5209
Diagnostic value of rs-fMRI indicators based on SVM classification in adult patients with MRI-negative temporal lobe epilepsy
Yang Fan1, JIA Wen xiao1, HANJIAERBIEKE KUKUN1, WANG Shao yu2, and WANG Yun ling1
1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing MR Scientific Marketing, Shanghai, China
1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing MR Scientific Marketing, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Epilepsy, fMRI (resting state)
Rs-fMRI technology provides a range of analytical approaches that expand the scope of epilepsy research, and these algorithms provide unique views on pathophysiological processes that complement each other in interpreting regional spontaneous brain activity. ALFF, fALFF and ReHo can effectively identify MRI negative TLE (MRIn TLE) patients based on support vector machine algorithm. We hypothesized that there were abnormal changes in DMN-related brain regions in MRIn TLE patients, and the brain function indexes of angular gyrus, precuneus, and inferior parietal angular gyrus could distinguish MRIn TLE patients from HC.Introduction
Approximately 1/3 of patients with TLE present negatively on conventional MRI 1, and many neuroimaging studies have used group comparison type analyses to investigate subtle differences between MRI-negative TLE (MRIn TLE) patients and healthy controls (HC), reporting abnormal brain regions present in multiple neural structures. Group level analyses typically require large samples and need to pass rigorous multiple corrections, alterations are often small and undetectable, and there is a lack of reliable differentiation between patients and controls 2, in addition, group-based analyses do not help to diagnose patients at the individual level 3.Purpose
Our study wanted to investigate the value of three functional indicators of rs-fMRI (ALFF, fALFF, ReHo) as three features for the diagnosis of MRIn TLE patients, based on the rs-fMRI technique with machine learning algorithms.Materials and Methods
A total of 113 patients with MRIn TLE and 68 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. All the subjects were performed rs-fMRI scanning on a 3T scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) with following parameters: TR/TE=2000/30; FA=90°; FOV=240×240mm; scan matrix=64×64; 36 slices; 180 volumes; 3.5-mm thickness without gap. The rs-fMRI data were post-processed with DPARSF tool (http://rfmri.org/DPARSF) to obtain ALFF, fALFF, and ReHo functional indicators, and then the diagnostic efficiency was analyzed by PRoNTo software (http://www.mlnl.cs.ucl.ac.uk/pronto).Results
In both classification groups, the accuracy of using the ALFF index as a classification criterion was 83.43% with an AUC value of 0.92; the accuracy of using the fALFF index as a classification criterion was 83.43% with an AUC value of 0.89; and the accuracy of using the ReHo index as a classification criterion was 86.74% with an AUC value of 0.95 (P=0.001). Based on the three rs-fMRI functional indices, the brain regions with the greatest differences between MRIn-negative TLE patients and controls were concentrated in the right angular gyrus, bilateral inferior parietal marginal angular gyrus, and right precuneus.Discussion
The data-driven analysis approach has led to the research and application of rs-fMRI, which can monitor spontaneous neural activity in the human resting brain and quantify the interactions between brain neurons. In this study, three functional indexes (ALFF, fALFF, ReHo) of rs-fMRI were classified and detected by applying multivariable pattern analysis method based on machine learning. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) is used to analyze and evaluate the performance of the classifier. Our preliminary study found that the use of neuroimaging-based computer-aided methods is feasible for distinguishing MRIn TLE from HC, and ALFF, fALFF, and ReHo groups of functional indicators may be effective biological indicators for discrimination. We explored the top 10 most discerning brain regions. Some unlisted brain regions may also contain valuable information and should also be considered in future research.Conclusions
MRIn TLE patients have abnormal changes in DMN-related brain regions. The computer-aided method based on rs-fMRI can identify MRIn TLE patients from health controls with ALFF, fALFF, and ReHo functional indicators.Key words
Temporal lobe epilepsy; Resting-state magnetic resonance imaging; Support vector machineAcknowledgements
Thanks to Siemens Mr. Wang Shaoyu for his support to our work.References
[1] Muhlhofer W, Tan Y L, Mueller S G, et al. MRI-negative temporal lobe epilepsy—What do we know?[J]. Epilepsia, 2017, 58 (5): 727-742.
[2] Kambeitz, Joseph, Cabral, et al. Detecting Neuroimaging Biomarkers for Depression: A Meta-analysis of Multivariate Pattern Recognition Studies[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2017, 82: 330-338.
[3] Amarreh I, Meyerand ME, Stafstrom C, Hermann BP , Birn RM. Individual classification of children with epilepsy using support vector machine with multiple indices of diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage Clin. (2014) 4:757–764.
Figures
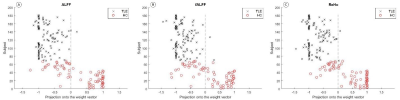
Fig1. Classification map based on functional
indexes ALFF, fALFF and ReHo respectively
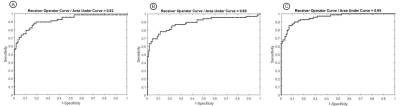
Fig2.
Receiver operating characteristic curve based on the distribution of functional
indexes ALFF, fALFF, and ReHo (A: ALFF as the classification index; B: fALFF
was used as the classification index; C: ReHo as a classification index)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/5209