5042
Use of an Automated Approach for Generating vADC for a Large Patient Population Studied with 129Xe MRI1School of Biomedical Engineering, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 3Lawson Health Research Institute, London, ON, Canada
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Segmentation, Deep learning, Transfer learning
Hyperpolarized 129Xe lung MRI is an efficient technique used to investigate and assess pulmonary diseases. However, the longitudinal observation of the emphysema progression using hyperpolarized gas MRI-based ADC can be problematic, as the disease-progression can lead to increasing unventilated-lung areas, which likely excludes the largest ADC estimates. One solution to this problem is to combine static-ventilation and ADC measurements following the idea of 3He MRI ventilatory ADC (vADC). We have demonstrated this method adapted for 129Xe MRI to help overcome the above-mentioned shortcomings and provide an accurate assessment of the emphysema progression.Purpose
The longitudinal-observation of the emphysema-progression using hyperpolarized gas MRI1,2-based ADC3-5 can be problematic, as the disease-progression can lead to increasing unventilated-lung-areas, which likely excludes the largest ADC-estimates. This can result in underestimation of the global-mean ADC-values, masking the emphysema-severity. The static-ventilation measurements providing the gas-distribution information should still show an increase in the ventilation-defects reflecting emphysema-progression, but these measurements do not provide the quantitative information about the lung-parenchyma-microstructure. A proposed solution to this problem is the use of ventilatory ADC (vADC).6 The feasibility of vADC has been recently demonstrated using the 3He/129Xe static-ventilation and diffusion-weighted data for small patient-population.6,7 Generation of vADC requires the calculation of VDP (ventilation-defect-percent) from the static-ventilation 129Xe images, which can be problematic for a large patient-population using a semi-automated-segmentation-approach.8 U-Net9 is a commonly used Deep Learning (DL) segmentation network which allows for fast and precise segmentation of images. In this research, we used an adaptation of U-Net named U-Net++10 for the DL-segmentation model. To overcome the dataset limitation challenge, we used transfer learning11 in our architecture to boost up the network training.We hypothesize that the use of a DL-segmentation should help to overcome the above-mentioned shortcomings existing for the large patient populations and provide an accurate assessment of the emphysema-progression. For this work, we used the static-ventilation and ADC data acquired using 129Xe MRI in a large group of study-subjects to demonstrate the feasibility of the xenon ventilatory ADC approach as a potential clinical-tool the longitudinal-observation and evaluation of emphysema-progression.
Methods
Ten study-subjects with written informed consent provided to an ethics-board-approved study protocol, underwent spirometry and 1H/129Xe MRI scanning. 129Xe imaging was performed at 3.0T (MR750, GEHC, WI) using whole-body gradients (5G/cm maximum) and a commercial 129Xe quadrature-flex RF coil (MR Solutions, USA).8 129Xe static-ventilation-images were acquired using a coronal plane 3D FGRE sequence (TE/TR/initial-flip-angle=1.5ms/5.1ms/1.3o, variable-flip-angle,12 Bandwidth=16kHz, reconstructed matrix-size=128x128x16, and FOV=40x40x24cm3, voxel size=3x3x15mm3) as previously described.8 All images were acquired in breath-hold (<16sec) after inspiration of 1.0L of gas (129Xe/4He mixture, 30/70) from functional-residual-capacity. Hyperpolarized 129Xe gas (polarization=35%) was obtained from a turn-key, spin-exchange polarizer system (Polarean-9820 129Xe polarizer).4 1H MRI was performed as previously described.13 Image SNR was calculated for the central-slices for each coronal-view.14 VDP was generated using the DL-segmentation. We used a pre-trained version of ResNet-15215 that was trained on the ImageNet dataset. To train the model, the Adam16 optimizer was selected as the optimization algorithm. To measure how far the model predictions were from the ground truths, we used cross-entropy loss.In all xenon measurements the diffusion-sensitization gradient pulse ramp up/down time=500μs, constant time=2ms, ΔXe=5.2ms, providing two b-values 0, and 12.0s/cm2. A multi-slice interleaved (two interleaves) centric 2D FGRE diffusion-weighted sequence was acquired for seven 30mm coronal slices (TE=10msec, TR=13msec, reconstructed matrix size=128x128, and FOV=40x40cm2, constant-flip-angle=4o, 14sec breath-hold). Matching static-ventilation images with 3x3x15mm3 voxel-size were obtained by as previously described.7 The ADC (b=0/b=12s/cm2) maps were generated as previously described17,18 for all xenon measurements. Calculated ADC values were normalized on the corresponding VDP-estimates to obtain vADC as it is shown on Fig.1.6
