4535
MRI One-stop-shop for Diagnosis of Shoulder Disease
Jienan Wang1, ShuQing Chen2, LiFei Ma2, Rui Zhang2, and XiaoMeng Wu2
1Department of Radiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People‘s Hosptial, Shanghai, China, 2Philips, Shanghai, China
1Department of Radiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People‘s Hosptial, Shanghai, China, 2Philips, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Bone, MSK, MRI One-stop-shop, T2 mapping, FRACTURE (FFE Resembling A CT Using Restricted Echo - spacing)
In this study, shoulder imaging was achieved by MRI one-stop imaging, which contained different sequences. After the post-processing, a variety of fusion images could be formed to comprehensively evaluate the soft tissue, nerve, cartilage and bone of the shoulder, and then gave us a comprehensive view of the shoulder.Introduction
The most unstable joint in human body, which meant sports-related shoulder pain and injuries represent a common problem. The injuries of labrum, rotator cuff and brachial plexus caused by acute trauma and chronic strain are common damage. Clinically, some unexplained shoulder pain and mobility disorders were diagnosed as scapulohumeral periarthritis by mistake, leading to misdiagnosis of osteoarthritis, rotator cuff injury, glenoid lip injury and some other diseases【1】. Non-trauma related diseases, such as tumors, also required MRI multi-parametric imaging to differentiate between soft tissue and bone origin. Including CT, MRI and high-frequency US, single imaging method might miss lesions. CT has low diagnostic accuracy for shoulder soft tissue and cartilage lesions, and MR Traditional sequence has shortcomings for bone and calcification. For example, most of the shoulder MRI examinations mainly focused on internal structures of the joint, while it was easy to ignore other structures such as the brachial plexus, which might lead to misdiagnose【2】.In this study, we evaluated soft tissue by PDWI-TSE-SPAIR, and observe cartilage by 3D-FFE/T2 mapping . We could evaluate the structural integrity, tissue structure and cartilage water content by T2 mapping, which detected cartilage lesions early. We observed bone by FRACTURE (FFE Resembling A CT Using Restricted Echo - spacing), and evaluated brachial plexus by 3D-TSE-T2WI (3D BrainView). One-stop MRI scan provided one-stop imagig of shoulder ligaments, synovium, tendons, nerves, cartilage and bone, thus completing a comprehensive assessment of soft tissue, nerves and bone imaging of the shoulder.
Method
Three subjects were involved in this study, and we showed one(female, 26 years old). This study were approved by local institutional review board and a written consent form was obtained from each subject.Volunteers underwent shoulder examination using a one-stop MRI scan. All MRI examinations were performed on a 3.0-Tesla system (Ingenia, software release R5.6; Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) with a 16-channel shoulder coil.FRACTURE (fast field echo resembling a CT using restricted echo-spacing), a high resolution 3D gradient echo pulse sequence with restricted echo-spacing combined with an automated post-processing, is described to provide a CT-like image【3】.
Fused images were reconstructed by VolumeView of ISP (Philips Healthcare).
Result
In this study, we observed different tissues by a series of magnetic resonance imaging. As shown in figure 1, Soft tissue could be observed with PDWI-TSE-SPAIR and nerve tracts and shape could be observed with 3D TSE T2WI. FRACTURE showed similar information with CT imaging. The fusion map of FRACTURE and 3D TSE T2WI provided the information of nerve and cortical bone at the same time, which was important for clinical. In addition, the fusion map of 3D FFE and T2 mapping provided Cartilage shape, thickness and water content as well.Discussion
The results showed that we evaluate soft tissue by PDWI-TSE-SPAIR, and observed cartilage by 3D-FFE/T2 mapping, and observe bone by FRACTURE. In addition, T2 mapping and 3D-FFE fusion map could accurately show water content in cartilage of different parts. 3D-TSE-T2WI(3D BrainView) and PDWI-TSE-SPAIR fusion map could show the innervation and anatomical relationship between nerves and muscles. Therefore, one-stop MRI imaging of shoulder joint could comprehensively evaluate the status of ligament, synovial membrane, tendons, nerve, cartilage and bones of shoulder.Conclusion
MRI One-stop-shop scan can help us to complete a comprehensive assessment of the soft tissue, nerve, and bone of the shoulder.Acknowledgements
noneReferences
1.Dias R, Cutts S, Massoud S. Frozen shoulder. BMJ. 2005 Dec 17;331(7530):1453-6.
2.pathology on routine shoulder MRI. Eur Radiol. 2021 Jun;31(6):3555-3563.
3.Johnson B, Alizai H, Dempsey M. Fast field echo resembling a CT using restricted echo-spacing (FRACTURE): a novel MRI technique with superior bone contrast. Skeletal Radiol. 2021 Aug;50(8):1705-1713.
Figures

Table 1. Relevant
imaging parameters:
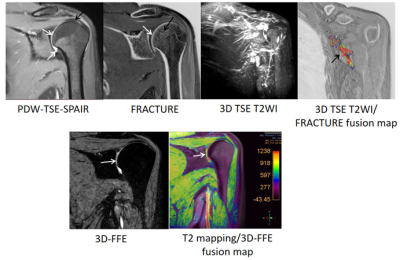
Figure 1. One-stop-shop images of shoulder. PDWI-TSE-SPAIR showed information
about soft
tissue, such as tendons(black arrow), ligaments, synovium, blood vessels, and Cartilage(white
arrow); FRACTURE showed cortical bone(white arrow) and trabecular bone(black
arrow); 3D TSE T2WI showed Nerve tracts and shape(black arrow); 3D-FFE showed Cartilage shape and thickness(white arrow); T2 mapping
showed Cartilage water content(white arrow).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4535