4826
The application of REACT based on CS-AI for abdominal vessel imaging in kidney-pancreas transplantation and diabetic nephropathy patients1Department of Radiology, the First Hosipital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Vessels, Image Reconstruction, REACT
Patients with diabetic nephropathy and terminal renal insufficiency and those requiring combined kidney-pancreas transplantation should avoid using gadolinium-based contrast agents MR Angiography due to its potential nephrotoxicity. Compressed SENSE (CS) Artificial Intelligence (CS-AI) reconstructed Relaxation-Enhanced Angiography without Contrast and Triggering (REACT) sequence provides a simultaneous depiction of abdominal arterial and venous vessels. This study aims to improve the image quality of REACT sequence with CS-AI and further quantitatively evaluate the image quality in patients with diabetic nephropathy, and CS-AI reconstructed REACT sequence was first applied to image transplanted renal arteries in patients with combined kidney-pancreas transplantation.Introduction
Diabetes is the fastest-growing global health emergency of the 21st century [1]. Chronic hyperglycemia could lead to progressive renal cell failure and eventually to terminal diabetic nephropathy. Combined kidney-pancreas transplantation represents an effective resolution of diabetic nephropathy, and preoperative imaging evaluation of bilateral renal and abdominal vascular anatomy may play a critical role. In clinical practice, gadolinium-based contrast agents have been routinely used to image arterial systems in MRI. However, the usage of external gadolinium-based contrast agents should be avoided in patients with kidney dysfunction. It has been reported that gadolinium-based contrast agents were associated with the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with severe kidney dysfunction [2,3]. Further, intravenous injected gadolinium may be deposited in the brain, which may have a certain toxic effect on the human body [4]. Relaxation-Enhanced Angiography without Contrast and Triggering (REACT) sequence, enabling excellent vascular contrast ratio in the free-breathing state without trigger, was employed in imaging vessels in recent years [5]. In addition, with the help of a new artificial intelligence (AI) reconstruction algorithm, Compressed SENSE with Artificial Intelligence (CS-AI) can not only effectively shorten scan time, but also ensure image quality [6]. The purpose of this study is to assessment the image quality of abdominal vessels of diabetic nephropathy using CS-AI reconstructed REACT sequence, and further investigate the feasibility of REACT sequence evaluation transplanted renal artery in patients with combined kidney-pancreas transplantation.Methods
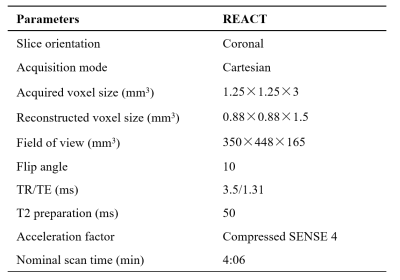
This study was approved by the local institutional review board. Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study. A total of 3 healthy volunteers and 6 patients were enrolled, including patients underwent combined kidney-pancreatic transplantation (n=3) and diabetic nephropathy (n=3). All volunteers were examined on a 3.0T whole-body clinical system (Ingenia Elition, Philips Healthcare) using a dedicated abdominal coil from August 2022 to October 2022. All volunteers were receiving an optimized REACT sequence and the parameters were shown in Table 1. The REACT images were reconstructed by CS and CS-AI with acceleration factor 4. Signal to noise ratio (SNR) and contrast to noise ratio (CNR) were measured and calculated by drawing the region of interest (ROI) in the same position on raw images. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism7.0. Values of p < 0.05 were considered significant for each analysis.Results
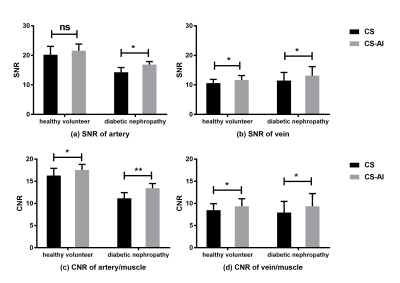
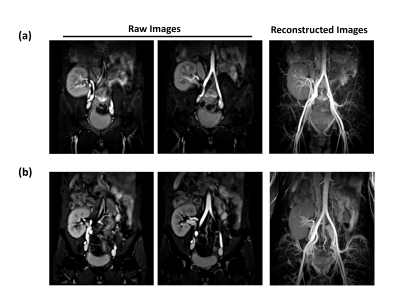
