4676
Cine magnetic resonance images: relationship to therapeutic effect evaluation and prognosis in light-chain amyloidosis
Keyan Wang1, Jie Zheng2, Jing An3, and Jingliang Cheng1
1MRI, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, St. Louis, MO, United States, 3Siemens Healthineer, Shenzhen, China
1MRI, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, St. Louis, MO, United States, 3Siemens Healthineer, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Myocardium
The study evaluated left ventricular (LV), right ventricular (RV), and left atrial (LA) myocardial strain and heart function derived from cine magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for chemotherapeutic efficacy and predicted their prognostic value in patients with light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. Our results demonstrated that these parameters may be noninvasive imaging markers allowing assessment of the chemotherapeutic effect and may offer independent prognostic information for all-cause mortality in patients with AL amyloidosis.Introduction
Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is characterized by the deposition of insoluble fibrinogen in the extracellular space of the myocardium. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis CA (AL-CA) is one of the most common types of disease. Amyloid protein can cause several morphologic changes and dysfunction, such as ventricular wall thickening, decreased myocardial perfusion, arrhythmias, and atrioventricular conduction delay. These conditions can lead to decreased cardiac output and heart failure.Chemotherapy for light amyloidosis aims to reduce or eliminate serum monoclonal immunoglobulin to quickly achieve adequate hematological remission. Simultaneously, the CA is primarily based on supportive treatment, which is expected to achieve heart organ remission through a self-cleaning mechanism. However, hematological efficacy cannot fully reflect heart organ efficacy, and as an indicator of cardiac organ remission, the NT-proBNP level lacks specificity. Cine MR imaging has unique advantages in the follow-up of cardiac structure and function because of its noninvasive, radiation-free, and contrast agent-free characteristics. However, research on the evaluation of the CA chemotherapy effect by this technology is lacking. This study comprehensively compared the changes in cine MR images before and after treatment to find reliable cine MR imaging indicators reflecting cardiac organ efficacy and to evaluate the prognostic value of cine MR imaging in amyloidosis.Methods
A total of 151 consecutive patients with AL amyloidosis, including 45 without and 106 with CA, were enrolled in this retrospective study. All enrolled patients underwent CMR cine images on a 3T scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) before chemotherapy. Forty-two patients with CA had a follow-up CMR scan after a standard course of chemotherapy. According to the clinical evaluation of cardiac efficacy, the patients were divided into a remission group (n=12) and a progression group (n=30). LA global peak longitudinal strain (LVGPLS), LAGPLS, RVGPLS, LV basal peak circumferential strain (LVBPCS), LV basal peak radial strain (LVBPRS), LV middle peak circumferential strain (LVMPCS), LV middle peak radial strain (LVMPRS), LV apex peak circumferential strain (LVAPCS), LV apex peak radial strain (LVAPRS), LV ejection fraction (EF), RVEF, and LV mass were evaluated. Strain parameters and heart function derived with cine MR imaging changes before and after treatment in patients with different organ responses were analyzed with a paired sample t-test. In addition, the association between those parameters and all-cause mortality was analyzed with the stepwise Cox regression model.Results
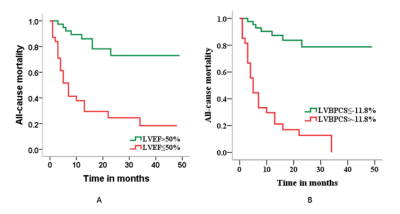
The median follow-up time was seventeen months (1-49 months). Sixty-seven patients died, and 84 survived. MR imaging parameters in the cardiac organ remission group did not change significantly (all P > 0.05) but did so in the cardiac organ progression group (all P < 0.05). Multivariate Cox analysis revealed that LVBPCS (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.241 per 1% absolute decrease; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.023 - 4.910; P = 0.044) and LVEF (HR = 1.070 per 1% absolute decrease; 95% CI: 1.006 - 1.137; P = 0.032) were independent predictors of all-cause mortality after adjustment for RVEF, LV mass, LVGPLS, LAGPLS, RVGPLS, LVBPRS, LVMPRS, LVMPCS, LVAPRS, and LVAPCS. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for predicting all-cause mortality with LVBPC was 0.849, with a cut-off of - 11.8%, sensitivity of 77.4%, and specificity of 92.3%. The area under the ROC curve for predicting all-cause mortality with LVEF was 0.808, with a cut-off of 50%, sensitivity of 79.5%, and specificity of 90.2%.Discussion & Conclusion
Strain parameters and heart function derived with cine MR imaging could be noninvasive imaging markers with which to evaluate the chemotherapeutic effect. In addition, LVBPCS and LVEF independently predicted all-cause mortality.Table 1. Cine MR parameters between cardiac amyloidosis and amyloidosis without cardiac involvement.
