4845
Vasodilator Stress Myocardial Strain in Coronary Artery Disease:An Animal Study With Histological Validation1Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College Fuwai Hospital, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Myocardium, Heart
ATP can cause a pronounced positive inotropic effect on human heart. CMR-FT even at rest provides an excellent negative predictive value for myocardial ischemia and infarction in patients with CAD. CMR-FT is easy to perform without the need for dedicated acquisition and complex post-processing which can be applied to standard CMR cine sequences. Rest myocardial strain might be a noninvasive option serving as an additional gatekeeper for CAD patients with a needle-free test. Human studies are needed to validate these findings in a multicenter setting and to test whether CMR-FT can be incorporated into clinical guidelines.Introduction/Purpose
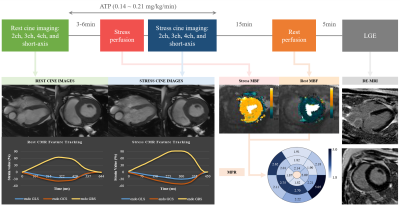
It is still challenging for cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) to detect myocardial ischemia and infarction without the use of gadolinium contrast. The aim of this study is to evaluate the potential value of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) stress myocardial strain derived from CMR-feature tracking (CMR-FT) as a novel option for the detection of myocardial ischemia and infarction in swine model. We hypothesized that the abnormality of myocardial motion after ischemia within the progressive coronary artery stenosis can be detected by CMR-FT at rest and during ATP stress.Method
Progressive obstructive coronary artery disease (POCAD) model was constructed using Ameroid constrictor. Rest and ATP stress cines, conventional myocardial rest and ATP stress perfusion imaging and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) were scanned and analyzed. Rest and ATP stress myocardial strain, fully absolute myocardial perfusion and LGE quantitation were analyzed among the normal, remote, ischemic, and infarcted myocardium. Associations between myocardial strain and conventional contrast myocardial perfusion and further diagnostic performance of strain were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.Results
A total of 20 healthy male Chinese miniature swine were prospectively enrolled in this study (10 normal control and 10 POCAD swine. All rest and ATP stress strain parameters were reduced significantly in ischemic segments compared with normal segments (all p<0.05); rest and ATP stress circumferential strain (CS) and radial strain (RS) were significantly different among remote, ischemic, and infarcted myocardium (all p<0.001). The areas under ROC curve for detecting ischemic and infarcted myocardium were 0.777 (95%CI 0.702, 0.853) and 0.940 (95%CI 0.900, 0.979) for stress RS, and 0.744 (95%CI 0.645, 0.843) and 0.935 (95%CI 0.886, 0.983) for rest RS (all p<0.001). Heat map visualization illustrated that RS and CS showed good correlations with perfusion parameters especially in infarcted segments. Normal controls showed significant higher absolute global CS and RS during ATP stress in comparison with baseline (-48.6%±9.5% vs. -41.6%±3.3% and 86.4%±9.0% vs.71.8%±10.3%, respectively, both p<0.05), without significant global longitudinal strain (LS) reactivity (-32.0%±3.9% vs. -29.8%±4.4%, p=0.132).Discussion
In this proof-of-principle study, we used myocardial strain parameters to quantitatively estimate myocardial motion and deformation in normal and IHD swine, and we found that ATP could cause distinctive PIE on myocardium, which can be detected by CMR-FT without gadolinium contrast. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first study to evaluate CAD using ATP stress myocardial strain by CMR-FT.Conclusions
ATP can cause a pronounced PIE in left ventricle which can be quantitatively detected by CMR-FT. Stress RS was the most powerful parameter to distinguish non-ischemic, ischemic and infarcted myocardium. Significantly reduced rest RS could make the same differentiation comparable to stress RS. Therefore, CMR-FT even at rest held promise for CAD evaluation without the need of gadolinium contrast. Such a noninvasive parameter might be a noninvasive option serving as an additional gatekeeper for IHD patients with a needle-free test.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Rahman H, Scannell CM, Demir OM, et al. High-Resolution Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for the Identification of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction. J A m Coll Cardiol Img. 2021;14:978-986.
2. Kotecha T, Chacko L, Chehab O, et al. Assessment of Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease Using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Pixelwise Quantitative Perfusion Mapping. J A m Coll Cardiol Img. 2020;13:2546-2557.
3. Shan K, Constantine G, Sivananthan M, Flamm SD. Role of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of myocardial viability. Circulation. 2004;109:1328-1334.
4. Ochs MM, Kajzar I, Salatzki J, et al. Hyperventilation/Breath-Hold Maneuver to Detect Myocardial Ischemia by Strain-Encoded CMR: Diagnostic Accuracy of a Needle-Free Stress Protocol. J A m Coll Cardiol Img. 2021;14:1932-1944.
5. Xu J, Yang W, Zhao S, Lu M. State-of-the-art myocardial strain by CMR feature tracking: clinical applications and future perspectives. Eur Radiol. 2022. 6. Schneeweis C, Qiu J, Schnackenburg B, et al. Value of additional strain analysis with feature tracking in dobutamine stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance for detecting coronary artery disease. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2014;16:72.
7. Schuster A, Kutty S, Padiyath A, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance myocardial feature tracking detects quantitative wall motion during dobutamine stress. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011;13:58.
8. Shaaban M, Tantawy SW, Elkafrawy F, Romeih S, Elmozy W. Multiparametric Rest and Dobutamine Stress Magnetic Resonance in Assessment of Myocardial Viability. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;54:1773-1781.
9. Romano S, Romer B, Evans K, et al. Prognostic Implications of Blunted Feature-Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain During Vasodilator Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Stress Imaging. J A m Coll Cardiol Img. 2020;13:58-65.
10. Hays JT, Mahmarian JJ, Cochran AJ, Verani MS. Dobutamine thallium-201 tomography for evaluating patients with suspected coronary artery disease unable to undergo exercise or vasodilator pharmacologic stress testing. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;21:1583-1590.