4965
Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging Using Low Rank Reconstruction for Multi-shot Variable Auto-Calibrating (vARC) Sampling with Volume Coil
Nitin Jain1, Ashok Kumar P Reddy1, Rajdeep Das1, Sajith Rajamani1, Rajagopalan Sundaresan1, Harsh Kumar Agarwal1, M Ramasubba Reddy2, and Ramesh Venkatesan1
1GE Healthcare, Bangalore, India, 2Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai, India
1GE Healthcare, Bangalore, India, 2Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai, India
Synopsis
Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Body
Diffusion weighted MR imaging (DWI) is key to pathology detection in anatomies such as brain, abdomen and prostate. Echo planar imaging (EPI) provides a rapid means to acquire DWI. EPI with variable k-space sampling scheme and an auto-calibrating image reconstruction technique, vARC, has recently been shown to reduce distortion in DWI and improve the image quality in single channel volume coil/body coil acquisitions. Here, we propose a new low rank reconstruction technique for robust reconstruction and improved image quality for DWI acquired using vARC’s EPI multi-shot acquisition scheme with single channel body coil.Introduction
Diffusion-weighted MRI(DWI) is widely used for routine clinical and neuroscientific applications[1]. The DWI images are typically acquired with multi-channel receive coils using single-shot or multi-shot echo-planar imaging (EPI)[2]. Fast-MRI techniques such as parallel imaging and partial-Fourier MRI is commonly used to reduce the amount of distortion in the EPI-DWI acquisition. Multi-shot acquisitions are used to acquire higher spatial resolution, but they are more prone to ghosting in reconstructions because of motion-induced phase errors among multi-shot excitations. There are many reconstructions techniques proposed for multi-shot DWI such as MUSE[3], POCS-MUSE[2] etc, however, they are limited to multi-channel acquisitions.Single-channel DWI suffers from distortions arising due to B0-inhomogeneity as parallel-imaging cannot be used with single-channel acquisition. Recently, EPI based variable multi-shot auto-calibrating (vARC) acquisition was proposed for single-channel DWI acquisition which can acquire DWI images with clinically acceptable image distortion[4]. The reduction in effective echo-spacing and fully sampled center phase encoding lines enable vARC to get improved SNR and resolution. We propose a locally low-rank regularization (LLR)[5] approach for reconstruction of vARC diffusion-weighted MRI reconstructions. This approach is quite suitable in dealing with motion induced phase errors among different single-channel vARC shots. The proposed vARC-LLR method will enable widespread adoption of volume coil-based DWI in obese patients who may not be scanned with surface-coil especially in the non-wide bore commercial MRI scanners where there is a chance of pinching of coil between patient abdomen and scanner bore. It may also find it’s use case in pediatric cases where diffusion imaging is done using smaller volume coils.
Methods
Data Acquisition: The data acquisition is same as that of the vARC[4], wherein the central k-space is fully sampled with certain calibration width. The outer k-space is subsampled by a factor of number of shots to be acquired. The subsampled outer k-space resembles typical multi-shot acquisitions.Low-Rank Reconstruction: The flow chart for proposed reconstruction technique is shown in Figure 1. The low-rank methods are sensitive to initialization, therefore, self-calibrated parallel imaging method, ARC[6], and partial-Fourier is used to generate robust initialization to the low rank reconstruction method. In ARC, multiple shots is treated as multiple coils to fill the missing k-space lines in the outer shot k-space region. Partial-Fourier using POCS reconstruction is done for each shot to generate fully sampled k-space estimate. The fully sampled k-space estimate is used as an initial guess in shot locally low-rank (LLR) regularization algorithm. Each iteration of the proposed low rank approach first applies low rank in the small neighborhood (kernel size=5x5) across all the shots followed by data consistency to match the acquired k-space with desired accuracy.
Prospective Data Acquisition: Volunteers were scanned for Abdomen MRI at commercial 1.5T Signa-HDxt MRI (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee) with informed consent in an institute’s IRB approved study. Commercial EPI-DWI pulse sequence was modified to prospectively acquire the proposed subsampled EPI-DWI acquisition. DWI of abdomen (FOV=24cmx24cm, Matrix Size=256x256 and b-values of 50 and 500s/mm2) was acquired with surface coil and body-coil. 12-channel surface-coil images were acquired with parallel imaging acceleration of 2 (12Ch-PI2), single shot and single channel volume coil (1Ch-SS), and single channel volume coil vARC with shot factor of 2 (1Ch-vARC2). The scan times are kept similar for all three DWI scans.
