4737
Implicit Temporal-compensated Adversarial Network for 4D-MRI Enhancement
Yinghui Wang1, Tian Li1, Haonan Xiao1, and Jing Cai1
1Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
1Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, 4D-MRI\Enhancement\Temporal-compensation
In this study, we proposed and evaluated a deep learning technique for refining four-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (4D-MRI) in the post-processing stage. More specifically, we designed an implicit temporal-compensated adversarial network (ITAN) based on the intrinsic property of 4D-MRI to improve image quality with neighboring phases. It can overcome its inherent challenges of data deficiency, misalignment between training pairs, and complex texture details. The qualitative and quantitative results demonstrated that the proposed model can suppress the noise and artifacts in 4D-MR images, recover the missing details and perform better than a state-of-the-art method.Introduction
Four-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (4D-MRI) has shown great potential in motion management, target delineation, and treatment planning1. However, most 4D-MRI techniques are still at the investigation stage and have several deficiencies. Current prospective 4D-MR images suffer from insufficient image quality, e.g., limited spatial resolution, relatively low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), motion artifacts caused by breathing variations, and failure to show anatomical structures in detail, which greatly hindered its application in real clinic2. Therefore, high-quality (HQ) 4D-MRI is warranted for the clinical adoption of 4D-MRI. One solution to generate HQ 4D-MR images is to refine low-quality (LQ) 4D-MRI images by capturing perceptually important image features and texture details from referenced HQ images. Recently, deep learning (DL) has snowballed and verified its feasibility in upgrading the quality of images3,4. However, existing DL-based models mainly aim at natural images instead of medical ones (more specifically, 4D-MR images) and fail to consider temporal information of 4D-MRI. For 4D-MR images, enhancement is more challenging: 1) training samples are relatively scarce which will easily lead to under-fitting/over-fitting; 2) the 4D-MR image and its corresponding HQ MR image are not perfectly matched due to significant motion; 3) abdominal 4D-MRI obtains abundant texture details and varied intensity distribution. Therefore, pioneering models such as enhanced deep super-resolution network (EDSR) 5 with pixel-wise L1 or L2 norm-based loss functions may not work well and are prone to over-smoothing. In this study, we propose a more sophisticated DL model for abdominal 4D-MRI to improve its overall quality via implicit temporal compensation.Methods
The dataset used for training and testing the proposed network contains 32 liver cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. The study protocol is approved by the institutional review board. Each patient underwent 4D-MRI using the TWIST volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination (TWIST-VIBE) MRI sequence. The corresponding HQ images are regular T1w (breath-hold) 3D MRI scan. In the thirty-two patients, 27 cases are used as training, while the others are used for testing. The original 4D-MR images are sorted into respiratory-correlated phases according to the body area. For each training pair, we choose the phase closest to the HQ counterpart as the target phase with its two neighboring phases and use Elastix6 to align HQ images and LQ 4D-MRI images.A detailed demonstration of the implicit temporal-compensated adversarial network (ITAN) is presented in Figure 1. Due to limited training samples and hardware capacity, ITAN is designed as a two-dimensional model for slice-by-slice enhancement. The architecture of the ITAN model takes advantage of conditional-GAN (cGAN)7 to learn an accurate mapping from the original 4D-MRI to its corresponding HR counterpart, which can overcome the potential mismatch of the training image pairs. The overall framework has two networks, a generator and a discriminator. The generator adopts a temporal-compensated strategy for diverse feature learning composed of three key modules: deblur block, align block, and TSA block. The slices of multiple phases are first fed into a deblur block containing stacked residual blocks to extract features and suppress motion artifacts. Subsequently, we use the deformable convolution in the align block to make implicit alignment at the feature level to achieve the interphase compensation. Afterwards, the aligned features are passed through the TSA block to aggregate information adaptively. The TSA block adopts temporal and spatial attention mechanisms to fully excavate the inter-phase temporal relations and intra-phase spatial features. Finally, the enhanced image is obtained by adding the predicted image residual to the original target phase image. The discriminator is based on a U-Net architecture.
