4537
Application value of compressed sensing-based MR FRACTURE sequence in bone and joint1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Bone, Bone
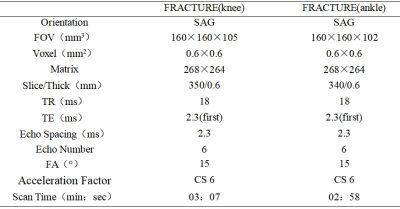
FRACTURE sequence does not need to control TE time within 1ms, but uses multi-echo three-dimensional fast field echo, FFE) sequence to perform magnetic resonance imaging with fixed echo interval. After scanning, bone images with high contrast and high signal-to-noise ratio can be obtained through echo accumulation, subtraction and gray scale inversion.Summary of Main Findings
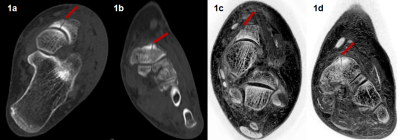
FRACTURE sequence can clearly show three kinds of bone changes: knee and ankle fracture, hyperosteogeny and bone destruction. FRACTURE sequence is highly consistent with CT in displaying the bone of knee joint and ankle joint, and has great clinical application value, especially for children and patients of childbearing age, and can be used as an alternative examination method of CT.Introduction
X-ray has ionizing radiation, which will cause uncertain damage to human body, so two groups of people should be highly cautious: ①minor patients; ②Patients of childbearing age. Therefore, it is urgent to use a new technology as a supplement to X-ray or CT examination, and apply it to clinical examination or repeated reexamination, so as to reduce the radiation dose of patients and reduce the psychological burden of patients and their families. The purpose of this study was To explore the value of FRACTURE MRI in assessment of knee and ankle joint lesions.Materials and methods
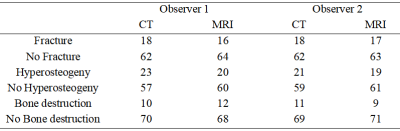
From Nov. 2020 to Nov. 2021, 17 patients with suspected of knee or ankle joint lesions underwent CT and MRI (FRACTURE) examination in the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, including 14 patients with knee joint examinations and 3 patients with ankle joint examinations. According to the composition of joints, 80 pieces of bones were exanimated for the 17 patients, including 14 pieces of femur and patella, 17 pieces of tibia and fibula, and 3 pieces of talus, scaphoid, medial cuneiform, medial cuneiform, lateral cuneiform and calcaneus, respectively. Two observers evaluated the fracture, hyperosteogeny, and bone destruction of the joint bones by using CT and FRACTURE images respectively. Kappa test was used to analyze the intra-observer and inter-observer consistency of bone lesion assessment, and to evaluate the performance of FRACTURE on visualization of bone structure.Results
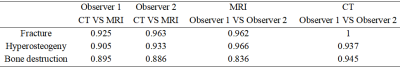
The two observers have a high degree of consistency in identification of the bone lesions of knee and ankle joint using FRACTURE images. The consistency for evaluations of fracture, hyperosteogeny, and bone destruction through CT and FRACTURE images were 0.925, 0.905 and 0.895 respectively for observer 1, and were 0.963, 0.933 and 0.886 respectively for observer 2. The consistency of evaluation fracture, hyperosteogeny, and bone destruction by FRACTURE images between observers 1 and 2 were 0.962, 0.966 and 0.836 respectively.Discussion and Conclusions
FRACTURE is a stable and reliable MRI method for visualization of bone structure of knee and ankle joints. And FRACTURE showed a high consistency with CT imaging for evaluation of bone lesions including fracture, hyperosteogeny, and bone destruction.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Gascho D, Zoelch N, Tappero C, et al. FRACTURE MRI: Optimized 3D multi-echo in-phase sequence for bone damage assessment in craniocerebral gunshot injuries[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2020, 101(9): 611-615.
[2] Murata S, Hagiwara A, Fujita S, et al. Effect of hybrid of compressed sensing and parallel imaging on the quantitative values measured by 3D quantitative synthetic MRI: A phantom study[J]. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021, 78: 90-97.
[3] Pfeifer C, Attenberger U, Schoenberg SO, et al. Diagnostic value of a 3D-SPACE-sequence with compressed sensing technology for the knee joint[J]. Radiologe. 2021, 61(2): 203-212.
[4] Chong LR, Lee K, Sim FY. 3D MRI with CT-like bone contrast-An overview of current approaches and practical clinical implementation[J]. Eur J Radiol. 2021, 143: 109915.
Figures