4577
A High Performance Gradient and RF Insert for Dental MRI1Division of Medical Physics, Department of Radiology, University Medical Center Freiburg, Germany, Freiburg, Germany, 2Division of Medical Physics, Department of Radiology, University Medical Center Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany, Freiburg, Germany
Synopsis
Keywords: Gradients, New Devices, Dental MRI
Dental MRI requires high resolution imaging, e.g., for detection of root canals, as well as, high readout bandwidth for short T2* tissues, such as dentin and nerve fibers. These requirements can only be satisfied by high-performance gradients. In this study, we show with Bloch simulations the necessity for high performance gradients, and consequently introduce a gradient and RF insert, which is optimized for dental MRI. We also explore the concept a cylindrical encoding for curved slices for 4-fold acceleration compared to conventional encoding.Introduction
The value of the dental magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) is evident in diagnosis of various pathologies in endodontics (1–3), orthodontics (4), craniomaxillofacial surgery (5), and implantology (6). dMRI requires high resolution imaging, e.g., for detection of root canals and, as well as, high readout bandwidth for short T2* tissues. To achieve this high resolution within clinically acceptable measurement times, high-performance gradients are essential (7). Head-only gradient systems offer higher efficiency and improves acquisition speed, resolution, and diffusion weighting while reducing distortions, e.g., in EPI, and increasing peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) thresholds compared to whole-body systems (8–11). Use of nonlinear spatial encoding (12,13) for local resolution enhancement (14–16), to accelerate imaging speed with enhanced undersampling schemes (17), and for imaging multiple regions simultaneously (18,19) was also demonstrated with local gradients, including gradient coil arrays (20–22). Furthermore, it has been shown, that local gradient coils developed for a target anatomy can achieve significantly higher sensitivity(26).Methods
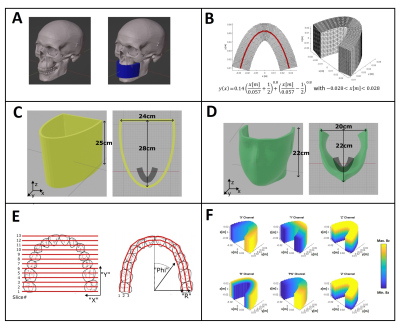
The imaging volume of the gradient and RF inset is defined for the upper and lower dental arch including the apices of the roots and the surrounding trabecular bone(Fig.1A) of a patient supine position. The gradient and RF insert are meant to be pushed into the scanner bore from the backside over the patient's head.The gradient coils were designed using the open-source, MATLAB-based software package COILGEN (30) using a stream function optimization method (32). For the current-carrying-surface (CCS), a half elliptical shape and a mask-like surface are proposed (Fig.1C-D). The central curve that defines the target field is taken from [27].
A standard linear x,y,z gradient field, and a curved (Phi,R,z) encoding field which follows the dental arch are defined (Fig.1,F). The idea of the later approach is to speed up the data acquisition by using curved slice profiles (28) and therefore reducing the number of slices (Fig.1F).
A Tx-array of five galvanically independent low-profile loop elements was designed similar to (29), to make efficient use of the space (Fig.3A).
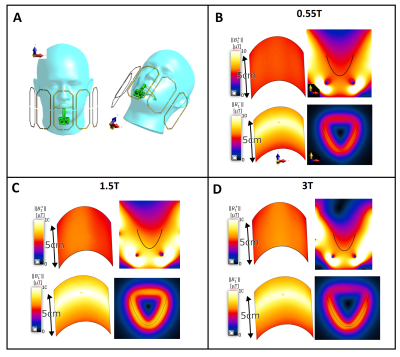
For high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) efficiency, an intraoral coil (IOC) was also included in the model as receiver (Rx) element [24,29]. Both Tx-array and the IOC were tuned for fLarmor corresponding to 0.55T, 1.5T, and 3T fields, respectively. B1+ and B1- distribution of the Tx-array and the IOC were calculated using an FDTD solver (Sim4Life-v7.0, ZMT, Zurich).
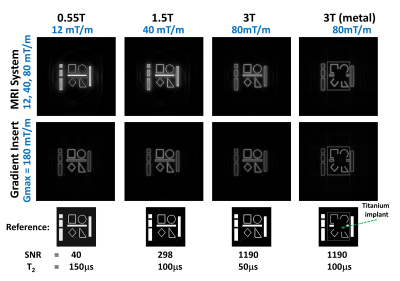
To highlight the effect of improved gradient strength, MATLAB based Bloch simulations for a numerical phantom were performed, comparing commercial MRI gradient strengths (12-80 mT/m) and the targeted strength of the proposed gradient insert of 180mT/m(See Fig.3). Metal artefact simulation was also performed for the 3T case
Results
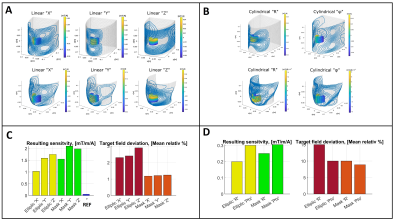
Gradient coil layouts were generated for the elliptic and mask-like surface, both for linear and cylindrical target fields (Fig.2). Obtained sensitivities are 1mT/m/A and 0.1 to 0.3mT/m/A for linear and cylindrical encoding fields, respectively. The linear gradients outperform the cylindrical fields with lower mean relative errors of 1-2% compared to 10-15% (Fig.2C,D).The mask-like surface has a significantly better performance in terms of sensitivity (~25% improvement) and field accuracy (around 1%, See Fig.2, C, D).
