4618
Joint K-b space reconstruction of under-sampled diffusion-weighted MRI1University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques
We developed a joint image reconstruction method in both k-space and b-space to reconstruct the under-sampled diffusion-weighted images acquired at different b-values and generate the corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient map simultaneously by solving an optimization problem. This method improved SNR in both diffusion weighted images and apparent diffusion coefficient map compared with the conventional method and allows 50% k-space data undersampling that has the potential of reducing image distortion and shortening acquisition time.
Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) provides clinically valuable quantitative information of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC). The conventional approach reconstructs the MR images and the ADC map separately in two steps, in which the magnitude DW image acquired at each b-value is reconstructed from its own k-space data, e.g., by Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), followed by a voxel-by-voxel fitting of the signal decay to derive the ADC map. K-space undersampling is commonly used in echo-planar imaging (EPI) acquisition to shorten the echo train length and thus reduce image distortion, or in fast spin echo (FSE) acquisition to reduce acquisition time, at the expense of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Low SNR in diffusion weighted (DW) images result in inaccurate ADC quantification. Considering the strong correlation of MR images in the spatial ($$$k$$$) and diffusion encoding ($$$b$$$) domains , this study proposes a joint k-b space reconstruction method with compressed sensing regularization to reconstruct DWI from an undersampled k-space.Methods
The reconstruction is viewed as an optimization problem as described in Eq. 1. $$min_{f,D}\frac{1}{2}\sum_{b}\sum_{c}|S^{1D}F^{1D}A^{1D}_{c}f_{c}(x,b) - g_{c}(b)|^2 + TV^{1D}(f_c(x,b)) + R[f(x,b),\lambda_1]+R[D(x),\lambda_2] \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(1)\\s.t. f(x,b) = f(x,0)e^{-D(x)b}, (b>0)\label{Eq1}$$ where $$$f(x,b)$$$ is the 2D image at each $$$b$$$-value, and $$$D(x)$$$ is the ADC map. $$$S^{1D}, F^{1D}, A^{1D}_c$$$ denotes the sampling pattern in phase-encoding direction, 1D Fourier transform operator and phase factor respectively, where $$$c$$$ stands for the index along frequency encoding direction. $$$g_c(b)$$$ is the measured k-space data. $$$TV^{1D}(.)$$$ is 1D total-variation regularizer and $$$R[.]$$$ is image domain regularization applied to MR images at different b-values and ADC map, taken as the block-matching and 3D filtering (BM3D)1 denoising form in this study, which was employed via the plug-and-play approach2. $$$\lambda_1$$$ and $$$\lambda_2$$$ are parameters for BM3D. The BM3D and 1D compressed sensing regularization3 enforce desired solution quality and remove the aliasing artifacts effectively in the image domain. The b-space constraint links solutions $$$f(x,b)$$$ and $$$D(x)$$$ via the exponential decay model, further suppressing the noise and artifacts. We solved this model using Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM)4.Results
The DWI data was acquired on a diffusion phantom consisting of 13 vials with 6 different ADC values. A single-shot DW-EPI sequence with 3 different b-values of 50, 400, 800 $$$s/mm^2$$$ was applied, with the number of excitation (NEX) set as 4 to achieve high SNR images, which were used as ground truth. Gaussian noise was added to the k-space data generated by Fourier transforming the DW images to generate the noisy data. Random undersampling was performed along the phase encoding direction ($$$k_y$$$ direction) with 50% $$$k_y$$$ unsampled. The 10% $$$k_y$$$ in the central k-space was always kept. The proposed method was compared with a conventional compressed sensing based reconstruction method, which was done by minimizing the lost function only containing the first 2 terms of Eq. 1. via gradient descent. The ADC map of the conventional method was then generated by fitting an exponential decay to each voxel of the reconstructed magnitude images. The image reconstruction results from both the conventional and the joint reconstruction methods are shown in Fig. 1, the SNR for the 3 DW images and the ADC map by the joint k-b reconstruction was improved by 5.2 ± 0.3 compared with conventional method. The pixel-wise ADC value distributions by conventional and joint k-b reconstruction methods are shown in Fig. 2. The mean ADC values measured by the joint reconstruction method were consistent with ground truth, and the standard error in the result of the proposed method (b) was greatly reduced compared with that in the conventional method (a).Discussion
Our model simultaneously reconstructs undersampled DW MR images and the corresponding ADC map, which takes advantage of regularizations along both spatial and diffusion encoding domains. The proposed method reconstructed images with higher SNR and better accuracy in ADC measurements from undersampled k-space by integrating compressed sensing in a joint k-b reconstruction scheme. Future work will include extending the joint k-b reconstruction method to FSE-based DWI reconstruction to accelerate image acquisition. The proposed method may be applied to more complex diffusion signal fitting models that requires DW signal fitting at higher b-values (i.e., $$$> 3000 s/mm^2$$$), which is more sensitive to excessive noises. In addition, a neural network maybe integrated in the optimization model as a more powerful denoising tool.Conclusion
We developed a novel joint k-b space optimization algorithm for simultaneous DW MR image and ADC map reconstruction from an undersampled data acquisition. It improved SNR and increased the stability of pixel-wise ADC measurements. Accurate ADC measurement with a short scan time is made possible with the proposed method.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (grant \#RP200573) and the National Cancer Institute (grant \#R01CA227289).References
1. Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on image processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095.
2. Venkatakrishnan S V, Bouman C A, Wohlberg B. Plug-and-play priors for model based reconstruction[C]//2013 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing. IEEE, 2013: 945-948.
3. Yang Y, Liu F, Jin Z, et al. Aliasing artefact suppression in compressed sensing MRI for random phase-encode undersampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 62(9): 2215-2223.
4. Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine learning, 2011, 3(1): 1-122.
Figures
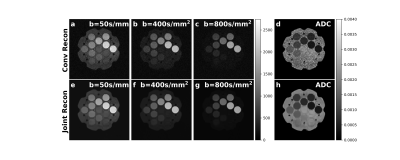
Fig. 1. The reconstructed DW MR images by the conventional compressed sensing method (a-d) and proposed joint reconstruction method (e-h) of the diffusion phantom.
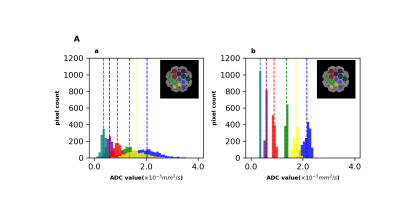
Fig. 2. Pixel-wise ADC measurement distribution for each group of vials with known ground truth ADC of the diffusion phantom. Measurement based on reconstruction by the conventional compressed sensing method (a) and the proposed joint reconstruction method (b), ADC measurement distributions for each group of vials are color-coded by the ground truth values as shown in the phantom image. The ground truth ADC value for each group of vials is plotted as the dash line.