4697
Cine T2 mapping reveals cardiac cycle-dependent T2 variability in cardiomyopathy
Michinobu Nagao1, Masami Yoneyama2, Yasuhiro Goto1, Isao Shiina1, Kazuo Kodaira1, Mana Kato1, Yasutomo Katsumata2, Yurie Shirai1, Atsushi Yamamoto1, Akiko Sakai1, Risako Nakao1, and Shuji Sakai1
1Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan
1Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Inflammation
We have successfully developed cardiac cine imaging to project T2 values using T2prep-based T2 mapping with dynamic multiple trigger-delay framework. We have demonstrated that diastolic T2 values on cine T2 mapping are temporarily prolonged in patients with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy and impaired left ventricular function. Cine T2 mapping is a new noninvasive in vivo imaging technique for myocardial edema that provides an effective means of elucidating the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy.Introduction
The perfusion pressure in the myocardium fluctuates with the cardiac cycle in parallel to left ventricular pressure. Changes in perfusion pressure are thought to alter the migration of water components in the myocardium and the degree of edema. They are thought to be related to the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy, but effective biological imaging has not been established. We devised cine T2 mapping, which projects T2 values onto cardiac cine imaging, to examine the significance of cardiac cycle T2 variability in cardiomyopathy.Methods
40 patients with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (mean age, 53 years) who underwent cardiac MRI (CMR) with 3 tesla scanner (Ingenia 3T CX, Philips Healthcare) were enrolled in this study. CMR protocol consisted of standard cine imaging, T1 mapping (modified Look-Locker inversion recovery sequence with a 3(3)5 scheme, MOLLI), T2 mapping (multi-echo gradient and spin-echo: mGRASE), T2 Black-Blood, and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE). In addition, CINE T2 mapping with 6 frames per heartbeat was performed using multiple breath-hold T2prep-based single-shot balanced turbo-field echo T2 mapping with dynamic multiple trigger-delay framework (DynTD). DynTD is based on the dynamic scan procedure with variable trigger delay among different dynamic scans, resulting in different time-phase T2 maps in one scan. For generating the T2 map, four images with different T2-preparation times (TE = 0, 27, 53 and 80ms) were acquired with interleaved acquisition at the respective heartbeats. The repetition time (TFE shot interval) was set to 2 heartbeats. Furthermore, fast elastic image registration (FEIR) is applied to minimize motion-induced misalignment, which can mitigate small changes of in-plane heart movement by registering the source images before creation of the T2 maps (Fig. 1).T1 and T2 values in the septum on mid-left ventricular short-axis mapping were measured (Fig. 2). In cine T2 mapping, a total of 6 heart phases of the maps were acquired, and T2 maps of systolic and diastolic phases were visually selected and T2 values of both phases were measured and evaluated.Results and Discussion
1. Cine T2 map versus T2-prepSystolic and diastolic T2 (52.1±6.1 msec, 56.1±8.6 msec) on cine T2 map were significantly prolonged compared to that on mGRASE (49.7±4.7 msec). Diastolic T2 was moderately correlated with that on mGRASE (Pearson r, 0.602), but systolic T2 had a slight correlation with that on mGRASE (Pearson r, 0.377). Diastolic T2 was significantly longer than systolic T2 (p<0.0001).2. Cine T2 map versus left ventricular functionDiastolic T2 was significantly prolonged for patients (n=11) with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40% than that for patients (n=29) with LVEF >=40% (62.1±8.3 msec vs. 53.9±7.8 msec, p=0.0106). There was no difference in systolic T2 (53.3±5.0 msec vs. 51.6±6.5 msec) between the two groups. Difference between diastolic T2 and systolic T2 (diastole-systole T2) was significantly greater for patients with LVEF <40% than that for patients with LVEF >=40% (8.7±6.1 msec vs. 2.3±4.2 msec, p=0.0024) (Fig. 3, 4). ROC analysis revealed that the optimal diastole-systole T2 could distinguish patients with LVEF <40% with an area under the curve of 0.804.3. Cine T2 map versus T1 mapping and LGEThere was no difference in systole and diastole T2 values with or without LGE, or with or without prolonged T1 values (<1300 msec. and >=1300 msec.).In the present study, LV dysfunction is seen in patients with large diastole-systole T2, which means temporary T2 prolongation during diastole. This infers that a large diastole-systole T2 value implies an increase in the water component in the myocardium, i.e., myocardial edema. T2 map is used to detect myocardial edema and inflammation and to monitor the activity of myocarditis and cardiomyopathy (Ref. 1, 2). This method could be an even more sensitive metho for detection of myocardial edema.Conclusion
We have successfully developed cardiac cine imaging to project T2 values using the DynTD CINE-T2mapping. Diastolic T2 values on cine T2 mapping are temporarily prolonged in patients with impaired left ventricular function. Cine T2 mapping will be a new bioimaging technique to evaluate myocardial edema.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (grant no. 22K07806).References
1. Bohnen S, Radunski UK, Lund GK, et al. Tissue characterization by T1 and T2 mapping cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging to monitor myocardial inflammation in healing myocarditis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2017; 18: 744-751.
2. Kikuchi N, Watanabe E, Nagao M, et al. Acute Myocarditis Complicating Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Detection and Evolution of Transmural Spiral Late Gadolinium Enhancement on Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Circulation Cardiovasc Imaging 2021; 14: e011319.
Figures

2D-CINE-T2-mapping were acquired each time-phase by dynamic multiple trigger-delay framework (DynTD).
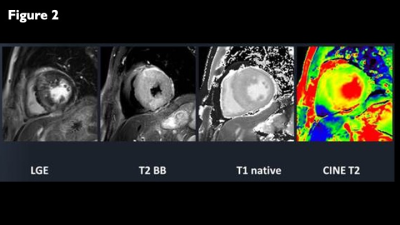
LGE, black-blood-T2WI, native-T1-mapping, and 2D-CINE-T2-mapping for a case of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
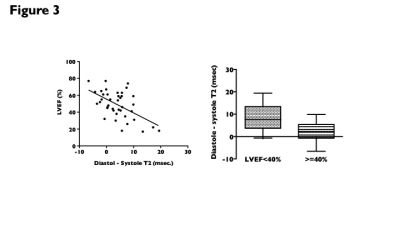
Correlation between LVEF and diastolic-systolic T2 value (left). Comparison of diastolic-systolic T2 value between LVEF <40% and >=40% (right). Diastolic-systolic T2 value had a significant negative correlation with LVEF (Pearson r, -0.601).
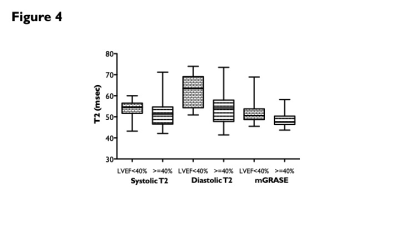
Comparison of T2 value on cine T2 mapping and mGRASE between patients with LVEF <40% and >=40%. Diastolic T2 was significantly prolonged for patients with LVEF <40% than that for patients with LVEF >=40%.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4697