Results
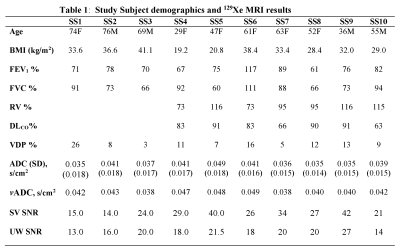
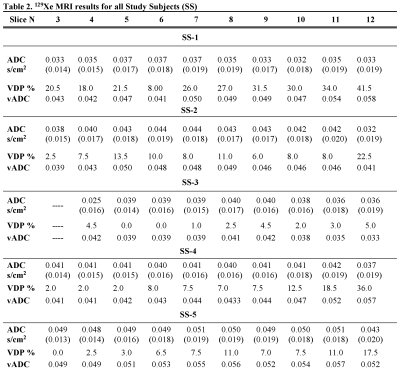
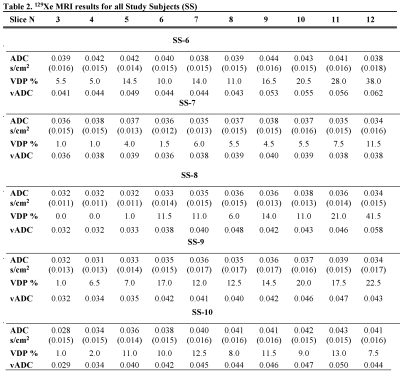
Fig.2 shows the acquired static-ventilation images (top-panel), matched voxel-size unweighted (b=0,) images (middle-panel) and correspondent ADC maps (bottom-panel) in coronal view for a representative study-subject demonstrating a good-match between static-ventilation and matched resolution unweighted-slices. Table 1 summarizes demographic and PFT-information, as well as imaging results including SNR (central-slice) for static-ventilation and matched voxel-size unweighted images, global-mean VDP, and global-mean ADC/vADC for all patients. The calculated mean SNR values across all images ranged between 10 and 35. Table 2 shows the slice-by-slice VDP, ADC, and vADC estimations for all study-subjects.The generated global-mean VDP estimates for the study-subjects were between 3% and 26%. The generated global mean ADC/(vADC) estimates for the study-subjects were between 0.035s/cm2/(0.038s/cm2) and 0.049s/cm2/(0.049s/cm2).
Discussion and Conclusion
In this proof-of-concept-study, we showed that the emphysema-progression can be potentially quantified with using the pulmonary static-ventilation and diffusion-weighted images of hyperpolarized 129Xe utilizing the ventilatory ADC approach powered by the DL-segmentation. The study results suggest that the matched resolution diffusion data had sufficient SNR to generate reliable ADC maps and reasonable matching with the static-ventilation data. A rigid and more homogenous coil19 combined with a phased-receive-array20 could substantially improve the ADC data quality and potentially replace the isotopically-enriched 129Xe with the natural-abundant xenon,21 and consequently, reduce the cost of 129Xe MRI for patients.We demonstrated that for the large patient group the 129Xe static-ventilation dataset can be segmented by using DL-based method to generate accurate biomarkers. The result of this proof-of-concept study suggests that 129Xe MRI coupled with the DL-based lung-segmentation can be used to rapidly evaluate the emphysema-progression. This is important in the light of the FDA approval16 for 129Xe MRI. Furthermore, this increases the opportunity for clinical translation of using 129Xe lung MRI as a tool for better treatment of patients with acute and chronic lung disease.
For future work, we plan rescan the study participants in twelve-months for an accurate assessment of the emphysema-progression over the year-interval.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, R5942A04.
References
1 Mugler, J. P., 3rd & Altes, T. A. Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI of the human lung. J Magn Reson Imaging 37, 313-331, doi:10.1002/jmri.23844 (2013).
2 Driehuys, B. et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: safety and tolerability of hyperpolarized 129Xe MR imaging in healthy volunteers and patients. Radiology 262, 279-289, doi:10.1148/radiol.11102172 (2012).
3 Kirby, M. et al. Hyperpolarized 3He and 129Xe MR imaging in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Radiology 265, 600-610, doi:10.1148/radiol.12120485 (2012).
4 Kaushik, S. S. et al. Diffusion-weighted hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI in healthy volunteers and subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Magn Reson Med 65, 1154-1165, doi:10.1002/mrm.22697 (2011).
5 Kirby, M. et al. Hyperpolarized 3He and 129Xe magnetic resonance imaging apparent diffusion coefficients: physiological relevance in older never- and ex-smokers. Physiol Rep 2, doi:10.14814/phy2.12068 (2014).
6 Westcott, A., Capaldi, D. P. I., Ouriadov, A., McCormack, D. G. & Parraga, G. Hyperpolarized (3) He MRI ventilatory apparent diffusion coefficient of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. J Magn Reson Imaging 49, 311-313, doi:10.1002/jmri.26202 (2019).
