5144
The impact of multiple sclerosis on cortical brain stiffness.1Berlin Center for Advanced Neuroimaging, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2Experimental and Clinical Research Center, Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Corporate Member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 3Department of Radiology, Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Corporate Member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 4Department of Neuroradiology, Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Corporate Member of Freie Universität Berlin and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Synopsis
Keywords: Elastography, Brain, Cortical stiffness
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neuroinflammatory disease that affects both white matter and cortical areas. While magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can image pathological changes in the white matter, it is limited in quantifying cortical tissue damage in MS. Therefore, cerebral 3D-MR elastography based on multifrequency wave excitation and tomoelastography postprocessing was developed to measure cortical stiffness. We found that the cerebral cortex in MS patients is markedly softer than global brain matter and deep gray matter indicating the use of cerebral tomoelastography as a potential new imaging marker for monitoring MS disability.Introduction
MR elastography (MRE) is a noninvasive method for the mechanical characterization of brain tissue[1, 2]. MRE has been used to study the mechanical behavior of the brain under physiologic and pathologic conditions including Multiple sclerosiss (MS)[3, 4]. It was shown that whole brain stiffness is reduced in MS patients and concluded that inflammation and demyelination may have affected the integrity of tissue in the brain[5-8]. Furthermore, MRE in preclinical mouse models and ex-vivo specimens revealed the importance of myelination[9, 10] and astrocytic-vascular junctions to brain stiffness[11]. However, little is known about the stiffness changes induced by MS in the cerebral cortex despite the emerging evidence that the pathology in gray matter is an important signature of disability induced by MS.[12, 13] Cortical brain lesions are characterized by demyelination with little leukocyte infiltration and stronger meningeal inflammation[12]. So far, low anatomical detail resolution of cerebral MRE has hampered studies of stiffness in small anatomical regions close to tissue boundaries such as cortical areas affected by MS[14, 15]. Our aim was to investigate possible MS induced stiffness alterations in the cerebral cortex in comparison to changes in whole brain matter and deep gray matter regions using multifrequency MRE based on tomoelastography data processing.Methods
In total 14 healthy volunteers (7 women, mean±sd: 38±19years) and 7 MS patients with stable relapsing-remitting MS (6 women, mean±sd: 38±9years) were included in this study. All patients were on standard pharmacological treatment while healthy volunteers had no history of neurological events. The study was approved by our IRB (EA1/085/17) and written informed consent was given prior to the examination. All participants were investigated by multifrequency brain MRE using a spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence at a 3.0-Tesla scanner (Siemens-Lumina). Eight phase offsets were recorded in 40 axial slices with 202x202mm2 field-of-view, 1.6x1.6x2.0mm3 voxel size, 70ms echo time and 4700ms repetition time. Harmonic vibrations at 20,25,35,40Hz were induced using compressed air drivers[16] consisting of two plastic cushions underneath the subject’s head. The average encoding efficiency was 8.4 rad/µm (1st-mom-nulling). Additionally, two images were acquired for distortion corrections[17]. SWS maps were reconstructed from motion- and distortion corrected raw data using the phase-gradient based k-MDEV inversion[18] in 3D with brain adapted pre-processing[19-21]. Harmonic wave images were corrected for interslice phase discontinuities[22] and smoothed with a lowpass Butterworth filter of first order with a threshold of 200 1/m. Wave images were high-pass filtered using the 3D curl operator followed by spatial filtering of 20 propagation directions and computation of the 3D phase gradient for reconstructing SWS maps.[21] Mean MRE magnitude images and SWS maps were normalized to the MNI space for tissue segmentation[23] and averaged over whole brain matter (WBM), cortical gray matter (CGM) and deep gray matter (DGM). Difference in SWS between healthy controls and MS patients was compared using an unpaired t-test with Holm-Bonferroni correction. p-values<0.05 were considered statistically significant.Results
