5286
Measurement of Sound Pressure Level (SPL) at 3T and 7T for optimization of Quiet Dynamic Zero Echo Time (ZTE) MRI1Champaign Imaging LLC, Shoreview, MN, United States, 2Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States, 3Champaign imaging LLC, Shoreview, MN, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Safety, Gradients, Acoustic Measurement, ZTE, 3D Radial, Silent
This abstract aims to provide a general method of measuring the acoustic noise produced by a scanning protocol and to present the acoustic differences in absolute sound pressure level. To demonstrate these methods we show results using conventional Cartesian and acoustically quieter ZTE based protocols on 3T and 7T systems.Purpose:
To provide a general method of measuring the acoustic noise produced by a scanning protocol and to display the acoustic differences in absolute weighted SPL of ZTE protocols and Cartesian protocols with examples at 3 and 7 Tesla (T) scanners.Background:
MRI system gradients are used to spatially encode magnetization for image formation and contrast optimization. However, many imaging approaches utilize rapid changes to the gradients resulting in the generation of acoustic noise [1]. This is a widely known challenge with MRI and hearing protection is routinely needed for conventional imaging. It is important to quantify the acoustic noise experienced by patients being scanned to evaluate the overall acoustic safety of each protocol and what safety measures need to be taken for each protocol. However, it is substantially difficult to measure the amount of acoustic noise produced due to the harsh magnetic field present within the scanner room. In this work, we present an approach to measure the sound pressure levels (SPL) of several MRI acquisitions as well as on different MRI systems (3T and 7T). In particular we demonstrate this approach in the setting of conventional Cartesian acquisitions as well as more acoustically optimized zero-echo time (ZTE) acquisitions [2].Methods:
To test the effect of different view-orders on acoustic noise, a 3D radial ZTE sequence was modified to accept table input for view-ordering [3]. In ZTE, a 3 dimensional (D) radial type of sequence, the readout gradient rotates rather than switching polarity [4], allowing for small changes in between successive acquisitions. An interleaved 3D radial view-order can also repeatedly sample a full sphere of k-space [5] . These characteristics make ZTE sequences potentially useful for acoustically quiet dynamic acquisition [6].A calibrated, non-magnetic fiber optic microphone (OptiSLM 1150, OptoAcoustics, Mazor, Israel) was positioned on the MRI head coil and used to record the audio waveform and measure the SPL (sound pressure level) for each individual scan . A fiber optic microphone was necessary to measure the SPL due to the powerful RF and gradient magnetic fields within the scanner as a fiber optic microphone is made out of non-magnetic material and does not utilize copper conductors. The electrical components of the microphone were placed outside of the Faraday cage located outside of the scan room MR scanner to minimize impacts due to the RF and magnetic fields. The microphone itself was placed on the coil within the bore of the scanner and the fiber optic cable threaded through the access waveguide to the control room. The microphone was secured to the RF coil via an acoustic decoupling device made out of ear plugs taped together which can be seen in (Figure 1). This was done to prevent the microphone head from vibrating against the plastic of the coil. Each protocol was recorded using the single channel output from the SPL meter using open source audio recording software (Audacity - https://www.audacityteam.org), . While the protocol was being recorded in Audacity, the average SPL readout of the microphone was recorded at one minute into each scan. The SPL meter was then switched to max hold mode, meaning that the meter readout the maximum SPL recorded until a new maximum was reached. The maximum SPL value was recorded at the end of each scan. Each file was saved as a .wav file and analyzed in Matlab using the acoustics toolbox ( Mathworks, Natick, MA).
Results:
Acoustic measurements were collected at 3T (Premier, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI) and 7T (Signa 7T, GE Healthcare) using conventional Cartesian acquisitions including T1 MP-RAGE and T2 CUBE. As well as conventional and modified 3D radial ZTE sequences with and without T1 and T2 preparations. See Table 1.Discussion:
All conventional sequences at 7T are louder than corresponding sequences at 3T. All 7T Silent (ZTE) preparation and vieworder variants are louder than the corresponding variants at 3T. Utilizing measurement method we continue to optimize the HEALPix vieworder to minimize SPL while maintianing acceptable time resolution for motion correction.Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by R43MH122028. JHH and VAM received salary support from P50HD103556 and the data for this project was collected on an instrument funded by NIH (S10OD025025). We thank Mr. Stephen Otto for project management and logistics related to this work.References
[1] Counter, S. A.; Olofsson, A.; Grahn, H. F. & Borg, E. (1997). MRI acoustic noise: sound pressure and frequency analysis., J Magn Reson Imaging 7 : 606-611. PMID: 9170052
[2] Alibek, S.; Vogel, M.; Sun, W.; Winkler, D.; Baker, C. A.; Burke, M. & Gloger, H. (2014). Acoustic noise reduction in MRI using Silent Scan: an initial experience., Diagn Interv Radiol 20 : 360-363. PMID: 24808439
[3] Corum, C. A.; Kruger, S. & Magnotta, V. A. (2020). HEALPix View-order for 3D+time Radial Self-Navigated Motion-Corrected ZTE MRI, 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) : 0409. PMID: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.10276v2
[4] Madio, D. P. & Lowe, I. J. (1995). Ultra-fast imaging using low flip angles and FIDs., Magn Reson Med 34 : 525-529. PMID: 8524019 [5] Park, J.; Shin, T.; Yoon, S. H.; Goo, J. M. & Park, J.-Y. (2016). A radial sampling strategy for uniform k-space coverage with retrospective respiratory gating in 3D ultrashort-echo-time lung imaging., NMR Biomed 29 : 576-587. PMID: 26891126 [6] Ljungberg, E.; Wood, T. C.; Solana, A. B.; Williams, S. C. R.; Barker, G. J. & Wiesinger, F. (2022). Motion corrected silent ZTE neuroimaging., Magnetic resonance in medicine 88 : 195-210. PMID: 35381110
Figures

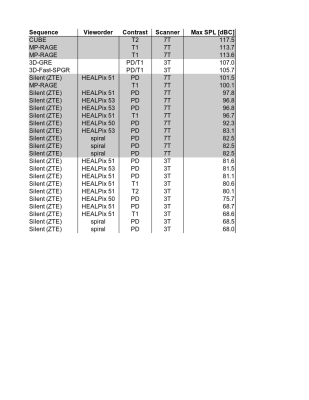
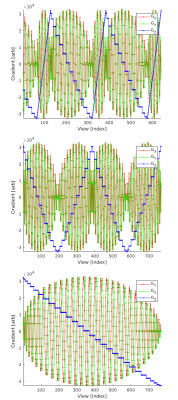
Figure 2: Sections of the gradient waveforms for vieworder 53, 51, and 50. The product vieworder is a non-interleaved isotropic spiral that has smoother gradient jumps.
Top: Vieworder 53 with 192 HEALPix segment and 64 Spiral Navigator segment.
Middle: Vieworder 51 with 192 HEALPix segment.
Bottom: Vieworder 50 with 768 HEALPix segment. Acoustically softer.