, Fieremans E, Tounekti S, Mekkaoui C, Augustinack J, Berger D, Shapson-Coe A, Lichtman J, Basser PJ, Wald LL, Rosen BR. Connectome 2.0: Developing the next-generation ultra-high gradient strength human MRI scanner for bridging studies of the micro-, meso- and macro-connectome. Neuroimage. 2021 Nov;243:118530. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118530. Epub 2021 Aug 28. PMID: 34464739; PMCID: PMC8863543.
3. Camerucci E, Campeau NG, Trzasko JD, Gray EM, Bernstein MA, Cogswell PM, Shu Y, Foo TK, Huston J 3rd. Improved Brain MR Imaging from a Compact, Lightweight 3T Scanner with High-Performance Gradients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Jan;55(1):166-175. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27812. Epub 2021 Jun 28. PMID: 34184362; PMCID: PMC8806246.
4. Foo TKF, Tan ET, Vermilyea ME, Hua Y, Fiveland EW, Piel JE, Park K, Ricci J, Thompson PS, Graziani D, Conte G, Kagan A, Bai Y, Vasil C, Tarasek M, Yeo DTB, Snell F, Lee D, Dean A, DeMarco JK, Shih RY, Hood MN, Chae H, Ho VB. Highly efficient head-only magnetic field insert gradient coil for achieving simultaneous high gradient amplitude and slew rate at 3.0T (MAGNUS) for brain microstructure imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2020 Jun;83(6):2356-2369. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28087. Epub 2019 Nov 25. PMID: 31763726.
5. Bhushan C, Abad N, Madhavan R, Marinelli L, Morris HD, Hood MN, DeMarco JK, Shih RY, Zhu A, Kohls G, Fiveland E, Kenney K, Ho VB, Foo TKF. Subject-specific Analysis for Diffusion and Kurtosis Changes in mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) Patients. Proceedings of the ISMRM-ESMRMB Joint Annual Meeting, 2022, London, England, May 6-12, 2022.
6. Pasquini J, Firbank MJ, Ceravolo R, Silani V, Pavese N. Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Microstructural Abnormalities in Multiple System Atrophy: A Comprehensive Review. Mov Disord. 2022 Oct;37(10):1963-1984. doi: 10.1002/mds.29195. Epub 2022 Aug 29. PMID: 36036378.
7. Steven AJ, Zhuo J, Melhem ER. Diffusion kurtosis imaging: an emerging technique for evaluating the microstructural environment of the brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014 Jan;202(1):W26-33. doi: 10.2214/AJR.13.11365. PMID: 24370162.
8. Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005 Jun;53(6):1432-40. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20508. PMID: 15906300.
9. Palacios EM, Owen JP, Yuh EL, Wang MB, Vassar MJ, Ferguson AR, Diaz-Arrastia R, Giacino JT, Okonkwo DO, Robertson CS, Stein MB, Temkin N, Jain S, McCrea M, MacDonald CL, Levin HS, Manley GT, Mukherjee P; TRACK-TBI Investigators. The evolution of white matter microstructural changes after mild traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal DTI and NODDI study. Sci Adv. 2020 Aug 7;6(32):eaaz6892. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz6892. PMID: 32821816; PMCID: PMC7413733.
10. Shetty T, Nguyen JT, Cogsil T, Tsiouris AJ, Niogi SN, Kim EU, Dalal A, Halvorsen K, Cummings K, Zhang T, Masdeu JC, Mukherjee P, Marinelli L. Clinical Findings in a Multicenter MRI Study of Mild TBI. Front Neurol. 2018 Oct 23;9:836. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00836. PMID: 30405511; PMCID: PMC6206843.
11. Morris HD, Abad N, Madhaven R Bhushan C, Zhu A, Marinelli L, Fiveland E, DeMarco JK, Shih R, Hood M, Kohls G, Kenney K, Foo T, Ho V. Diffusion Imaging comparison of high-performance Gradient system (MAGNUS) with clinical MR system. Proceedings of the ISMRM-ESMRMB Joint Annual Meeting, 2022, London, England, May 6-12, 2022.
Figures
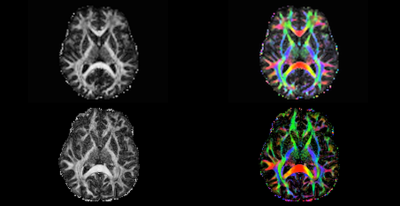
Figure 1. Comparison of FA maps for conventional 3T and MAGNUS 3T diffusion scans. With stronger gradient systems we can achieve higher SNR, thinner slices and resolution can be seen with MAGNUS 3T compared to conventional 3T. Both sequences have been optimized for their respective scanners for comparison. The top row shows FA maps from a whole-body 3T scanner using the multi-shell (3 tensor values) with maximum b value 2800 and slice thickness 2.2 mm (10). The bottom row shows FA maps from the MAGNUS 3T using a multi-shell (3 tensor) DTI with a maximum b value 4000 and slice thickness 1.5mm.