4808
Machine learning for detecting sensorineural hearing loss utilizing functional imaging with a combination of static and dynamic brain features1Radiology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Head & Neck/ENT, fMRI (resting state)
Alterations of static and dynamic brain function have been found in sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL). The combination of data-driven machine learning based classifiers and multiple imaging features can identify SNHL and healthy controls automatically. The spearman rank correlation with radial basis functional kernel support vector machine (SVM) and sigmoid SVM provides promising neural biomarkers for clinical classifier of SNHL.Objectives
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is most common sensory deprivation and often unrecognized by patients, inducing not only auditory but also non-auditory symptoms [1]. Many studies used traditional methodologies to diagnose SNHL presence with the help of clinical doctors, while machine learning has been widely applied to automatically identify various datasets and risk factors of diseases. Existing researches conducted machine learning models with hearing thresholds and RNA expressions to diagnose hereditary hearing loss [2], noise-induced hearing loss [3] and SNHL [4], but they ignored the involvement of neural functions. fMRI based radiomics can be utilized to explore neurological disease biomarkers and underlying mechanism, such as cognitive impairments and depression [5-7]. Data-driven classifier modeling with the combination of neural static and dynamic imaging features could be effectively used to classify SNHL and Healthy Controls (HCs).Methods
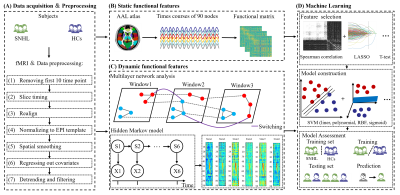
We conducted hearing evaluation, neurological scale tests and resting-state MRI on 110 SNHL and 106 HCs (Figure 1). Static brain characteristics includes f1ALFF (0.01–0.027 Hz), f2ALFF (0.027–0.073 Hz), ReHo, binary DC (BDC) and weighted DC (WDC). we applied multilayer network and HMM to time courses which were extracted from 90 nodes. 1267 static and dynamic imaging characteristics were extracted from MRI data, then three methods of feature selection were computed, including spearman rank correlation test, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and t test as well as LASSO. Linear, polynomial, radial basis functional kernel (RBF) and sigmoid support vector machine (SVM) models were chosen as the classifiers with five-fold cross-validation. The ROC, AUC, sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were calculated for each model.Results
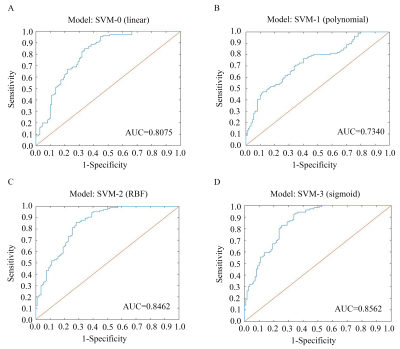
SNHL subjects had higher hearing thresholds in every frequency, as well as worse performance in cognitive and emotional evaluations than HCs. After comparison, the significant brain regions using LASSO based on static and dynamic features was consistent with between-group analysis, including auditory and non-auditory areas. The subsequent AUCs of four SVM models (linear, polynomial, RBF and sigmoid) were as follows: 0.8075, 0.7340, 0.8462 and 0.8562 (Figure 2). RBF and sigmoid SVM had relatively higher accuracy, sensitivity and specificity.Conclusions
Our research raised the attention on dynamic alterations underlying hearing deprivation. Model learning-based models might provide several useful biomarkers for classifier and diagnosis SNHL.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Doctoral Program of Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Jiangsu Province (JSSCBS20211544), Xinghuo Talent Program of Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Special Fund for Health Science and Technology Development (YKK21133).References
1. Tordrup, D., et al., Global return on investment and cost-effectiveness of WHO's HEAR interventions for hearing loss: a modelling study. Lancet Glob Health, 2022. 10(1): p. e52-e62.
2. Luo, X., et al., Machine learning-based genetic diagnosis models for hereditary hearing loss by the GJB2, SLC26A4 and MT-RNR1 variants. EBioMedicine, 2021. 69: p. 103322.
3. Chen, F., et al., Contributions and limitations of using machine learning to predict noise-induced hearing loss. Int Arch Occup Environ Health, 2021. 94(5): p. 1097-1111.
4. Shew, M., et al., Using Machine Learning to Predict Sensorineural Hearing Loss Based on Perilymph Micro RNA Expression Profile. Sci Rep, 2019. 9(1): p. 3393.
5. Chand, G.B., D.S. Thakuri, and B. Soni, Salience network anatomical and molecular markers are linked with cognitive dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment. J Neuroimaging, 2022. 32(4): p. 728-734.
6. Shin, N.Y., et al., Cortical Thickness from MRI to Predict Conversion from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia in Parkinson Disease: A Machine Learning-based Model. Radiology, 2021. 300(2): p. 390-399.
7. Shi, Y., et al., Multivariate Machine Learning Analyses in Identification of Major Depressive Disorder Using Resting-State Functional Connectivity: A Multicentral Study. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2021. 12(15): p. 2878-2886.
Figures