5377
Application of Multi-Shot Echo Planar Imaging Diffusion Weighted Imaging of the Skull Base
Hedan Luo1, Qingwei Song1, Yanwei Miao1, Haonan Zhang1, Na liu1, Yukun Zhang1, Ailian Liu1, and Liangjie Lin2
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Danlian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Danlian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Data Acquisition, Head & Neck/ENT, multi-shot echo planar imaging diffusion weighted imaging;
Exploring the performance of Image Reconstruction Using Image-space Sampling (IRIS)-based Multi-shot Echo Planar Imaging Diffusion Weighted imaging (MS-EPI DWI) for the skull base region.Objective
Exploring the effect of Image Reconstruction Using Image-space Sampling(IRIS)-based muti-shot echo planar imaging diffusion weighted imaging(MS-EPI DWI) on the image quality of the skull base area.Materials and methods
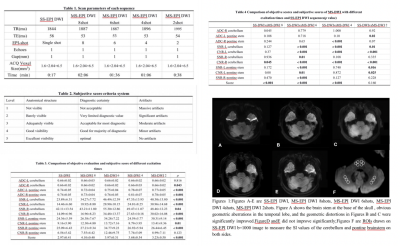
Eighteen healthy volunteerss were recruited, with an average age of 38.23±18.99 years old.All patients underwent conventional single-shot Echo Planar Imaging Diffusion Weighted Imaging (SS-EPI DWI) and IRIS-based multiple-shot diffusion-weighted imaging (8, 6, 4, 2).The scan parameters of each sequence are shown in Table 1.The ADC values, Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) and Contrast to Noise Ratio (CNR) of bilateral cerebellum,brainstem and pons were measured and calculated. The two observers used a five-point scoring method to evaluate the quality of the images(Table2). The Kappa test was adopted to evaluate the consistency of the scores from the two radiologists. The difference between ADC, SNR, CNR and subjective scores of MS-EPI DWI with different number of shots and SS-EPI DWI using Friedman test. If the differences were statistically significant, the Bonferroni test was used for pairwise comparisons.Discuss
The objective assessment of this study showed that when the number of excitation was 8, the SNR and CNR values of the images were generally lower than 6 times, and the blood and cerebrospinal fluid pulsation artifacts were more severe, leading to an increase in noise and a decrease in the combined effect of the data, which is consistent with previous studies[1]. In addition, in the left cerebellum and pontocerebellar brainstem, the CNR values with excitation number 2 were greater than those with excitation number 4. The CNR of the left pontocerebellar brainstem with excitation number 4 was smaller than that of the SS-EPI DWI, probably due to noise fluctuations caused by the smaller ROI outline due to the anatomical structure of the measured background dentate nucleus. When the number of excitation was reduced from 6 to 2, the sites with statistically significant differences compared with SS-EPI DWI gradually decreased; when the number of excitation was 6, the differences in ADC values of each site compared with SS-EPI DWI were not statistically significant, and the SNR, CNR and subjective scores were higher than SS-EPI DWI and the differences were statistically significant, and the image quality of this number of excitation was significantly higher than that of SS- EPI DWI was significantly improved; in terms of scan time, the time was shortened by 23.8% relative to the excitation number of 8.Conclusion
Compared with the traditional SS-EPI DWI sequence, MS-EPI DWI technology can solve the problems of geometric distortion and high signal artifact at the base of the skull. Considering the balance of time and image quality, MS-EPI DWI with 6 excitation times is recommendedAcknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Miller KL, Pauly JM. Nonlinear phase correction for navigated diffusion imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2003,50(2):343-353. DOI: 10.1002/mrm.10531.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/5377