Results and Discussion
The abdomen DWI with breadth hold (top row) and respiratory trigger (bottom row) are shown in Figure 2. The corresponding ADC maps are shown in Figure 3. The vARC acquisitions with new reconstruction algorithm demonstrate improved liver diffusion imaging when compared to corresponding single shot acquisitions for both breath hold and respiratory cases on volume coil. The values in vARC ADC maps are more uniform (over short T2 anatomies such as liver) as compared to the values in single-shot ADC maps. The results are shown for a single volunteer data with vARC sampling 32 calibration lines.The vARC central calibration region helps in getting k-space filled with the right phase, which can be difficult in plain multi-shot or external navigator acquisitions. The vARC-LLR approach does not require explicit estimations of the phase maps, instead, it relies on converting smooth phase-modulations between shots as null space-vectors of a structured matrix. The unacquired data points in original k-space are filled-in using locally low rank algorithm applied on structured shot matrix iteratively with support of the initial fully filled k-space guess, subject to data consistency.
The vARC sampling provides a way to change the width of central calibration region. It is found that distortions in the final image is dependent on the width of this region. At the same time, vARC helps in filling the k-space guess and reduction in aliasing by reducing the phase mismatch between shots in reconstruction algorithm. The same algorithm with incorporation of channel sensitivity information is expected to work for multi shot-multi-channel data.
Conclusions
DWI-MRI of obese patients acquired using body coil can be done using the proposed vARC-LLR image acquisition and image reconstruction scheme. The qualitative results show robustness to micro-/macro-motion induced phase variations across multiple shots and NEX which would have otherwise caused aliasing. Qualitative result showed improved SNR with less distortions when compared to single-shot single-channel images. Further assessment with patient population is required.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Le Bihan, D., Poupon, C., Amadon, A. and Lethimonnier, F., 2006. Artifacts and pitfalls in diffusion MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 24(3), pp.478-488.
- Kuei-Chen N, Guidon A, Chang HC, Truong TK, Song Aw, Chen NK. A robust multi‐shot scan strategy for high‐resolution diffusion weighted MRI enabled by multiplexed sensitivity‐encoding (MUSE). NeuroImage. 2013;72:41–47.
- Chu ML, Chang HC, Chung HW, Truong TK, Bashir MR, Chen NK. POCS‐based reconstruction of multiplexed sensitivity encoded MRI (POCSMUSE): a general algorithm for reducing motion‐related artifacts. Magn Reson Med. 2015;74:1336–1348.
- Reddy A, Agarwal H, Das R, Sundaresan R, Ahmed S, Rajamani S, Mehta B, Wu G, Reddy MR, Venkatesan R. Multi-Shot Liver Diffusion MRI Using Variable Auto-Calibrating (vARC) Sampling Across Averages, 1146, Proc ISMRM, 2022.
- Hu Y, Levine EG, Tian Q, et al. Motion-robust reconstruction of multishot diffusion-weighted images without phase estimation through locally low-rank regularization. Magn Reson Med. 2019;81:1181–1190.
- Brau, A.C., Beatty, P.J., Skare, S. and Bammer, R. Comparison of reconstruction accuracy and efficiency among auto-calibrating data‐driven parallel imaging methods. Magn Reson Med, 2008;59(2): 382-395.
Figures
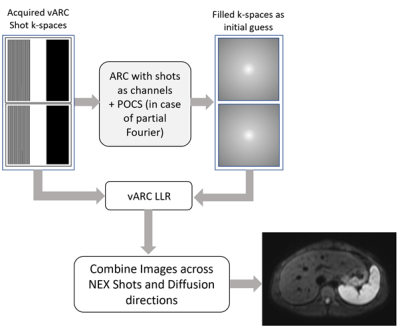
Figure 1. Flow chart of
reconstruction technique. ARC and POCS reconstructions are done for each
shot to generate fully sampled k-space estimate. The fully sampled k-space
estimate along with acquired vARC k-space are used as an initial guess in vARC-LLR algorithm.
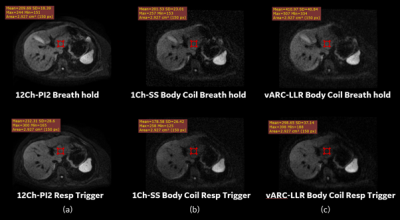
Figure 2: A slice =500 s/mm2 DWI
MRI. (a) 12Ch-PI2 DWI (b) 1Ch-SS Body Coil DWI (c) vARC-LLR
with two shot Body Coil DWI. The
vARC-LLR reconstruction algorithm demonstrate improved liver diffusion imaging
when compared to corresponding single shot acquisitions for both breath hold
and respiratory cases on volume coil.
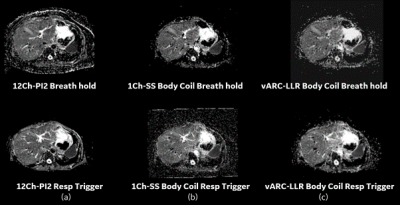
Figure 3: ADC Maps. (a) 12Ch-PI2 DWI
(b) 1Ch-SS Body Coil DWI (c) vARC-LLR with two shot Body Coil DWI. The values in vARC-LLR ADC
maps are more uniform (over short T2 anatomies such as liver) as compared to
the values in single shot ADC maps.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4965