4645
Acceleration of Phase-contrast Magnetic Resonance Venogram by Compressed SENSE
Yukun Zhang1, Na Liu1, Geli Hu2, Liangjie Lin2, Yanwei Miao1, and Qingwei Song1
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, beijing, China
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Parallel Imaging, Vessels, compressed sensitivity encoding
The clinical application of phase-contrast magnetic resonance venogram (PC-MRV) is limited by the long scan time. This study aims to accelerate the acquisition of PC-MRV by the compressed sensitivity encoding (CS-SENSE) technique and find the optimal acceleration factor. Results show that the image quality of fast PC-MRV based on CS-SENSE was significantly higher than that based on conventional sensitivity encoding (SENSE) technology, and the CS-SENSE factor 9 was recommended for mild to moderate patients, and CS AF=12 for critical patients.Introduction
Magnetic resonance magnetic resonance venogram (MRV) techniques mainly includes single-phase contrast-enhanced MRV (CE-MRV), two-dimensional time-of-flight MRV (2D TOF MRV) and phase-contrast MRV (PC-MRV)1. PC MRV has no risk of injectable contrast compared to CE-MRV and has a better sensitivity to the detection of slow blood flow compared with 2D TOF MRV, but the long scan time limits its clinical applications 2. The compressed sensitivity encoding (CS-SENSE) technique has been proved to be efficient for acceleration of different imaging sequences across human body. This study aims to explore the feasibility and clinical value of PC-MRV accelerated by compress SENSE, and find the optimal acceleration factor (AF).Methods
Eighteen healthy volunteers were prospectively recruited and underwent PC-MRV scans with different AFs, including SENSE AF=9; CS SENSE AF=9, 12, 15, 18 and 21 (abbreviated as SENSE9, CS9, CS12, CS15, CS18 and CS21) at 3.0T (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). Two radiologists delineated the regions of interest (ROI) for the superior sagittal sinus (SUPSS), left sigmoid sinus (SGS) and left transverse sinus (TRS) and adjacent white matter on two raw images (PC phase [PCA-P] and FFE modulus [FFE-M]). The signal intensity and standard deviation were recorded for further calculation of the signal to noise ratio (SNR) and contrast to noise ratio (CNR). Meanwhile, the overall image quality of PC MRV with different AFs and 13 pre-defined venous structures (8 dural sinuses and 5 cerebral veins) were scored using 4-point scale subjective criteria. The consistency of measurements and subjective scores of the two observers were analyzed using Kappa and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) test. The difference in measurement data and subjective score between different AFs was analyzed by pairs comparison (Paired t-test or U-test).Results
The measured data and subjective scores of the two observers were in good consistent (Kappa: 0.668-0.884, ICC: 0.702-0.968). The subjective analysis results for PCA-P and FFE-M were basically the same: the SNR and CNR of each part measured by CS9 and CS12 were significantly higher compared with SENSE9, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); and there was no statistically significant difference in SNR and CNR of each part measured by CS12 compared with CS9 (P>0.05) (Tab.1 and 3). Subjective analysis showed that CS21 was statistically different from SENSE9 in terms of Cerebral vein and ALL segments; CS18 were statistically different from SENSE9 in terms of Cerebral vein. CS21 is statistically different from CS9 in terms of Dural sinuses, cerebral vein and ALL segment; CS18 are statistically different from CS9 in Cerebral vein and ALL segment (Tab. 2 and 3).Discussion
By comparison,we found that the venous images of different AFs showed comparable background suppression efficiency and venous lumen contour (Fig.1). The subjective analysis showed that compared to SENSE,the overall image quality and display of dural sinuses contours were basically comparable among different CS SENSE AFs , but when CS AF≥18, The display of cerebral vein is not convincing. The objective analysis results show that the SNR/CNR of each part in CS9, CS12 and CS15 is significantly higher than that of SENSE9. However, SNR/CNR value of some parts decreases significantly in CS15 compared with CS9, which is statistically different. Therefore, CS9 and CS12 have the potential to become the optimal AF. When CS AF=9, it is best in both objective data measurement and subjective venous structure evaluation, but the time reduction is less than 5%, so it can be used in patients with vascular disease in good condition. When CS AF=12, a balance between image quality and scan time was achieved, and the whole brain vein image that meets the diagnostic requirements can be obtained in a short time (2min55s, shortening by 25%), suitable for screening of venous disease in critically ill patients. When the CS AF≥15, the image quality no longer meets the diagnostic conditions.Conclusions:
PC-MRV accelerated by CS SENSE can be used for non-invasively fast acquisition of whole-brain vein images, and it is suitable for screening and follow-up examination of venous disease in patients with severe renal attenuation. AF9 is recommended for patients with mild to moderate disease and an AF12 for severe patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Dolic K, Siddiqui, AH, Karmon, Y, et al. The role of noninvasive and invasive diagnostic imaging techniques for detection of extra-cranial venous system anomalies and developmental variants. BMC Med. 2013; 11 155.
2. Dmytriw AA, Song JSA, Yu E, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis: state of the art diagnosis and management [J]. Neuroradiology, 2018, 60(7): 669-685.
Figures
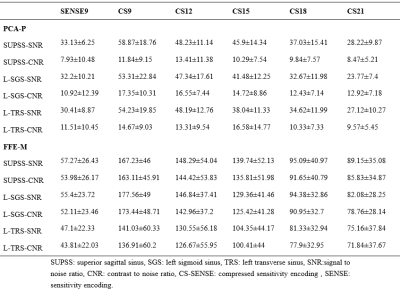
Tab. 1 Objective analysis value of PC MRV with different AFs
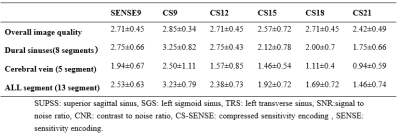
Tab.2 Subjective analysis
scoring of PC MRV with different AFs
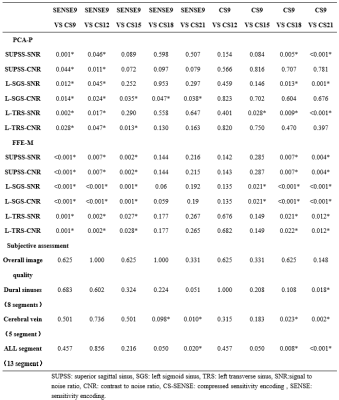
Tab. 4 results
of subjective and objective analysis between different AFs
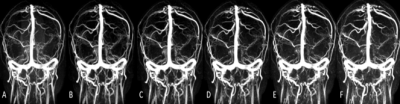
Fig.1 A-F were the PC MRV images with
different AFs obtained by the same volunteer (a 34-year-old healthy man), and the AFs are SENSE9,
CS9, CS12, CS15, CS18, and CS21, respectively. PC-MRV: phase-contrast magnetic resonance venogram,
AF: acceleration factor, CS-SENSE: compressed sensitivity encoding , SENSE: sensitivity
encoding.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4645