5029
Synthesized 7T MRI from 3T MRI using generative adversarial network: validation in clinical brain imaging1Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Beijing, China, 3Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences‒Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Brain
Ultra-high field 7T MRI provides exceptional tissue contrast and anatomical details but is often cost-prohibitive and not widely accessible in clinics. A generative adversarial network (SynGAN) was developed to generate synthetic 7T images from the widely used 3T images. The synthetic 7T images achieved improved tissue contrast and anatomical details compared to the 3T images. Meanwhile, the synthetic 7T images showed comparable diagnostic performance to the authentic 7T images for visualizing a wide range of pathology, including cerebral infarction, demyelination, and brain tumor.Introduction
Currently, ultra-high field 7T MRI is an emerging technique to provide images with higher resolution and signal-to-noise ratio compared to the routine 3T and 1.5T MRI.1 However, 7T MRI scanners are much more expensive and not always available in clinics.2 Therefore, synthesizing 7T MR images from the widely used 3T images is highly desirable for clinical and research applications.3 In this study, we developed a deep learning framework to synthesize high-quality 7T images from 3T images. We investigated the performance of synthetic 7T images in terms of image quality and visualization of pathology in clinical brain imaging.Methods
To synthesize 7T images with good texture details and perceptual quality, a deep learning model (SynGAN) based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) was proposed in this work.4 SynGAN consists of a generator and a discriminator, as shown in Figure 1. The generator synthesizes 7T images from the corresponding 3T images, and the discriminator tries to distinguish the synthetic 7T images from the real ones.MRI examinations were performed at a whole-body 7T scanner (MAGNETOM Terra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using an 8-channel transmitting and 32-channel receiving head coil (Nova Medical, Wilmington, MA, USA) and a whole-body 3T scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using a 20-channel head coil. For both 3T and 7T MRI, a 3D magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo (MPRAGE) sequence was used to acquire the T1-weighted images. Imaging parameters of the 7T MRI were: repetition time = 2300 ms, echo time = 1.95 ms, inversion time = 1050 ms, field of view = 224 × 210, slice thickness = 0.7 mm, voxel size = 0.7 × 0.7 × 0.7 mm3. Imaging parameters of the 3T MRI were: repetition time = 2300 ms, echo time = 2.99 ms, inversion time = 900 ms, field of view = 224 × 210, slice thickness =1.0 mm, voxel size = 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 mm3.
The paired 3T and 7T data were acquired from 66 participants, including 33 healthy, 10 brain tumor, 14 cerebrovascular disease, 8 multiple sclerosis, and 1 other participants. The 3T images were registered to the corresponding 7T images using FLIRT in the FSL package. After bias field correction and skull removal, the image intensities of the 3T and 7T images were normalized to [0, 1]. The paired data were then randomly split into the training and the test datasets (80% training and 20% test).
