5077
DOuble tuned and DOuble matched large-size loop coil (DODO) design and evaluation for 17O MRSI and 1H MRI application at 7T1Department of Radiology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States, 2School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, University of Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Non-Array RF Coils, Antennas & Waveguides, RF Arrays & Systems
Current state-of-the-art RF coils for X-nuclear MRS/MRI studies typically use two separate sets of RF coils operating at the X-nuclear and proton frequencies, respectively. Here, we introduce a new coil concept whereby large-size loop coil with split capacitors which can be simultaneously tuned and matched to 17O and 1H Larmor frequencies for 7T human imaging application. Importantly, this novel coil exhibits excellent performance in proton and X-nuclear imaging, therefore, it provides a simple RF coil solution, particularly for ultrahigh field (UHF) multinuclear brain MR imaging applications.Introduction:
In vivo X-nuclear MRSI at ultrahigh field (UHF) offers unique capabilities for studying brain energy metabolism in normal and disease states 1. However, it requires the coil operating at the X-nuclear frequency and 1H frequency (for B0 shimming and anatomical imaging) 2. Current state-of-the-art X-nuclear/1H coils typically use two separate sets of coils for X-nuclear and 1H operations 3-5, which may degrade 1H and/or X-nuclear coil performance due to cross coil interactions. Here we combine X-nuclear and 1H operations into a single coil and introduce the DODO (DOuble tuned and DOuble matched large size loop) coil that can be tuned and matched to 17O and 1H frequencies at the same time, showing excellent imaging performance at both the operation frequencies.Methods:
Coil schematics and bench measurements:The 15cm diameter single-loop 17O-1H dual-frequency DODO coil shown in Fig. 1A can be independently tuned/matched at the same time to 7T 17O (40.3MHz) and 1H (297MHz) Larmor frequencies with a huge frequency difference of >250 MHz. The DODO coil circuit is shown in Fig. 1C. We also made a quadrature two-loop DODO array coil using two identical DODO coils (Fig. 1B).
To evaluate the DODO coil performance, we built another 15cm diameter single-loop 17O-1H dual-frequency coil as control (Fig. 1D) based on the similar coil design 6,7 without the split capacitors, which can be tuned and matched to 40.3MHz or 297MHz, respectively.
Phantom study at 7T:
We acquired 7T 17O FSW-weighted CSIs 8 (1ms square pulse, 9×9×7 matrix size, 200ms TR, 12×12×12cm3 FOV and 30k spectral bandwidth) from a head-sized NaCl solution phantom using the DODO and control coils as transceiver. The CSI data acquired with varied RF pulse voltages were fitted with a “sine” function to generate two types of RF magnetic field (B1) maps: transmission (|B1+|) and reception (|B1-|) field 9. The SNRs are calculated from fitted 17O water peak signals divided by the CSI baseline noise level. Finally, we collected 1H localizers with the head-shape phantom(εr= 45 at 298 MHz) for 1H performance evaluation.
Electromagnetic (EM) simulations of DODO coil:
We simulated the single-loop DODO coil loaded with “Duke” human model using the CST Studio 2019 with Hexahedral Time Domain solver to generate the H-field spatial distributions and the coil surface current density at 40.3MHz and 297 MHz driven by 1 volt forward RF pulse voltage.
Results:
The single-loop DODO coil was tuned and matched to 40.3 MHz and 297 MHz simultaneously with S11< - 20 dB (Figs. 2A&2B). The two overlapping-DODOs (Fig. 1B) are decoupled at 40.3MHz with decoupling efficiency better than -20dB (Fig. 2D). At this condition, moderate decoupling around -10dB (Fig. 2C) was also achieved at 297MHz.The 1H MRI and 17O B1 maps of the control and single-loop DODO coils are shown in Fig. 3. The DODO coil provides higher quality 1H MRI (Fig. 3B vs. Fig. 3A), and superior 17O CSI performance as shown by the |B1-| and SNR maps (Fig. 3D vs. Fig. 3C). Furthermore, quadrature-driven DODO array coil showed further improvement in both 1H MRI (Fig. 4A) and 17O CSI B1 strength (Fig. 4B) compared to the single-loop DODO coil (Fig. 3) at 7T. Figure 4C shows the SNR comparison results among the three coils. The single-loop DODO coil has two times higher SNR compared to control coil, and the quadrature-driven DODO array coil has ~1.8 times higher SNR gain compared to single-loop DODO coil.
