5245
Diagnostic value of multi-b-value DWI for endometrial carcinoma and the optimal b value exploring1Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Uterus, Cancer
Selecting the appropriate b value in DWI scanning to maximize the signal difference between endometrial tissues with different properties is conducive to the detection and accurate diagnosis of the endometrial lesion. The multiple b value DWI, especially b value > 1000 s/mm2, may play a crucial role in the detection of EC. To better identify malignant endometrial lesions from benign lesions, b-value around 2000 s/mm2 was recommended for DWI scanning.Objective
To explore the value of multi-b-value diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging (DWI) in the detection and qualitative diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma (EC) and to identify the optimal b value.Methods
Study population were pathologically confirmed with EC , endometrial hyperplasia and normal endometrium respectively. Before endometrial biopsy, all enrolled patients in the three groups underwent MR DWI scanning with multiple b values (including high b values). The endometrial signal intensity on DWI with different b values was observed and measured. The b value of DWI with the maximal difference in the mean signal intensity of endometrium among the three groups was identified as optimal. Also, the endometrium-to-myometrium signal intensity ratio and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value on the DWI with the optimal b value were calculated, and the differences of the ratio and ADC value were statistically analyzed among the three groups.Results
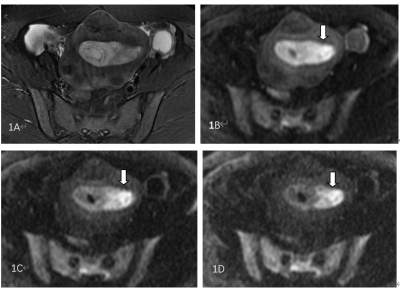
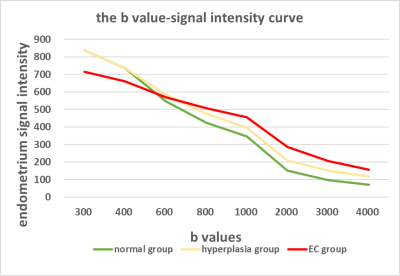
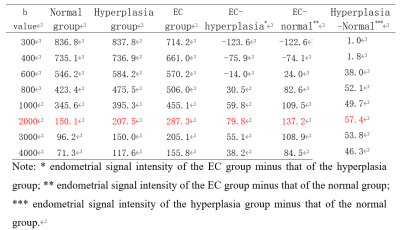
85 patients were studied, including 30 cases of EC, 34 cases of hyperplasia, and 21 normal subjects. With the increasing of b values, the endometrium signal intensity on DWI in three groups showed a downward trend, and the decrease of EC group was lower than that of hyperplasia and normal groups. When b=2000 s/mm2, the difference among the three groups was largest (p < 0.001). On DWI with b=2000 s/mm2 (the optimal b value), the endometrial signal intensity in the EC group was significantly higher than that of the normal group (p = 0.001) and hyperplasia group (p = 0.015), and the endometrium-to-myometrium signal intensity ratio and the ADC value among the three groups were statistically different.Discussion
Currently, the widely used b values in the DWI scanning of endometrial lesions were 600, 800, or 1000 s/mm2. Because of T2 shine-through effect, the normal and the hyperplasia endometrial tissues manifested as high signal intensity on DWI within this range of b values similar to that of malignant endometrial tissue, which was due to the diffusion limitation of water molecules, thereby causing indistinguishable endometrial lesions by naked eyes. This phenomenon was the reason for the inability of DWI in the detection of EC and in the differentiation of benign and malignant lesions.When b=2000 s/mm2, the difference reached the maximum and could be distinguished by the naked eyes. Continuous observation of the evolution of endometrial signal intensity on the multi-b-values DWI can improve the confidence for differential diagnosis. The DWI with multiple b values, especially b value > 1000 s/mm2, can play a crucial role in the detection of EC. The results of this study suggested that 2000 s/mm2 was the optimal b value for DWI sequence to identify the endometrial lesions.Conclusion
Multi-b-value, especially high-b-value (b>1000 s/mm2) DWI was superior to the currently widely used b values (600–1000 s/mm2) in the detection of EC and distinguishing between endometrial benign and malignant lesions. On the DWI with b=2000 s/mm2, the difference in signal intensity among EC, hyperplasia, and normal endometrium was maximal, which was beneficial to the display of malignant endometrial lesions. Therefore, it was recommended as the optimal b value for DWI scanning in order to identify the endometrial lesions.Acknowledgements
noneReferences
【1】Nougaret S, Horta M, Sala E, et al. Endometrial Cancer MRI staging: Updated Guidelines of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology[J]. European Radiology, 2018:1-14.
【2】Qiu Bi, Yuhui Chen, Kunhua Wu, et al. The Diagnostic Value of MRI for Preoperative Staging in Patients with Endometrial Cancer: A Meta-Analysis[J]. Acad Radiol 2019:1-9.
【3】 Felix TS, Federico C, Jalid S, et al. Preoperative Evaluation of Myometrial Invasion in Endometrial Carcinoma: Prospective Intra-individual Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Volumetry, Diffusion-weighted and Dynamic Contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging[J]. Anticancer Research. 2018,38: 4813-4817.
【4】 Ghosh A, Singh T, Singla V, et al. Read-out segmented echo planar diffusion imaging of the female pelvis–utility in endometrial carcinoma–a preliminary experience. Br J Radiol 2018; 91: 20180018.
Figures