The qualitative image quality of 3T, 7T, and synthetic 7T images were individually and blindly scored by two experienced radiologists (with 10 and 7 years of experience in brain MRI interpretation) in terms of overall image quality, artifacts, sharpness, contrast, and visualization of vessels with scores ranging from 1 (nondiagnostic) to 5 (excellent).5
Results
Figure 2 shows representative 3T, 7T and synthetic 7T images of a healthy subject and a patient with left middle cerebral artery occlusion. The synthetic 7T images provide improved tissue contrast and texture details compared with the 3T images and show comparable image quality to the 7T images. Representative images of 3T, 7T and synthetic 7T in the presence of pathologic diseases are shown in Figure 3. In these patients, the synthetic 7T images show clearer sharpness and lesion conspicuity compared to the 3T images and offer similar diagnostic image quality as the authentic 7T images for the visualization of various pathology. Compared to 3T images, the synthetic 7T images achieve significantly higher overall image quality, sharpness, contrast, and visualization of vessels (P < 0.001), with no difference in artifacts (P = 0.24). Compared to non-enhanced T1-weighted images at 7T, the synthetic 7T images achieve slightly lower scores in terms of sharpness (P = 0.027) and visualization of vessels (P < 0.001), with no significant difference in overall image quality, artifacts, and contrast (P > 0.05).Discussion and conclusion
In this study, we developed and evaluated a SynGAN approach for synthesizing high-quality 7T images from 3T images. Synthesis of 7T images from the corresponding 3T images is challenging because the two images differ not only in resolution, but also in contrast.2 In this work, we adopted a GAN-based framework to learning the complex 3T-to-7T mapping, because GAN can effectively capture the high frequency details.4 Although previous studies have demonstrated the feasibility of synthesizing 7T image using deep learning, the applicability of this method for clinical brain imaging is yet to be explored. Therefore, extensive test data were used evaluate the performance of synthetic 7T images in this study.Our results show that the synthetic 7T images significantly outperformed the 3T images in terms of overall image quality, sharpness, contrast, and visualization of vessels. In addition, the synthetic 7T images achieved similar overall image quality and visualization of pathology compared with authentic 7T images, providing an alternative way for applying ultra-high field 7T MRI in clinical brain imaging.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81825012, 81730048 and 82151309).References
[1] Rutland J W, Delman B N, Gill C M, et al. Emerging use of ultra-high-field 7T MRI in the study of intracranial vascularity: state of the field and future directions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020;41:2–9.
[2] Qu L, Zhang Y, Wang S, et al. Synthesized 7T MRI from 3T MRI via deep learning in spatial and wavelet domains. Med Image Anal. 2020;62:101663.
[3] Bahrami K, Shi F, Rekik I, et al. 7T‐guided super‐resolution of 3T MRI. Med Phys. 2017;44:1661–1677.
[4] Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2017;1125–1134.
[5] Chen F, Taviani V, Malkiel I, et al. Variable-density single-shot fast spin-echo MRI with deep learning reconstruction by using variational networks. Radiology. 2018;289:366.
Figures
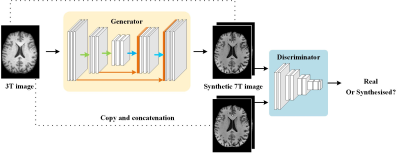
Figure 1. The scheme of SynGAN for synthesizing 7T images from 3T images. The SynGAN consists of a generator and a discriminator.
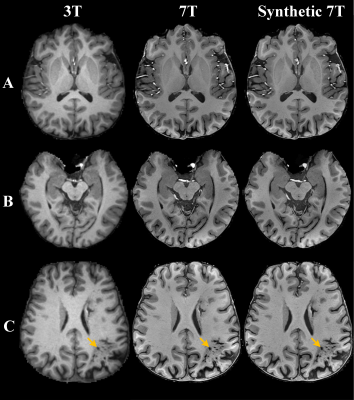
Figure 2. Comparison of representative 3T, 7T and synthetic 7T images. A-B, T1-weighed images in a 22-year-old healthy participant. C, T1-weighed images in a 31-year-old patient with left middle cerebral artery occlusion. Improved tissue contrast and texture details are observed in the corresponding synthetic 7T images.
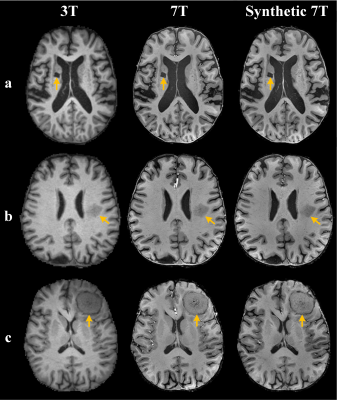
Figure 3. Comparison of representative 3T, 7T and synthetic 7T images. A, T1-weighed images in a 70-year-old man with ischemic cerebrovascular disease. B, T1-weighed images in a 56-year-old man with a left paraventricular lesion. C, T1-weighed images in a 63-year-old woman with meningioma. The synthetic 7T images provide clearer sharpness and lesion conspicuity than the 3T images.