In Fig.3, ||B1+|| fields are shown for a transverse slice and along a curved trajectory matching the target field used to design the gradient coils. Maximum deviation from the mean ||B1+|| was 7.1%, 13.2%, and 17.1% within the target region, for 23.7, 63.9, and 127.7MHz, respectively. ||B1-|| simulations of the IOC show that the transverse loop design is sensitive to the target region and the sensitivity profile is constrained within the target region.
Simulation results (Fig.4) show that imaging performance can be improved at field strengths of 0.55, 1.5 and 3T using high power gradients. Metal artefacts are reduced using high bandwidth offered by the gradient insert.
Discussion
The sensitivities for linear encoding for both dedicated surfaces, outperform a standard whole body system by more than an order of magnitude (Fig.2C).Unfortunately, the coil layouts for the cylindrical target fields yield lower sensitivity (0.2-0.3mT/m/A) and higher field error (>10%, Fig.2,D). This is most reasonably due to the higher power demands in generating curved gradient fields.
Despite the better performance of the mask-like surface, the semi-elliptical approach remains easier to manufacture.
We show that suitable Tx and Rx coils can be designed for the proposed gradient insert for optimal performance in dental MRI applications. A low profile Tx array makes efficient use of the available space. Since the array performance was not sensitive to up to 20% phase and amplitude deviations, it can be driven by a fixed power distribution circuit instead of parallel Tx unit. We have shown previously that intraoral coils provide up to 10-fold higher SNR than external coils. Constrained sensitivity of the IOC is also useful to avoid signal acquisition from unwanted regions. Therefore, the gradient and the RF coil system proposed in this work forms an optimal combination for dental MRI. Tx coils will be simulated together with the gradient coils for more accurate field distributions. SAR and peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) simulations will also be performed using anatomical human models using the complete system model.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Ariji Y, Ariji E, Nakashima M, Iohara K. Magnetic resonance imaging in endodontics: a literature review. Oral Radiol. 2018;34:10–16 doi: 10.1007/s11282-017-0301-0.
2. Leontiev W, Bieri O, Madörin P, et al. Suitability of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Guided Endodontics: Proof of Principle. J. Endod. 2021;47:954–960 doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2021.03.011.
3. Juerchott A, Pfefferle T, Flechtenmacher C, et al. Differentiation of periapical granulomas and cysts by using dental MRI: a pilot study. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018;10:17 doi: 10.1038/s41368-018-0017-y.
4. Juerchott A, Freudlsperger C, Weber D, et al. In vivo comparison of MRI- and CBCT-based 3D cephalometric analysis: beginning of a non-ionizing diagnostic era in craniomaxillofacial imaging? Eur. Radiol. 2020;30:1488–1497 doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06540-x.
5. Juerchott A, Freudlsperger C, Zingler S, et al. In vivo reliability of 3D cephalometric landmark determination on magnetic resonance imaging: a feasibility study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020;24:1339–1349 doi: 10.1007/s00784-019-03015-7.
6. Hilgenfeld T, Juerchott A, Jende JME, et al. Use of dental MRI for radiation-free guided dental implant planning: a prospective, in vivo study of accuracy and reliability. Eur. Radiol. 2020;30:6392–6401 doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07262-1.
7. Reeder SB, McVeigh ER. The effect of high performance gradients on fast gradient echo imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994;32:612–621 doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910320510.
8. Tan ET, Lee S-K, Weavers PT, et al. High slew-rate head-only gradient for improving distortion in echo planar imaging: Preliminary experience. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016;44:653–664 doi: 10.1002/jmri.25210.
9. Foo TKF, Tan ET, Vermilyea ME, et al. Highly efficient head‐only magnetic field insert gradient coil for achieving simultaneous high gradient amplitude and slew rate at 3.0T (MAGNUS) for brain microstructure imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020;83:2356–2369 doi: 10.1002/mrm.28087.
10. Tang F, Hao J, Freschi F, et al. A cone-shaped gradient coil design for high-resolution MRI head imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019;64:085003 doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab084a.
11. Kang L, Tang F, Xia L, Liu F. Design of an insertable cone-shaped gradient coil matrix for head imaging with a volumetric finite-difference method. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021;92:124709 doi: 10.1063/5.0060194.
12. Hennig J, Welz AM, Schultz G, et al. Parallel imaging in non-bijective, curvilinear magnetic field gradients: a concept study. Magn. Reson. Mater. Physics, Biol. Med. 2008;21:5 doi: 10.1007/s10334-008-0105-7.