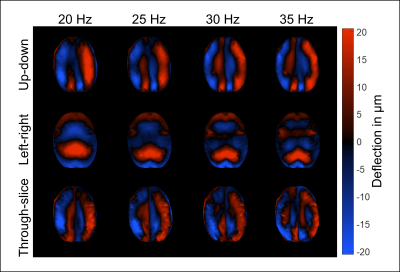
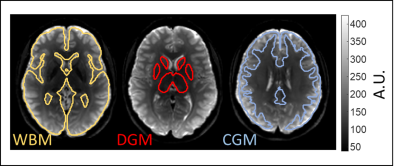
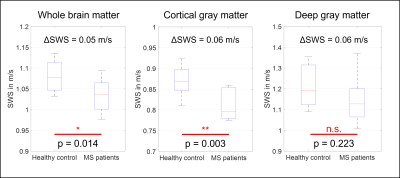
Figure 1 shows shear wave deflections in all three encoding directions and for all driving frequencies in a central slice for one volunteer. Wave amplitudes slightly decreased for higher frequencies. In Figure 2 three representative anatomical slices normalized to MNI space are displayed. Atlas segmentations for WBM, DGM and CGM are demarcated by yellow, red, and blue lines, respectively. Brain regions were well matched by MNI segmentation. Five representative slices of the MNI averaged SWS maps from 3D k-MDEV for healthy controls and MS patients are presented in Figure 3. CSF-tissue boundaries were well defined and some DGM structures were identifiable by eye e.g., putamen. DGM appeared stiffer than WM and CGM appeared softer than WM. Figure 4 shows group mean SWS values for WBM, CGM, and DGM for healthy controls and MS patients. Earlier reports of stiffness decrease in WBM in MS patients[5, 6] were confirmed (HC: 1.08±0.04 m/s; MS: 1.03±0.04 m/s; p=0.014). In addition, for the first time, we were able to measure significant softening of CGM (CGM-HC: 0.87±0.03 m/s; CGM-MS:0.81±0.04 m/s, p=0.003) in contrast to non-significant DGM softening (DGM-HC: 1.21±0.09 m/s; DGM-MS: 1.15±0.12 m/s, p=0.223) induced by MS.Discussion and conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study which compares stiffness of cortical brain tissue in healthy subjects with MS patients. Additionally, we compared brain softening in whole brain matter and deep gray matter using novel tomoelastography with 3D-k-MDEV inversion. In agreement to previous studies, we found an overall softening of brain tissue in MS patients[5, 6]. Beyond this state of knowledge, our study has shown that MRE can reliably measure cortical stiffness in the human brain and that this gain in resolution can be used for the detection of MS. Brain MRE is usually hampered by abundant slip interfaces and large heterogeneity of brain tissue resulting in blurry stiffness maps with limited ability to resolve anatomical landmarks and CSF-tissue interfaces with axial symmetry between hemispheres. Cerebral tomoelastography overcomes those artifacts and allows an improved depiction of anatomical details of brain stiffness[21]. In summary, using brain MRE based on 3D-tomoelastography postprocessing in MS patients, we found predominant softening in cortical areas. This raises the prospect of using cortical softening measured by MRE as novel imaging marker for risk stratification and therapy monitoring in MS.Acknowledgements
Funding from the German Research Foundation (GRK 2260 BIOQIC, SFB1340 Matrix in Vision) and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Program (ID 668039, EU FORCE – Imaging the Force of Cancer) is gratefully acknowledged.References
[1] Z. Yin, A.J. Romano, A. Manduca, R.L. Ehman, J. Huston, 3rd, Stiffness and Beyond: What MR Elastography Can Tell Us About Brain Structure and Function Under Physiologic and Pathologic Conditions, Top Magn Reson Imaging 27(5) (2018) 305-318.
[2] L.V. Hiscox, C.L. Johnson, E. Barnhill, M.D.J. McGarry, J. Huston, E.J.R. van Beek, J.M. Starr, N. Roberts, Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of the human brain: technique, findings and clinical applications, Physics in Medicine and Biology 61(24) (2016) R401-R437.
[3] M.C. Murphy, J. Huston, 3rd, R.L. Ehman, MR elastography of the brain and its application in neurological diseases, Neuroimage 187 (2019) 176-183.
[4] S. Hirsch, J. Braun, I. Sack, Magnetic Resonance Elastography: Physical Background And Medical Applications, Wiley-VCH2017.
[5] J. Wuerfel, F. Paul, B. Beierbach, U. Hamhaber, D. Klatt, S. Papazoglou, F. Zipp, P. Martus, J. Braun, I. Sack, MR-elastography reveals degradation of tissue integrity in multiple sclerosis, Neuroimage 49(3) (2010) 2520-5.
[6] K.J. Streitberger, I. Sack, D. Krefting, C. Pfuller, J. Braun, F. Paul, J. Wuerfel, Brain viscoelasticity alteration in chronic-progressive multiple sclerosis, PloS one 7(1) (2012) e29888.
[7] A. Fehlner, J.R. Behrens, K.J. Streitberger, S. Papazoglou, J. Braun, J. Bellmann-Strobl, K. Ruprecht, F. Paul, J. Wurfel, I. Sack, Higher-resolution MR elastography reveals early mechanical signatures of neuroinflammation in patients with clinically isolated syndrome, J Magn Reson Imaging 44(1) (2016) 51-8.
