4564
Simultaneous Saturation and Excitation (SatEx) pulse1Centre for Advanced Imaging, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Australia, 2ARC Training Centre for Innovation in Biomedical Imaging Technology, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Australia, 3chool of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Australia, 4Siemens Healthcare Pty Ltd, Brisbane, Australia, 5Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 6Division of Health Sciences and Technology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: RF Pulse Design & Fields, Velocity & Flow
We propose a new slice-selective excitation pulse that simultaneously saturates magnetization adjacent to it. The Saturation and Excitation (SatEx) pulse is a summation of two asymmetric sinc pulses whose leading lobes have been cut combined with an asymmetric excitation pulse with its final lobes truncated. The saturation and excitation slice profile were validated in simulations and a flow-phantom scan. The flow-phantom scan showed strong saturation of inflow effects. Since the SatEx pulse is as short as a conventional sinc excitation pulse, it can be implemented in a wide range of fast imaging sequences to suppress inflow effects without lengthening TR.Introduction
In slice-selective acquisitions, the presence of moving fluids such as blood and cerebral spinal fluid can bring fresh magnetization into the excitation slice, which can modulate the MR signal intensity1. Perfusion and angiography imaging techniques, such as arterial spin labelling and time of flight, leverage inflow effects to create desirable image contrast2,3. However, inflow effects cans also be a source of artifacts. For example, functional MRI (fMRI) experiments that use only one or a small number of gapped slices in combination with short TR can be biased by inflow effects4. One way to mitigate inflow effects in single-slice imaging experiments is the use of saturation modules, played every TR, to eliminate the longitudinal magnetization outside the area of interest (Fig. 1). Although effective, the additional RF pulses and gradients lengthen the effective TR (Fig. 1). In this study, we proposed a new RF pulse that enables simultaneous slice-selective excitation and saturation of longitudinal magnetizations outside of the slice.Theory
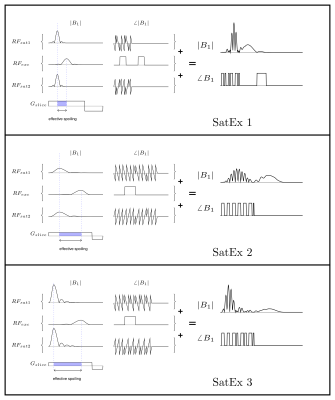
Our simulations Saturation and Excitation (SatEx) pulse is a summation of RF pulses targeting different frequency bands. Importantly, there is either asymmetry in duration or shape of the pulse components covering excitation and saturation bands (Fig.2). Most efficient is the use of truncated (asymmetric) sinc pulses. In this case the waveforms that aim to saturate magnetization outside of the imaging slice are truncated at the start, and the excitation wave-form is truncated at the end (Fig. 2). Therefore, the gradient moment accumulated between the peaks will not be rewound, effectively spoiling the magnetization outside of the excitation band (fig. 2). To eliminate flow from either side of the slice, two of a pair of bands can be designed to eliminate the magnetization on either side of the slice. Typically, these will have the same shape and opposite RF frequency shifts:$$SatEx(t)=RF_{sat}(t)e^{i\omega t} +RF_{exc}(t)+ RF_{sat}(t)e^{-i\omega t}$$
where, $$$\omega$$$ is a frequency offset to saturate outside of the slice. The amount of frequency shift must be carefully chosen not to interact with the target slice.
Methods
Slice profile simulations: To evaluate the potential of SatEx pulses, Bloch simulations were performed to estimate the expected slice profile. For the simulation, three SatEx pulses were designed (Fig.2).SatEx 1 is consisted of time asymmetric pulse, SatEx 2 consists of asymmetrically shaped pulses, and SatEx 3 is consisted of asymmetric pulses with optimized TBWP and flip angle to get a stronger saturation effect.
SatEx 1: time-bandwidth product (TBWP) =6, flip angle =20˚, all of pulses are sinc pulse, pulse duration of $$$RF_{exc}(RF_{sat})$$$=2.56ms (1.28ms), $$$\omega$$$=2945 Hz, slice thickness = 3mm.
SatEx 2: TBWP =6, flip angle =20˚, pulse duration 2.56ms, $$$\omega$$$=2480 Hz, two initial sidelobes were cut for $$$RF_{sat}$$$, two last sidelobes were cut for $$$RF_{exc}$$$, slice thickness = 3mm.
SatEx 3: TBWP$$$_{RF_{exc}}$$$=6, TBWP$$$_{RF_{sat}}$$$=12, flip angle of $$$RF_{exc}(RF_{sat})$$$ =20˚(40˚), pulse duration 2.56ms, $$$\omega$$$=2480Hz, five initial sidelobes were cut for $$$RF_{sat}$$$, two last sidelobes were cut for $$$RF_{exc}$$$, slice thickness = 3mm.
