5065
A Triple-nuclear four-channel RF coil for Simultaneous acquisition of 1H/19F/23Na MR imaging at 3T
Nan Li1,2, Feng Du1,2, Xiaoliang Zhang3, Xin Liu1,2, Hairong Zheng1,2, and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, United States, Buffalo, NY, United States
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, United States, Buffalo, NY, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems
As the lower natural abundance of X-nuclei, it is important to enhance that the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the X-nuclei is as high as possible by designing a well-designed multiple-tuned coils. In this study, a new triple-tuned RF coil system capable of 1H / 19F / 23Na imaging was proposed. The performance of the triple-tuned coil was evaluated compared to their counterpart single-tuned coils by the numerical electromagnetic simulation. Imaging tests at 3T MRI were performed on the phantom by using the triple-tuned RF coil.Introduction
X-nuclei MRI are able to provide important cellular processes, morphological and metabolic information in tissues, which is significant for enabling both anatomical visualizations, as well as quantification of physiological processes1,2. The main challenge with X-nuclei NMR signal detection is that the sensitivity and the concentration of X-nuclei is much less than that of 1H. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in X-nuclei MRI largely depends on the electromagnetic properties and performance of radio frequency (RF) coils. A well-designed multi-tuned RF coil is required with the ability of simultaneous provide the minimum coupling between channels and nuclei-of-interest as well as highest achievable SNR and homogenous B1+ fields at both 1H and X-nuclei 3-5.In this study, we proposed a new triple-tuned four-channel RF coil array, which can operate at 1H/19F/23Na frequencies within the single physical loop structure. There is no need to consider interference between the 1H and X-nucleus as the coil resonates at three frequencies generated in one structure achieved by triple-tuned circuits added in the excited ports. The feasibility of the proposed coil was analyzed by the numerical electromagnetic simulation in the scattering parameters and B1+ field distributions. The performance of the triple-tuned coil was compared to their counterpart single-tuned coils by analyzing the maximum, minimum, mean value of the B1+ field, as well as the homogeneity and standard deviation. The phantom experiments at 3T were shown the ability of the triple-tuned RF coil system MR imaging of 1H / 19F / 23Na / imaging.
Method
Modeling and simulations of the 1H/19F/23Na triple-tuned four-channel RF coil (Fig.1) and their counterpart single-tuned coils were performed using the software Computer Simulation Technology, (Darmstadt, Germany). The triple-tuned four loop coil was 16 cm in diameter. The size of each triple-tuned loop array was set 16mm×6mm with the 1mm copper width. The matching and tuning network of the triple-tuned resonating at 1H/19F/23Na as shown in Fig.1 (b) were added in the excited ports in a circuit co-simulation. Excitation signal sources with phase difference of 90 degrees were selected to generate an ideal circularly quadrature mode. The simulations were performed for a cylindrical phantom setup with size 12 cm in diameter and 300 mm length (conductivity permittivity). The performance the proposed triple-tuned coil was evaluated by S-parameters and B1+ field in the simulations. B1+ field maps of the central transverse plane were scaled to an accepted power of 1W. For the simulation results, the maximum, minimum, mean value of the B1+ strength, as well as the homogeneity and standard deviation were calculated and compared to their counterpart single-tuned coils. The homogeneity of the B1+ field in the region of interest (ROI) was calculated as follows:B1+homogeneity = (B1+max-B1+min) / (2×B1+mean)
All MR measurements studies were carried out on a 3T MR system. A 12 cm diameter cylindrical phantom containing H3PO4 with a concentration of 85 %, 300 mmol/L NaCl and C6F6 solution with a concentration of 98%. The MR images of 1H/19F/23Na were acquired by using the self-made GRE sequence with scan parameters of TR/TE=500ms/5.4ms.FOV=200mm× 200mm, Thickness=20mm, Matrix=128×128. Average=4, Scan time= 3 min 40 s
Results
Fig.2 shows the S-parameters of the triple-tuned four-channel RF coil. The results displayed good tuning, matching and decoupling between the channels at 1H / 19F / 23Na frequencies. Fig.3 shows the B1+ field maps of the triple-tuned coil and their counterpart single-tuned coils. Table 1 shows simulated B1+ field data. At 1H frequency, the triple-tuned coil provided 87.55% maximum of B1+ field strength generated by the single-tuned 1H coil, it provided the same minimum and mean value as the single-tuned coil, to within 0.4%. It provided 99.55% homogeneity and 99. 59% standard deviation of B1+ field strength generated by the single-tuned 1H coil. At 19F frequency, the triple-tuned RF coil provided 98.96 % maximum of B1+ field strength generated by the single-tuned 19F coil, it provided the same minimum and mean value as the single-tuned coil, to within 1.2 %. It provided 99.50 % homogeneity and 97.96 % standard deviation of the B1+ field strength generated by the single-tuned 19F coil. At 23Na frequency, the triple-tuned RF coil provided 99.55 % maximum value compare with the single-tuned 23Na coil, it provided the same minimum and mean of B1+ field as the single-tuned coil, to within 0.3%. It provided 98.29% homogeneity and 98.07% standard deviation of the B1+ field strength generated by the single-tuned 23Na coil.Fig. 4 shows the 1H / 19F / 23Na MR measured results obtained with the specific phantom which including the three nuclei signals simultaneously.