[8] K. Schregel, E. Wuerfel, P. Garteiser, I. Gemeinhardt, T. Prozorovski, O. Aktas, H. Merz, D. Petersen, J. Wuerfel, R. Sinkus, Demyelination reduces brain parenchymal stiffness quantified in vivo by magnetic resonance elastography, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(17) (2012) 6650-5.
[9] J. Wuerfel, E. Tysiak, T. Prozorovski, M. Smyth, S. Mueller, J. Schnorr, M. Taupitz, F. Zipp, Mouse model mimics multiple sclerosis in the clinico-radiological paradox, Eur J Neurosci 26(1) (2007) 190-8.
[10] J. Weickenmeier, R. de Rooij, S. Budday, P. Steinmann, T.C. Ovaert, E. Kuhl, Brain stiffness increases with myelin content, Acta Biomater 42 (2016) 265-272.
[11] S. Wang, J.M. Millward, L. Hanke-Vela, B. Malla, K. Pilch, A. Gil-Infante, S. Waiczies, S. Mueller, P. Boehm-Sturm, J. Guo, I. Sack, C. Infante-Duarte, MR Elastography-Based Assessment of Matrix Remodeling at Lesion Sites Associated With Clinical Severity in a Model of Multiple Sclerosis, Front Neurol 10 (2019) 1382.
[12] J.J.G. Geurts, F. Barkhof, Grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis, Lancet Neurol. 7(9) (2008) 841-851.
[13] M. Calabrese, R. Magliozzi, O. Ciccarelli, J.J. Geurts, R. Reynolds, R. Martin, Exploring the origins of grey matter damage in multiple sclerosis, Nat Rev Neurosci 16(3) (2015) 147-58.
[14] K. Riek, J.M. Millward, I. Hamann, S. Mueller, C.F. Pfueller, F. Paul, J. Braun, C. Infante-Duarte, I. Sack, Magnetic resonance elastography reveals altered brain viscoelasticity in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, Neuroimage Clin 1(1) (2012) 81-90.
[15] H. Herthum, S. Hetzer, M. Scheel, M. Shahryari, J. Braun, F. Paul, I. Sack, In vivo stiffness of multiple sclerosis lesions is similar to that of normal-appearing white matter, Acta Biomater 138 (2022) 410-421.
[16] F. Schrank, C. Warmuth, H. Tzschätzsch, B. Kreft, S. Hirsch, J. Braun, T. Elgeti, I. Sack, Cardiac-gated steady-state multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography of the brain: Effect of cerebral arterial pulsation on brain viscoelasticity, Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 40(5) (2020) 991-1001.
[17] A. Fehlner, S. Hirsch, M. Weygandt, T. Christophel, E. Barnhill, M. Kadobianskyi, J. Braun, J. Bernarding, R. Lutzkendorf, I. Sack, S. Hetzer, Increasing the spatial resolution and sensitivity of magnetic resonance elastography by correcting for subject motion and susceptibility-induced image distortions, J Magn Reson Imaging 46(1) (2017) 134-141.
[18] H. Tzschatzsch, J. Guo, F. Dittmann, S. Hirsch, E. Barnhill, K. Johrens, J. Braun, I. Sack, Tomoelastography by multifrequency wave number recovery from time-harmonic propagating shear waves, Med Image Anal 30 (2016) 1-10.
[19] H. Herthum, S.C.H. Dempsey, A. Samani, F. Schrank, M. Shahryari, C. Warmuth, H. Tzschätzsch, J. Braun, I. Sack, Superviscous properties of the in vivo brain at large scales, Acta Biomater 121 (2021) 393-404.
[20] H. Herthum, S. Hetzer, M. Scheel, M. Shahryari, J. Braun, F. Paul, I. Sack, In vivo stiffness of multiple sclerosis lesions is similar to that of normal-appearing white matter, Acta Biomaterialia (2021).
[21] H. Herthum, S. Hetzer, B. Kreft, H. Tzschätzsch, M. Shahryari, T. Meyer, S. Görner, H. Neubauer, J. Guo, J. Braun, Cerebral tomoelastography based on multifrequency MR elastography in two and three dimensions, (2022) http://dx.doi.org/10.17169/refubium-35668.
[22] E. Barnhill, M. Nikolova, C. Ariyurek, F. Dittmann, J. Braun, I. Sack, Fast Robust Dejitter and Interslice Discontinuity Removal in MRI Phase Acquisitions: Application to Magnetic Resonance Elastography, IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(7) (2019) 1578-1587.
[23] W.D. Penny, K.J. Friston, J.T. Ashburner, S.J. Kiebel, T.E. Nichols, Statistical parametric mapping: the analysis of functional brain images, Elsevier2011.
Figures