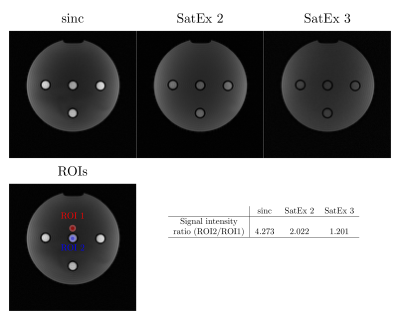
Flow phantom scan: To evaluate the saturation property, a home-built cylindrical flow phantom5 containing 4 tubes with flowing water was scanned at a 3T MAGNETOM Prisma (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using a 64 Ch head coil (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany). The flow rate was approximately 1.5cm/s. Images were acquired using a single-slice fast low angle shot (FLASH) sequence with the use of a conventional sinc pulse TBWP =6, SatEx 2 and SatEx 3 with Following parameters; TR=10ms, TE=5ms, slice thickness=3mm, resolution=1.5mmx1.5mm, matrix size=128x128.
Results and Discussion
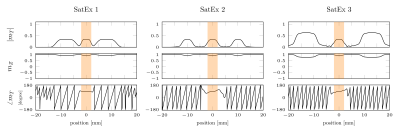
Slice profile simulations: Figure 3 shows that transverse magnetization outside of the slice is highly dephased, while maintaining a stable phase in the slice of the interest. As expected, the SatEx 3 pulse has the most effective spoiling (a larger change in phase per unit of distance). In theory even higher levels of saturation can be achieved by increasing the width and amplitude of saturation bands.Flow phantom scan: When using the traditional sinc pulse, bright spots are observed in the tubes filled with flowing water, highlighting a significant inflow effect. This signal in these tubes was suppressed by 53% when SatEx 2 was used, and further suppression by 72% using our SatEx 3 pulse. The Specific absorption Rate (SAR) as reported by the scanner console was increased from 3% (sinc and SatEx2) to 6% (SatEx 3).
Conclusions
In this work, we have introduced a simple RF pulse design (SatEx), that enables simultaneous slice-selective excitation and saturation of longitudinal magnetization outside of the excitation slice. SatEx pulses can be used with minimal SAR cost and without influencing the timing of the sequence. This would be particularly beneficial for fMRI application with cutting-edge fast and small coverage acquisition6,7. The SatEx inflow saturation will enable to acquire pure fMRI weighted signals, which may provide better understandings of fMRI signal dynamics and underlying biophysics.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by ARC Future fellowship grant FT200100329, by the NIH NIBIB (grants P41-EB03006, R01-EB019437 and R01-EB032746) and by the BRAIN Initiative (NIH NIMH grant R01-MH111419 and NINDS grant U19-NS123717). The authors acknowledge the facilities of the National Imaging Facility at the Centre for Advanced Imaging.References
1. Suryan G. Nuclear resonance in flowing liquids. InProceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences-Section A 1951 Feb (Vol. 33, No. 2, pp. 107-111). Springer India.
2. Golay, X., Hendrikse, J., & Lim, T. C. (2004). Perfusion imaging using arterial spin labeling. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 15(1), 10-27.
3. Miyazaki, M., & Lee, V. S. (2008). Nonenhanced MR angiography. Radiology, 248(1), 20-43.
4. Gao JH, Liu HL. Inflow effects on functional MRI. Neuroimage. 2012 Aug 15;62(2):1035-9.
5. Wu C., Jin J., Dixon C., Maillet D., Barth M. & Cloos M. Velocity selective arterial spin labelling using parallel transmission. In Proc. of the 31st Annual Meeting of ISMRM. London, England UK.
6. Toi PT, Jang HJ, Min K, Kim SP, Lee SK, Lee J, Kwag J, Park JY. In vivo direct imaging of neuronal activity at high temporospatial resolution. Science. 2022 Oct 14;378(6616):160-8.
7. Lewis LD, Setsompop K, Rosen BR, Polimeni JR. Fast fMRI can detect oscillatory neural activity in humans. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences. 2016 Oct 25;113(43):E6679-85.
Figures
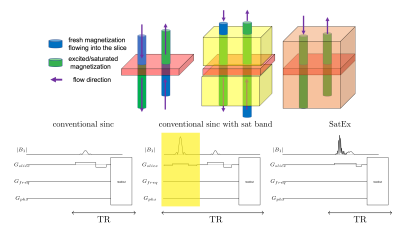
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the inflow effects. Three examples are shown, no saturation (conventional sinc pulse), sinc with saturation band, SatEx implementaiton. The red highlighted areas represents the excitation slice. The yellow boxes represent saturation bands. Orange area represents saturated area by SatEx pulse. Since SatEx pulse does not require saturation module, TR is not lengthened with saturaitons.