Discussion/Conclusion
In this study, a new triple-tuned four-channel RF coil array was proposed, which can operate at 1H/19F/23Na three frequencies within the single physical loop structure. The proposed coil can provide the almost same performance of B1+ field compared to their counterpart single-tuned coils proved by analyzing the maximum, minimum, mean value of the B1+ field, as well as the homogeneity and standard deviation. Simultaneous 1H / 19F / 23Na MR images at 3T are successfully acquired in phantom using the developed triple-nuclear RF coil with a self-made 3T multinuclear MR RF system. Future investigation will focus on the animal study.Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China, 2021YFE0204400; NSFC grant 81627901; the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, XDB25000000; National Natural Science Foundation of China, U22A20344; Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS No. Y2021098; Key Laboratory Project of Guangdong Province, 2020B1212060051; Shenzhen city grant, RCYX20200714114735123.
References
- Ruomin Hu, Dennis Kleimaier, Matthias Malzacher et al. “X-Nuclei Imaging: Current State, Technical Challenges, and Future Directions”. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2020; 51: 355–376.
- Chang-Hoon Choia, Suk-Min Hong, Jörg Felder, N. Jon Shaha, “The state-of-the-art and emerging design approaches of double-tuned RF coils for X-nuclei, brain MR imaging and spectroscopy: A review”. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2020; 72: 103–116.
- Nan Li, Feng Du, Xiaoliang Zhang, Xin Liu, Hairong Zheng,Ye Li. Design of a double-layered quadruple-nuclear birdcage coil system for 1H / 19F / 23Na/31P MR imaging at 3T. Proc. 30th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, London, Virtual Con-ference & Exhibition, 3230. 2022.
- YongHyun Ha, Chang-Hoon Choi, and N. Jon Shah. Development and Implementation of a PIN-Diode Controlled, Quadrature-Enhanced, Double-Tuned RF Coil for Sodium MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2018; 37(7): 1626–1631.
Figures
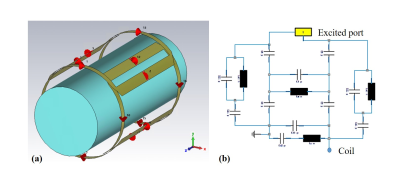
Fig.1(a)
simulation model of the triple-tuned four-channel RF coil. (b) matching and
tuning network of the triple-tuned circuit in the excited ports
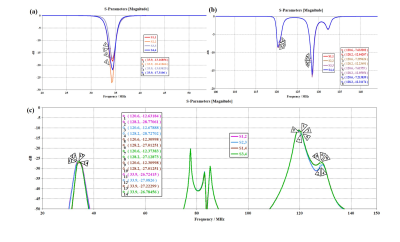
Fig.2
the S-parameters of the triple-tuned four-channel RF coil loaded with the
phantom in the simulations
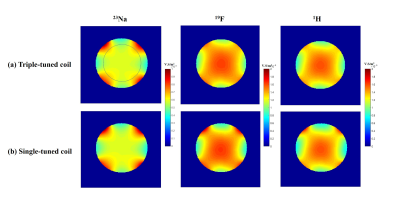
Fig. 3 the
B1+ field distributions of the triple-tuned four loop coil and their
counterpart single-tuned coils
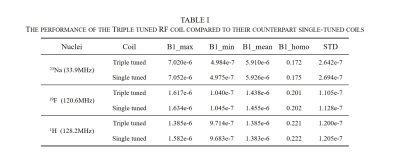
The performance
of the triple tuned RF coil compared to their counterpart single-tuned coils
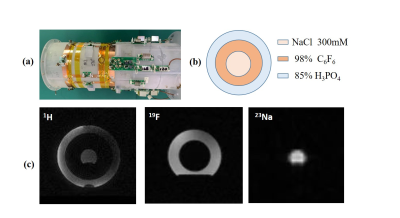
(a) The
structure of the triple-tuned RF coil (b) The specific phantom filled with
three kinds of solution simultaneously. (c) The 1H/19F/23Na MR measured images
obtained with the phantom.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/5065