4972
SENSE factor optimization for 2D RF based Reduced Field of View DWI on Cardiac at 3.0T
Yang Wu1, Peng Sun2, Zhigang Wu2, Xiaoxiao Zhang2, Jing Zhang2, and Jiazheng Wang2
1Department of Medical Imaging, Wuhan Asia General Hosipital, Wuhan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1Department of Medical Imaging, Wuhan Asia General Hosipital, Wuhan, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Myocardium, Cardiovascular
Diffusion MRI delivers unique information about the heart without the use of external contrast agents, Because of B0 inhomogeneity within the thorax and short transverse relaxation durations, which cause substantial distortion and signal loss, it has proven technically problematic. DWI with Zoom imaging with 2D RF pulse (iZoom) could significantly minimize distortion, but it is still vulnerable to field inhomogeneity when it is big. iZoom with SENSE could reduce distortion and signal loss even further. An in vivo research on volunteers with various SENSE factors revealed that combining iZoom with SENSE considerably improves visual quality.Introduction
Diffusion MRI provides unique information on the structure, organization, and integrity of the myocardium without the need for exogenous contrast agents1. The conventional single-shot EPI (ssEPI) remains suffering from geometric distortion and blurring due to B0 inhomogeneity and tissue susceptibility. Diffusion MRI in the heart, however, has proven technically challenging because of the intrinsic non-rigid deformation during the cardiac cycle, displacement of the myocardium due to respiratory motion, signal inhomogeneity within the thorax, and short transverse relaxation times1-2. By exciting a small region of interest (ROI), 2D RF could realize zoomed imaging (iZoom) for specific ROI3, which could help in acquiring high resolution imaging, reducing distortion with reduced FOV, and reducing image blurring and other artifacts from non-interesting areas. SENSE can also be used to reduce distortion and signal loss4. iZoom combined with SENSE should be further improve the image quality of DWI, however due to the reduced FOV will have geometry penalty for parallel imaging, there has no any study on this combination on 3T. We hereby do a preliminary study of iZoom using SENSE to find an optimized SENSE for cardiac diffusion MRI.Methods
iZoom could excited the specific reduced the FOV using 2D RF pulse, Fig. 1 shows the pulse sequence for iZoom. Due to the reduced FOV the variation of coil sensitivity map will also be decreased than full FOV, which will reduce the performance of parallel imaging, such as SENSE. To investigate the feasibility of iZoom with SENSE, different SENSE factor was used to evaluate the performance on decreasing signal loss and reducing of distortion. bTFE for morphology imaging, Conventional DWI based on ssEPI with Full FOV (sDWI), iZoom with SENSE 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 was compared by volunteer test. Diffusion weighted and ADC map were both compared. All scans were scanned on a Philips 3.0T system (Elition, Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherland) with a 32-ch torso and spine coil. Detailed scan parameters were summarized in Table 1.Results
Fig 2 shows that the comparison between singl shot balanced turbo FFE (sbTFE) as anatomical images without distortion (A), sDWI with SENSE = 2.0 (B), and DWI based on iZoom with SENSE 1.0(C), 1.5(D), 2.0(E) respectively. To spatially compare the degree of image distortion, the ROIs for Left ventricle and right ventricle were manually delineated on each subject’s sbTFE images, and were mapped to all DW images acquired by the abovementioned schemes. The scan time It shows that DWI based on iZoom has less signal loss (as brown arrow marked) and less distortion as freeform polygon showed. To evaluate the SENSE performance for iZoom, Fig 3 showed that iZoom were separate as different b value with different SENSE factors. It showed iZoom with SENSE = 1.5 has best performance, iZoom with SENSE = 2.0 could see some noise breakthrough. Fig.4 showed that the comparison of ADC map for sDWI and iZoom with different SENSE factor. It shows the ADC map sDWI has the largest nonuniform map, its ADC value is significantly low than all ADC map based on iZoom. It also showed iZoom with SENSE = 1.5 has best performance, iZoom with SENSE = 2.0 could see some noise breakthrough.Discussion and conclusions
The preliminary study shows that iZoom with SENSE could reduce the distortion and signal loss further for cardiac diffusion MRI, due to iZoom could only excite the signal of the region of interest. With 3.0T system, the geometry penalty is relatively small, the results showed that iZoom with SENSE equals 1.5 is the best option for cardiac diffusion in this study. This technique holds the potential for swift clinical translation and implementation for major vendors with simplicity. This strategy could enhance the applicability of cardiac diffusion.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement.References
1. Timothy GR, Marcel PJ, Himanshu B and David ES, Diffusion MRI in the heart, NBM 2017;30:e3426.
2. Sonia NV, Andrew S, Pedro F, Zohya K, Dudley P, David F, Cardiac Diffusion: Technique and Practical Applications. J. MAGN. RESON. IMAGING 2020;52(2):348-368.
3. Wu ZG, Zhang J, Fang WX, Huang F, B1 insensitive zoomed FOV imaging, ISMRM., 2015; 0953.
4. Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger M, Boesiger P,SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI, Magn. Reason. Med., 1999;42(5):952-62.
Figures
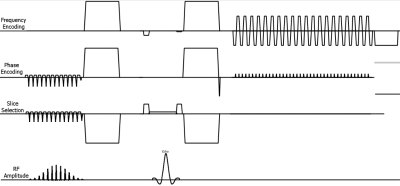
Figure
1. Sequence diagram of iZoom
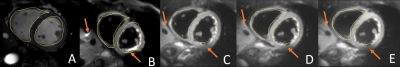
Figure 2. Volunteer test, (A) balanced FFE ; (B) conventional DWI based on
ssEPI, SENSE = 2.0; (C) iZoom, SENSE = 1.0; (D) iZoom, SENSE = 1.5 (C); (E)
iZoom, SENSE = 2.0. All diffusion images have same b value (b=20s/mm2).

Figure
3. Volunteer test, comparison between two groups with different SENSE factor,
one column is b value 20 s/mm2, another column is b value 300 s/mm2.
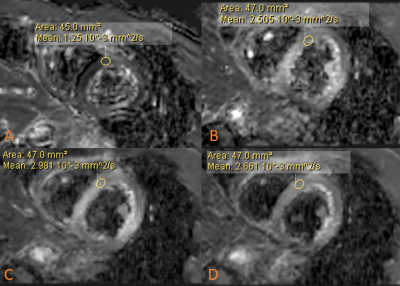
Figure 4. Volunteer test, ADC map comparison, (A) conventional DWI based on
ssEPI, SENSE = 2.0; (B) iZoom, SENSE = 1.0; (C) iZoom, SENSE = 1.5; (D) iZoom,
SENSE = 2.0.
Table 1. Scan parameters for protocols
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4972