Representative abdominal vessel images (including raw images and reconstructed images) of diabetic nephropathy patients and healthy volunteers using CS and CS-AI reconstructions are shown in Figure 1. As shown in Figure 2, CS-AI reconstructions significantly increased the image SNR of arteries and veins in diabetic nephropathy patients compared to CS (16.87±1.03 vs 14.29±1.61, p<0.05 and 13.17±3.03 vs 11.46±2.75, p<0.05, respectively). The CNR of artery/muscle, and the CNR of vein/muscle in CS-AI reconstructed images were also higher than that of CS in both healthy volunteers (17.56±1.25 vs 16.29±1.63, p<0.05 and 9.37±1.69 vs 8.48±1.46, p<0.05, respectively). In the group of diabetic nephropathy patients, CS-AI reconstructions also enhanced the CNR of artery/muscle and vein/muscle compared with CS (13.44±1.06 vs 11.15±1.30, p<0.01 and 9.38±2.84 vs 7.93±2.52, p<0.05, respectively). Additionally, we performed CS-AI reconstructed REACR sequence scans in patients with combined kidney-pancreas transplantation and obtained clear anatomical images of the transplanted renal arteries, abdominal vessels, even the small branches of distal renal arteries (Figure 3).Discussion
In this study, we assessed a novel REACT sequence based on CS-AI reconstruction for abdominal vessel imaging in patients with diabetic nephropathy or combined kidney-pancreatic transplantation. REACT sequence enables simultaneous depiction of abdominal arterial and their tiny branches even the venous vessels, the CS-AI reconstruction algorithm has shown improved image quality and enhanced SNR and CNR results compared to CS. The advantage of non-contrast agent makes REACT sequence especially suitable for patients with kidney dysfunction, such as diabetic nephropathy and hypertensive nephropathy. CS-AI reconstructed REACT sequence could delineate the contour and branches of renal arteries in patients with combined kidney-pancreas transplantation, providing important anatomical information of abdominal vessels preoperative pancreatic kidney transplantation for surgeons. The acceleration factor is only set to 4 in this study, more acceleration factors need to be further evaluated and verified in more patients.Conclusion
The results of SNR and CNR show that CS-AI significantly improves the image quality of REACT sequence. CS-AI reconstructed REACT sequence provides better image quality of abdominal vessels in patients with diabetic nephropathy and combined kidney-pancreas transplantation, and it might be clinically useful for assessment of abdominal vessels.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Cloete L. Diabetes mellitus: an overview of the types, symptoms, complications and management. Nurs Stand. 2022 Jan 5;37(1):61-66.
[2] Grobner T. Gadolinium--a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006 Apr;21(4):1104-8.
[3] Marckmann P, Skov L, Rossen K, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: suspected causative role of gadodiamide used for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006 Sep;17(9):2359-62.
[4] Errante Y, Cirimele V, Mallio CA, et al. Progressive increase of T1 signal intensity of the dentate nucleus on unenhanced magnetic resonance images is associated with cumulative doses of intravenously administered gadodiamide in patients with normal renal function, suggesting dechelation. Investigative Radiology. 2014 Oct;49(10):685-690.
[5] Yoneyama M, Zhang S, Hu HH, et al. Free-breathing non-contrast-enhanced flow-independent MR angiography using magnetization-prepared 3D non-balanced dual-echo Dixon method: A feasibility study at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Nov; 63:137-146.
[6] Vranic JE, Cross NM, Wang Y, et al. Compressed Sensing-Sensitivity Encoding (CS-SENSE) Accelerated Brain Imaging: Reduced Scan Time without Reduced Image Quality. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Jan;40(1):92-98.
Figures