The EM simulations show highly efficient H-field (Fig. 5B) and good coverage in the “Duke” (model) brain for the single-loop DODO coil at both 1H and 17O operating frequencies. The real part of the coil surface current density is shown in Fig. 5C. The surface current at 297MHz is relatively uniform, with majority of the currents reside on the lower part of the large loop away from the feeds. Lastly, at 40.3 MHz, the surface currents are uniformly distributed on the large coil loop.
Discussion:
We presented a novel concept of the dual-frequency DODO coil design that demonstrated good performance on both 7T 1H and 17O imaging using a large single-loop coil. Additionally, we have shown that it is possible to construct array coils using multiple overlapping DODO coils, for instance, the quadrature DODO array coil as demonstrated herein. Adding split capacitors (60-80 pF) on the large coil loop makes the coil surface currents at the 1H and 17O frequencies uniform on the large resonating loop, which is different from the previous coil design in which most of the 1H surface current resides on the matching circuit near the feed 6, therefore, the 1H B1 strength in the imaging object is significantly attenuated.Conclusion:
Through 7T phantom imaging measurements and EM simulations, we demonstrate a novel and simple dual-frequency DODO coil design with a large loop size that can be simultaneously tuned and matched to the 7T 1H and 17O frequencies, exhibiting excellent performance at both frequencies. This advanced RF coil should be highly valuable for performing X-nuclear MRSI in the human brain at UHF.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by NIH grants of U01 EB026978, R01 CA240953 and P41 EB027061.References
1. Zhu, X. H., Lu, M. & Chen, W. Quantitative imaging of brain energy metabolisms and neuroenergetics using in vivo X-nuclear 2H, 17O and 31P MRS at ultra-high field. J Magn Reson 292, 155-170, doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2018.05.005 (2018).
2. De Graaf, R. A. In vivo NMR spectroscopy: principles and techniques. Book: In vivo NMR spectroscopy: principles and techniques, (John Wiley & Sons, 2019).
3. Wang, B., Zhang, B., Yu, Z., Ianniello, C., Lakshmanan, K., Paska, J., Madelin, G., Cloos, M. & Brown, R. A radially interleaved sodium and proton coil array for brain MRI at 7 T. NMR Biomed 34, e4608, doi:10.1002/nbm.4608 (2021).
4. Avdievich, N. I., Ruhm, L., Dorst, J., Scheffler, K., Korzowski, A. & Henning, A. Double‐tuned 31P/1H human head array with high performance at both frequencies for spectroscopic imaging at 9.4T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 84, 1076-1089, doi:10.1002/mrm.28176 (2020).
5. Yan, X., Xue, R. & Zhang, X. A monopole/loop dual-tuned RF coil for ultrahigh field MRI. Quant Imaging Med Surg 4, 225-231, doi:10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.08.03 (2014).
6. Zhang, G., Zhu, W., Li, X., Zhu, X.-H., Wang, T. & Chen, W. B1+ efficiency of a single-loop dual frequency surface coil for proton and deuterium or oxygen-17 magnetic resonance imaging at 16.4T. in Proceedings of the 31st Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 4112, p. 4112 (2022).
7. Soon, S. H., Waks, M., Wiesner, H. M., Li, X., Zhu, X.-H. & Chen, W. Development of 8-Channel 1H-2H Dual-Frequency loop coil array with LC tanks for 1H MRI and 2H MRS imaging of human brain at 7 Tesla. in Proceedings of the 31st Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 1542, p. (2022).
8. Hendrich, K., Hu, X. P., Menon, R. S., Merkle, H., Camarata, P., Heros, R. & Ugurbil, K. Spectroscopic Imaging of Circular Voxels with a Two-Dimensional Fourier-Series Window Technique. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series B 105, 225-232, doi:10.1006/jmrb.1994.1128 (1994).
