4895
Quantitative MR T1 Value of Arterial Plaque using 3D Black-blood MP2RAGE:A Feasibility Study
Qizeng Ruan1, Zehe He1, Zeping Liu2, Yuhui Nie2, Liping Liao1, Qingchun Li1, Mingxia Tan1, Lanbin Huang1, Guoxi Xie2, YuanLi Wang1, and Minglu Zhou1
1The First People’s Hospital of Qinzhou, Qinzhou, China, 2Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
1The First People’s Hospital of Qinzhou, Qinzhou, China, 2Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Relaxometry, Cardiovascular, T1 mapping
Carotid plaque is an important cause of stroke. The T1 value of the plaque could provide potential information for the diagnosis. In this work, we compared the performance of T1 mapping of BB-MP2RAGE and conventional MP2RAGE in carotid plaque. Experiments demonstrated BB-MP2RAGE could achieve more accurate measurement of T1 value for diagnosis of carotid plaque.Purpose
MR T1 value of arterial plaque is associated with its T1-weighted signal intensity, which has been used for identifying vulnerable plaque [1]. However, quantitative plaque T1 value remains a big challenge because it is hard to differentiate the plaque from bright arterial blood based on conventional T1-mapping approaches. Recently, a novel black-blood T1 mapping technique which is based on DANTE black-blood preparation and MP2RAGE readout (BB-MP2RAGE) was developed [2]. In this study, we sought to quantitative arterial plaque T1 value using BB-MP2RAGE technique and assessed its capability and reliability on plaque T1 mapping.Methods
The technique was conducted first on 6 healthy volunteers (24.0 ± 2.9 years; 4 males) to assess its capability on carotid artery wall T1-mapping and then conducted on 7 patients with carotid plaques (mean age, 69.8 ± 10.4 years; 5 males) at a 3T system (Skyra, Siemens, Germany) with a 32-channel coil. Conventional MP2RAGE which is a bright-blood T1-mapping technique was also conducted for comparison. Imaging parameters for BB-MP2RAGE and conventional MP2RAGE included: field of view = 204×225 mm2, spatial resolution = 0.88×0.88×2.00 mm3 (interpolated to 0.44×0.44×1.00 mm3), TR/TE = 5000/2.73 ms, TI 1/TI 2 = 600/2600 ms, flip angle 1/flip angle 2 = 8/8°, scan time = 2min30sec. The images of BB-MP2RAGE and conventional MP2RAGE were randomized and reviewed by two radiologists with > 5 years’ experience independently. T1 values of plaques were measured two times by each reader. The agreement of T1 values between two different readers and between two measurements was analyzed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) with consistency intervals reported at the 95%.Results
Blood flow signals were effectively suppressed in BB-MP2RAGE images both in volunteer and patient experiments (Figure 1&2). T1 values of carotid artery wall and plaques measured on BB-MP2RAGE were lower than that of conventional MP2RAGE (Table 1&2). Interreader agreement of BB-MP2RAGE was better than MP2RAGE both in the T1 values of carotid artery wall (0.958 vs. 0.832) and plaques (0.996 vs. 0.868) (Table 1&2). The results of test-retest agreement were also similar in volunteer and patient experience: BB-MP2RAGE and MP2RAGE got the comparable test-retest agreement (volunteer: 0.968 vs. 0.941 by reader 1, and 0.986 vs. 0.978 by reader 2; patient: 0.979 vs. 0.962 by reader 1, and 0.995 vs. 0.959 by reader 2).Discussion
This is the first attempt to quantify plaque T1 value by using MR approaches. As the blood flow signals were suppressed, partial volume effect between blood flows and plaques was reduced, allowing accurate plaque T1 measurement on BB-MP2RAGE images. In addition, the boundaries of the carotid artery wall were displayed much clearer on BB-MP2RAGE images than on MP2RAGE images, which helps to identify plaque and thus achieves excellent inter-/intra-reader agreements on T1 measurement of plaque.Conclusion
BB-MP2RAGE is a novel black-blood T1 mapping technique which can effectively suppress arterial blood flow signals and thus allows more accurate measurement of T1 value in carotid plaque.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Qiao H, Li D, Cao J, et al. Quantitative evaluation of carotid atherosclerotic vulnerable plaques using in vivo T1 mapping cardiovascular magnetic resonaonce: validation by histology. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020;22(1):38.
[2] Nie H, et al. Three-Dimensional Black-Blood T1 Mapping: Sequence Design & Initial Experience. ISMRM. 2022.
Figures
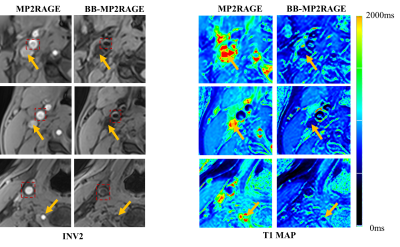
Figure 1. INV2 images and T1 maps
obtained by MP2RAGE and BB-MP2RAGE in healthy volunteer experiments. Blood flow
signals on MP2RAGE images were effectively suppressed on BB-MP2RAGE (yellow
arrows). The boundaries of the carotid artery wall (red dashed boxes) were
shown clearly on BB-MP2RAGE images, which can be used for contouring plaque for
T1 measurement.
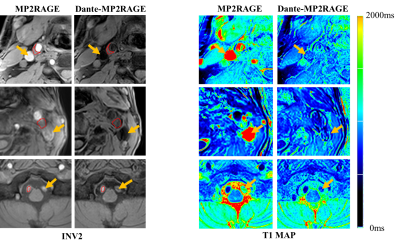
Figure 2. INV2 images and T1 maps
obtained by MP2RAGE and BB-MP2RAGE in patient experiments. High-intensity blood
flow signals in MP2RAGE were effectively suppressed in BB-MP2RAGE (yellow
arrows). The boundaries of the plaques (red curves) were shown more clearly in BB-MP2RAGE.
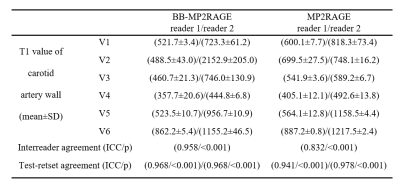
Table 1. Results of T1 measurement
of carotid artery wall and agreement between the two readers and the two
measurements in volunteer experiment.
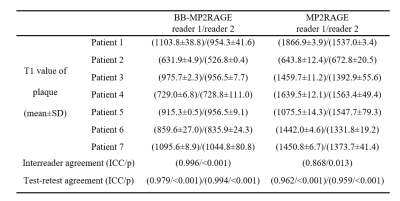
Table 2. Results of T1 measurement of
plaques and agreement between the two readers and the two measurements in
patient experiment.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4895