The total loss function comprises three parts: an adversarial loss, L1-norm-based loss and a multi-scale structural similarity index (MS-SSIM)-norm-based loss to restore high-frequency features to the most extent.
$$\mathcal{L}\left(\boldsymbol{G},\boldsymbol{D}\right)=\lambda_{1}\mathcal{L}_{{cGAN}}\left({\boldsymbol{G}},{\boldsymbol{D}}\right)+{\lambda_{2}\mathcal{L}}_{L1}\left({\boldsymbol{G}}\right)+{\lambda_{3}\mathcal{L}}_{MS-SSIM}\left({\boldsymbol{G}}\right)$$
$$\mathcal{L}_{cGAN} \left(\boldsymbol{G},\boldsymbol{D}\right)=\mathbb{E}_{\left(I_{LQ}\,,\,I_{HQ}\right)}\left[log\boldsymbol{D}\left(I_{LQ},I_{HQ}\right)\right] +\mathbb{E}_{I_{LQ}}\left[\log{\left(1-\boldsymbol{D}\left(I_{LQ},\boldsymbol{G}\left(I_{LQ}\right)\right)\right)}\right] $$
$$\mathcal{L}_{L1}\left(\boldsymbol{G}\right)=\mathbb{E}_{\left(I_{LQ}\,,\,I_{HQ}\right)}\left[\vert\vert{I_{HQ}-\boldsymbol{G}\left(I_{LQ}\right)}\vert\vert_{1}\right]$$
$$\mathcal{L}_{(MS-SSIM)}\left(\boldsymbol{G}\right)=1-MS\text{-} SSIM\left(I_{HQ},\boldsymbol{G}\left(I_{LQ}\right)\right)$$
To quantitatively measure the recovery accuracy of ITAN, we adopted three reference-based image similarity metrics: mean square error (MSE), structural similarity index (SSIM), and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), and a non-reference metric Laplacian.
Results
In order to verify the improved performance of the proposed method, we employed the state-of-the-art EDSR for comparison. The qualitative comparison of different planes between the original 4D-MRI, the EDSR, and the proposed method ITAN of an example patient is shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that the image quality of 4D-MRI by ITAN is vastly improved from the three views. The shape information of organs shows better visibility with fewer artifacts and less noise. The quantitative results are shown in Table 1. As the results suggest, the prediction of ITAN shows closer to HQ MR images and has better visibility among the three images.Discussion
In this study, we developed a DL-based 4D-MRI enhancement technique named ITAN. The ITAN can fully excavate temporal and spatial information to boost the quality of 4D-MRI. The enhanced 4D-MR images can show better shape and outline of organs with fewer motion artifacts and less noise.Conclusion
This study investigated an effective and robust enhancement technique for abdominal 4D-MRI. This post-processing technique enables the reconstruction of HQ 4D-MR images and has excellent promises in medical image analysis and MR-guided radiotherapy for abdominal regions.Acknowledgements
This research was partly supported by research grants of the General Research Fund (GRF 15102118, GRF 15104822) the Health and Medical Research Fund (HMRF 06173276), Hong Kong Special Administrative Regions.References
- Stemkens, Bjorn, Eric S. Paulson, and Rob HN Tijssen. "Nuts and bolts of 4D-MRI for radiotherapy." Physics in Medicine & Biology 63.21 (2018): 21TR01.
- Liu, Yilin, et al. "Four dimensional magnetic resonance imaging with retrospective k‐space reordering: a feasibility study." Medical physics 42.2 (2015): 534-541.
- Li, Guofa, et al. "A deep learning based image enhancement approach for autonomous driving at night." Knowledge-Based Systems 213 (2021): 106617.
- Yang, Wenhan, et al. "From fidelity to perceptual quality: A semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement." Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2020.
- Lim, Bee, et al. "Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution." Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 2017..
- Klein, Stefan, et al. "Elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration." IEEE transactions on medical imaging 29.1 (2009): 196-205..
- Mirza, Mehdi, and Simon Osindero. "Conditional generative adversarial nets." arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784 (2014).
Figures
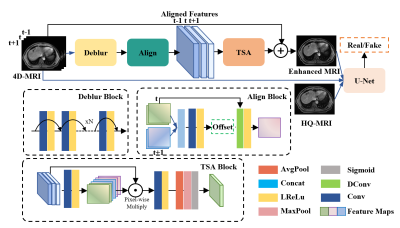
Figure 1: The design of the proposed ITAN model for 4D-MRI
enhancement. The ITAN includes three key mechanisms: Deblur block to
pre-suppress motion artifacts; Align block to make alignment between
phases; and TSA block to adaptively aggregate phases and reconstruct enhanced
MR images based on temporal and spatial attention.
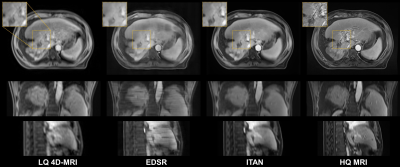
Figure
2: The qualitative results of 4D-MRI enhancement using ITAN for a liver case in transversal, sagittal and coronal planes. Compared to the state-of-the-art EDSR method, our
method shows significantly improved image quality with more details, fewer
artifacts, and less noise.
Table 1: The quantitative results under
different evaluation metrics compared with LQ 4D-MRI and EDSR.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4737