7 Parniyany, E., Woodward, E., Wu, T., Fox, M. & Ouriadov, A. Feasibility of the Ventilatory ADC Approach Using Hyperpolarized 129Xe Pulmonary MRI. ISMRM 30th Annual Meeting, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 7679 (2022).
8 Svenningsen, S. et al. Hyperpolarized (3) He and (129) Xe MRI: differences in asthma before bronchodilation. J Magn Reson Imaging 38, 1521-1530, doi:10.1002/jmri.24111 (2013).
9 Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P. & Brox, T. 234-241 (Springer International Publishing).
10 Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M. M. R., Tajbakhsh, N. & Liang, J. UNet++: Redesigning Skip Connections to Exploit Multiscale Features in Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39, 1856-1867, doi:10.1109/TMI.2019.2959609 (2020).
11 Pan, S. J. & Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 22, 1345-1359, doi:10.1109/tkde.2009.191 (2010).
12 Ouriadov, A. V., Lam, W. W. & Santyr, G. E. Rapid 3-D mapping of hyperpolarized 3He spin-lattice relaxation times using variable flip angle gradient echo imaging with application to alveolar oxygen partial pressure measurement in rat lungs. MAGMA 22, 309-318, doi:10.1007/s10334-009-0181-3 (2009).
13 Kirby, M., Pike, D., Coxson, H. O., McCormack, D. G. & Parraga, G. Hyperpolarized (3)He ventilation defects used to predict pulmonary exacerbations in mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Radiology 273, 887-896, doi:10.1148/radiol.14140161 (2014).
14 Dominguez-Viqueira, W., Ouriadov, A., O'Halloran, R., Fain, S. B. & Santyr, G. E. Signal-to-noise ratio for hyperpolarized (3)He MR imaging of human lungs: a 1.5 T and 3 T comparison. Magn Reson Med 66, 1400-1404, doi:10.1002/mrm.22920 (2011).
15 He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S. & Sun, J. in 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 770-778.
16 Kingma, D. & Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. International Conference on Learning Representations (2014).
17 Abascal, J. F. P. J., Desco, M. & Parra-Robles, J. Incorporation of prior knowledge of the signal behavior into the reconstruction to accelerate the acquisition of MR diffusion data. ArXiv e-prints 1702 (2017). <http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017arXiv170202743A>.
18 Ouriadov, A., Lessard, E., Sheikh, K., Parraga, G. & Canadian Respiratory Research, N. Pulmonary MRI morphometry modeling of airspace enlargement in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Magn Reson Med 79, 439-448, doi:10.1002/mrm.26642 (2018).
19 Farag A, Wang J, Ouriadov A, Parraga G & G., S. Unshielded and asymmetric RF transmit coil for hyperpolarized 129Xe human lung imaging at 3.0 T. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Melbourne, Australia, 1233 (2012).
20 Chang, Y. V., Quirk, J. D. & Yablonskiy, D. A. In vivo lung morphometry with accelerated hyperpolarized (3) He diffusion MRI: a preliminary study. Magn Reson Med 73, 1609-1614, doi:10.1002/mrm.25284 (2015).
21 Stewart, N. J., Norquay, G., Griffiths, P. D. & Wild, J. M. Feasibility of human lung ventilation imaging using highly polarized naturally abundant xenon and optimized three-dimensional steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med 74, 346-352, doi:10.1002/mrm.25732 (2015).
Figures
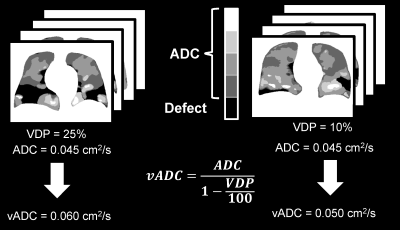
Figure 1: Figure showing the ventilatory ADC (vADC) approach which requires combination of static-ventilation and ADC measurements. VDP=ventilation defect percent; ADC=apparent diffusion coefficient.
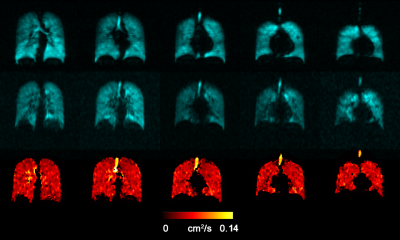
Figure 2: Representative 129Xe MRI static-ventilation images (top-panel), matched voxel-size unweighted (b=0,) images (middle-panel) and correspondent ADC maps (bottom-panel) in coronal view obtained for Parcipant-4. Images demonstrating a good match between static-ventilation and key-hole-based unweighted slices. ADC=apparent diffusion coefficient.