4924
High Resolution Image Quality Improvement of T2 FLAIR Coronal Hippocampal Imaging by Deep Learning Reconstruction
Yang Jing1, Li Qiong Ge1, Wu Tao2, Qi Zhi Gang1, Zhao Cheng1, and Lu Jie1
1Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, xuanwu hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2General Electric Medical System Trade Development (Shanghai) Co., Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, xuanwu hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2General Electric Medical System Trade Development (Shanghai) Co., Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Brain, Hippocampus, Deep learning reconstruction, Epilepsy
Deep learning reconstruction (DL Recon) method can improve the image signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio without prolonging the scanning time and affecting the signal intensity difference of bilateral hippocampus. It can improve the image quality of hippocampus toe and surrounding small lesions dramatically as in Fig.1.Synopsis
Deep learning reconstruction (DL Recon) method can improve the image signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio without prolonging the scanning time and affecting the signal intensity difference of bilateral hippocampus. It can improve the image quality of hippocampus toe and surrounding small lesions dramatically as in Fig.1Background
Hippocampus is an important brain functional area for learning and short-term memory. The volume[1,2]and signal intensity of hippocampus may impact the clinical diagnosis of epilepsy, cognitive impairment and schizophrenia. The absence of hippocampus toe and black belt found by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an important index to diagnose medial temporal lobe sclerosis and intractable epilepsy with the sensitivity 92%, and the significance 100%[3-5]. However, the resolution of hippocampus based on clinical T2FLAIR coronal imaging is about 1mm/pixel, which can show the black belt along the sulcus of hippocampus, but all levels of the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus are not clear. Therefore, the improved resolution of hippocampus may improve clinical diagnosis. But if the resolution is increased to 0.6mm/pixel, the scanning time and the image noise would increase simultaneously. This study investigates whether deep learning reconstruction (DL Recon) can improve the image quality of high-resolution T2-FLAIR coronal MRI without increasing the scanning time, in order to observe more internal structures of hippocampus, and provide more help for clinical diagnosis of hippocampal diseases.Materials and Methods
Prospectively, 36 patients with nervous system diseases were enrolled. The 3.0T magnetic resonance scanner (Signa Premier, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, USA) was used for MRI examination, and 48-channel head coil was used for high-resolution T2-FLAIR coronal scan of hippocampus. The images were reconstructed by DL Recon. Subjective evaluation on the noise, artifact, hippocampal structure identification, lesion identification and diagnosis acceptance of the original reconstructed (OR) image and DL Recon image, and objective measurement and calculation of the signal-to-noise ratio, contrast noise ratio and signal intensity difference of bilateral hippocampus of the two groups were conducted. Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to test the difference of subjective results of images. Paired sample t-test was used to test the difference of objective results.Results
The image noise, hippocampal structure clarity, lesion detection and diagnosis acceptance score based on DL Recon were higher than those from OR T2-FLAIR hippocampal coronal image (P<0.001), and there was no significant difference in artifact score (Z=-1.730; P=0.084); The SNR and CNR values of the coronal images of DL Recon T2-FLAIR hippocampus were significantly higher than those of OR T2-FLAIR hippocampus (t=-13.061; P<0.001 and t=-16.224; P<0.001); (The overall comparison score and SNR comparison are listed in Table 1 and 2, and respective images are shown in Figure 1). There was no significant difference in signal difference between the two groups (t=-0.29; P=0.977)。Conclusion
The deep learning reconstruction method can obviously improve the definition of hippocampal structure and small lesions in high-resolution T2-FLAIR coronal images, reduce the noise and provide high-quality images for clinical diagnosis.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Rebsamen M,Radojewski P,McKinley R,et al.A quantitative imaging biomarker supporting radiological assessment of hippocampal sclerosis derived from deep learning-based segmentation of T1w-MRI[J].Front Neurol,2022,13:812432.DOI:10.3389/fneur.[2] Pan K,Zhao L,Gu S,et al.Deep learning-based automatic delineation of the hippocampus by MRI: geometric and dosimetric evaluation[J].Radiat Oncol,2021,6(1):12.DOI:10.1186/s13014-020-01724-y. [3]Oppenheim C,Dormont D,Biondi A,et al.Loss of digitations of the hippocampal head on high-resolution fast spin-echo MR: a sign of mesial temporal sclerosis[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,1998,19(3):457-63. [4] Howe KL, Dimitri D, Heyn C,et al. Histologically confirmed hippocampal structural features revealed by 3T MR imaging: potential to increase diagnostic specificity of mesial temporal sclerosis[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2010,31:1682-9.DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A2154.[5] Huesmann GR,Schwarb H,Smith DR,et al. Hippocampal stiffness in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy measured with MR elastography: Preliminary comparison with healthy participants[J].NeuroimageFigures
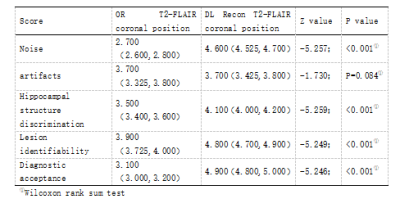
Table1.Subjective score of coronal images of OR T2-FLAIR and DL Recon T2-FLAIR.
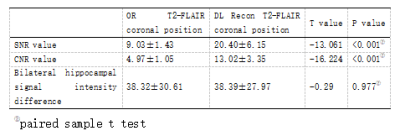
Table2.SNR value, CNR value and signal intensity difference of bilateral hippocampus of OR T2-FLAIR and DL Recon T2-FLAIR coronal images.
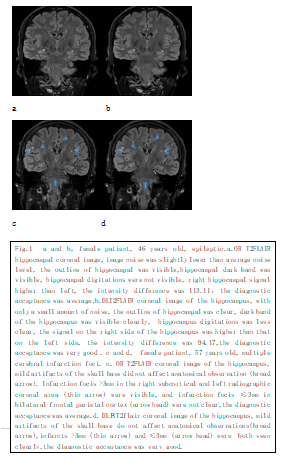
Fig.1 Contrast of coronal images of the hippocampus with OR T2-FLAIR and DL Recon T2-FLAIR.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4924