| Parameters | CA group n=106 | No CA n=45 | P-value |
| LVBPRS (%) | 15.5±9.6 | 30.4±6.1 | <0.0001 |
| LVBPCS (%) | -10.4±5 | -17.8±2.3 | <0.0001 |
| LVMPRS (%) | 19.2±12.6 | 33.9±5.9 | <0.0001 |
| LVMPCS (%) | -12.4±5.9 | -19.4±2.3 | <0.0001 |
| LVAPRS (%) | 31±19 | 52.7±10.8 | <0.0001 |
| LVAPCS (%) | -16.9±7.1 | -24.4±3.1 | <0.0001 |
| LVGPLS (%) | -8±4.7 | -13.7±3.7 | <0.0001 |
| RVGPLS (%) | -13±6.6 | -19.9±6.1 | <0.0001 |
| LAGPLS (%) | -7.5±5.2 | -11.9±3.6 | 0.002 |
| LVEF | 50.9±15.4 | 63.5±7.4 | 0.002 |
| LV Mass | 141.9±51.4 | 82.1±25.4 | <0.0001 |
| RVEF | 43.6±18.3 | 58.9±8.1 | 0.001 |
Table 2. Baseline and 12-month follow-up cine CMR imaging parameters of cardiac efficacy in the remission and progression groups.
| | Remission group (n=12) | | Progression group (n=30) | ||||
| Parameters | Baseline | 12-month follow-up | P-value | | Baseline | 12-month follow-up | P-value |
| LVBPRS (%) | 21.1±6.9 | 22±7.6 | 0.495 | | 13.3±9.6 | 11.3±9.6 | P<0.001 |
| LVBPCS (%) | -13.7±3.4 | -15±5.6 | 0.214 | | -9.2±5 | -6.7±5.1 | P<0.001 |
| LVMPRS (%) | 27.6±13 | 26.6±14.4 | 0.473 | | 16.1±10.7 | 10.7±10.7 | P<0.001 |
| LVMPCS (%) | -16.3±5.7 | -16.6±6.7 | 0.789 | | -11±5.2 | -4±5.3 | P<0.001 |
| LVAPRS (%) | 40.6±21.6 | 39.3±22 | 0.499 | | 27.6±16.2 | 21.7±16.3 | P<0.001 |
| LVAPCS (%) | -20.1±7.3 | ‘-23.2±8 | 0.006 | | -15.8±6.4 | -12.3±6.5 | P<0.001 |
| LVGPLS (%) | -11.1±4.4 | -12.2±5 | 0.235 | | -6.9±4.3 | -4±4.3 | P<0.001 |
| RVGPLS (%) | -16.5±5.9 | -17.6±6 | 0.411 | | -12.3±6.5 | -7.4±3.8 | P<0.001 |
| LAGPLS (%) | -10.3±4.6 | -11.9±5.6 | 0.107 | | -6.5±5 | -4.7±4.1 | P<0.001 |
| LVEF | 60.6±15.8 | 60.7±14.3 | 0.918 | | 47±13.9 | 41±14.1 | P<0.001 |
| LV Mass | 130.8±54.8 | 129.1±55.4 | 0.399 | | 145.5±51.2 | 149.5±51.9 | P=0.035 |
| RVEF | 56.2±15.5 | 57.8±14.7 | 0.172 | | 38.4±17.3 | 30.4±17.2 | P<0.001 |
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4676