13. Schultz G, Ullmann P, Lehr H, Welz AM, Hennig J, Zaitsev M. Reconstruction of MRI data encoded with arbitrarily shaped, curvilinear, nonbijective magnetic fields. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010;64:1390–1403 doi: 10.1002/mrm.22393.
14. Layton KJ, Gallichan D, Testud F, et al. Single shot trajectory design for region-specific imaging using linear and nonlinear magnetic encoding fields. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013;70:684–696 doi: 10.1002/mrm.24494.
15. Witschey WRT, Cocosco CA, Gallichan D, et al. Localization by nonlinear phase preparation and k-space trajectory design. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012;67:1620–1632 doi: 10.1002/mrm.23146.
16. Tam LK, Stockmann JP, Galiana G, Constable RT. Null space imaging: Nonlinear magnetic encoding fields designed complementary to receiver coil sensitivities for improved acceleration in parallel imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012;68:1166–1175 doi: 10.1002/mrm.24114.
17. Knoll F, Schultz G, Bredies K, et al. Reconstruction of undersampled radial PatLoc imaging using total generalized variation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013;70:40–52 doi: 10.1002/mrm.24426.
18. Parker DL, Hadley JR. Multiple-region gradient arrays for extended field of view, increased performance, and reduced nerve stimulation in magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006;56:1251–1260 doi: 10.1002/mrm.21063.
19. Ertan K, Taraghinia S, Sadeghi A, Atalar E. A z-gradient array for simultaneous multi-slice excitation with a single-band RF pulse. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018;80:400–412 doi: 10.1002/mrm.27031.
20. Jia F, Schultz G, Testud F, et al. Performance evaluation of matrix gradient coils. Magn. Reson. Mater. Physics, Biol. Med. 2016;29:59–73 doi: 10.1007/s10334-015-0519-y.
21. Littin S, Jia F, Layton KJ, et al. Development and implementation of an 84-channel matrix gradient coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018;79:1181–1191 doi: 10.1002/mrm.26700.
22. Ertan K, Taraghinia S, Atalar E. Driving mutually coupled gradient array coils in magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019:mrm.27768 doi: 10.1002/mrm.27768.
23. Idiyatullin D, Corum C, Nixdorf DR, Garwood M. Intraoral approach for imaging teeth using the transverse B 1 field components of an occlusally oriented loop coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014;72:160–165 doi: 10.1002/mrm.24893
24. Ozen AC, Idiyatullin D, Adriany G, et al. Design of an Intraoral Dipole Antenna for Dental Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021;68:2563–2573 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3055777 23. Amrein, P, Jia, F, Zaitsev, M, Littin, S. CoilGen: Open-source MR coil layout generator. Magn Reson Med. 2022; 88( 3): 1465- 1479. doi:10.1002/mrm.29294
25. Ludwig, U., Eisenbeiss, AK., Scheifele, C. et al. Dental MRI using wireless intraoral coils. Sci Rep 6, 23301 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23301 25. Flügge T, Ludwig U, Winter G, Amrein P, Kernen F, Nelson K. Fully guided implant surgery using Magnetic Resonance Imaging - An in vitro study on accuracy in human mandibles. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020 Aug;31(8):737-746. doi: 10.1111/clr.13622. Epub 2020 Jul 12. PMID: 32459868.
26. Jia F, Littin S, Amrein P, Yu H, Magill AW, Kuder TA, Bickelhaupt S, Laun F, Ladd ME, Zaitsev M. Design of a high-performance non-linear gradient coil for diffusion weighted MRI of the breast. J Magn Reson. 2021 Oct;331:107052. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2021.107052. Epub 2021 Aug 14. PMID: 34478997
27. Braun S, Hnat WP, Fender DE, Legan HL. The form of the human dental arch. Angle Orthod. 1998 Feb;68(1):29-36. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(1998)068<0029:TFOTHD>2.3.CO;2. PMID: 9503132.
28. Weber, H., Gallichan, D., Schultz, G., Cocosco, C.A., Littin, S., Reichardt, W., Welz, A., Witschey, W., Hennig, J. and Zaitsev, M. (2013), Excitation and geometrically matched local encoding of curved slices. Magn Reson Med, 69: 1317-1325. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24364
29. Özen, AC, Spreter, F, Schimpf, W, et al. Scalable and modular 8-channel transmit and 8-channel flexible receive coil array for 19F MRI of large animals. Magn Reson Med. 2022; 1- 14. doi:10.1002/mrm.29490
30. Amrein, P, Jia, F, Zaitsev, M, Littin, S. CoilGen: Open-source MR coil layout generator. Magn Reson Med. 2022; 88( 3): 1465- 1479. doi:10.1002/mrm.29294
31. https://www.siemens-healthineers.com/magnetic-resonance-imaging/0-35-to-1-5t-mri-scanner/magnetom-aera
32. Tomasi D. Stream function optimization for gradient coil design. Magn
Reson Med. 2001 Mar;45(3):505-12. doi:
10.1002/1522-2594(200103)45:3<505::aid-mrm1066>3.0.co;2-h. PMID:
11241710
Figures