9. Chen, W., Lee, B. Y., Zhu, X. H., Wiesner, H. M., Sarkarat, M., Gandji, N. P., Rupprecht, S., Yang, Q. X. & Lanagan, M. T. Tunable Ultrahigh Dielectric Constant (tuHDC) Ceramic Technique to Largely Improve RF Coil Efficiency and MR Imaging Performance. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39, 3187-3197, doi:10.1109/TMI.2020.2988834 (2020).
Figures
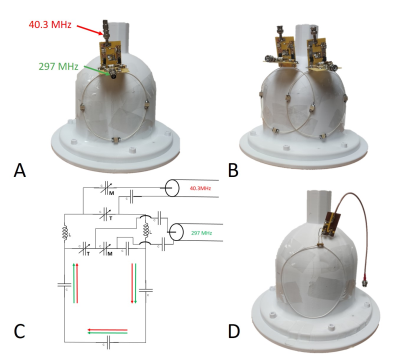
Figure 1. Coil setups and DODO coil schematic and prototype photos. A: Prototype of the 17O-1H dual-frequency single loop DODO coil with 15 cm diameter. B: Prototype of the 17O-1H dual-frequency two-loop overlapped DODO array coil with passive decoupling. C: Schematic of the 17O-1H dual-frequency DODO coil circuit. D: Prototype of traditional single loop coil as control, which can be tuned and matched to O17 and 1H at each time.
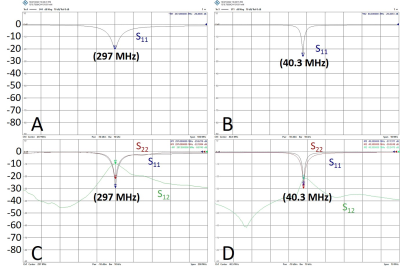
Figure 2. S-parameters for the 17O-1H dual-frequency single-loop DODO (A & B) and the two 17O-1H dual-frequency overlapped DODO array coil (C & D) under the loaded condition. The S-parameters near the 7T 17O operation frequency (40.3MHz) and 7T 1H operation frequency (297MHz) are shown in separate plots, due the limits of the displayed frequency span.
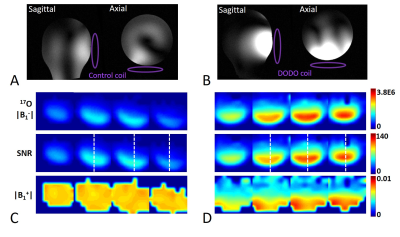
Figure 3. Coil imaging performance comparison between the control and single loop DODO coils in the transceiver mode. A and B are the 7T 1H localizers of a head-shape phantom (εr = 45 at 298 MHz) for the control coil (A) and DODO coil (B), respectively. C & D are the |B1-|, SNR and |B1+| maps in axial orientation through a NaCl solution phantom for the control coil (C) and DODO coil (D), respectively, indicating large improvement of |B1-| and SNR using the DODO coil. The white dash lines are 1D SNR profile lines for the comparison for different coils as used in Fig. 4C.

Figure 4. (A) 7T 1H localizers, (B) 7T 17O |B1-| and |B1+| and SNR maps in axial orientations acquired by the quadrature-driven DODO array coil. (C) Representative 1D SNR profiles through 3 slices marked by the vertical white dash lines for single loop DODO coil, two-loop DODO array coil, and single loop baseline coil, respectively.
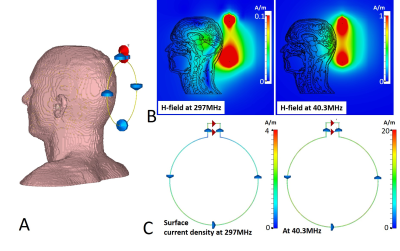
Figure 5. H-field spatial distributions and the real part of coil surface current density at 40.3 MHz and 297 MHz driven by 1 volt forward voltage. A: a 15cm diameter DODO coil is loaded with the “Duke” human model. B: H-field spatial distributions for 297 MHz (left) and 40.3MHz (right). C: Real part of the coil surface current density for 297 MHz (left) and 40.3MHz (right), indicating that the majority of the current is located in the large coil loop for both operation frequencies.