4518
AI algorithms for classification of the mpMRI image sequences and segmentation of the prostate gland: an external validation study
Kexin Wang1
1Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
1Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Prostate, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence
In this study we evaluate the generalization of the AI algorithms for the classification of the mpMRI image sequences and the segmentation of the prostate gland with multicenter external dataset. A total of 719 patients who underwent multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) of the prostate were collected retrospectively from two hospitals. AI algorithms were tested for classification of the image type and segmentation of the prostate gland. The AI models demonstrated good performance in the external validation in the task of image classification and prostate gland segmentation.Purpose
To evaluate the generalization of the AI algorithms for the classification of the mpMRI image sequences and the segmentation of the prostate gland with a multicenter external dataset.Methods
A total of 719 patients who underwent multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) of the prostate were collected retrospectively from two hospitals. Two AI models were tested for their generalization. One AI model was used to classify the MR images into nine types, i.e., DWI_HighBValue, DWI_LowBValue, ADC map, T2WI_withoutFatSat, T2WI_FatSat, TIWI_InPhase, T1WI_OutOfPhase, DCE_BeforeContrastEnhanced, and DCE_AfterContrastEnhanced. Another AI model was used to segment the area of the prostate gland on T2WI. The effectiveness of the image classification model was evaluated by two radiologists. The accuracy of the segmentation model was evaluated in terms of the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), volume similarity (VS), and average Hausdorff distance (AHD) and subjectively evaluated by two radiologists.Results
719 MR studies obtained from 9 MR scanners were included, with 11,497 scan sequences and 20551 image groups. The classification AI model predicted 20,274 correct and 277 incorrect for 20,551 image groups. The accuracy of the model for the overall classification of all sequences was 0.989 (95% CI: 0.949-0.955), and the kappa was 0.932 (95% CI: 0.929-0.937). The median DSC predicted by the segmentation model was 0.960 [0.0200, 1.00], the median VS was 0.990 [0.0200, 1.00], and the median AHD was 4.50 [0.510, 71.0] mm. The radiologists subjectively evaluated 715 (99.9%) segmentation results as acceptable, and 1 (0.1%) segmentation result as unacceptable.Conclusion
The AI models demonstrated good performance in the external validation in the task of image classification and prostate gland segmentation.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
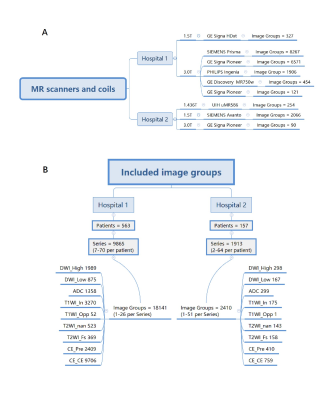
Figure 1 Inclusion data of the MR scanner, pulse sequence, and image groups in the study.
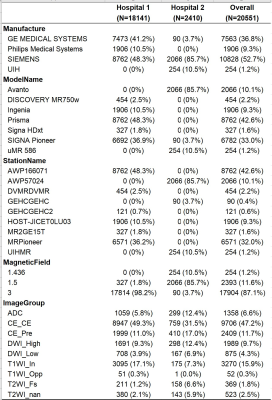
Figure 2 In formation of the MR scanner, pulse sequence, and image groups in the study.
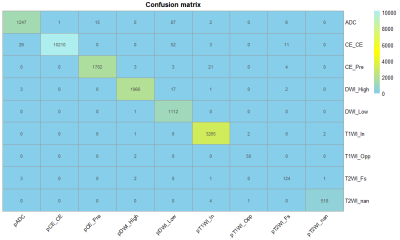
Figure 3 Confusion matrix of the AI algorithm in the classification of different image
types.
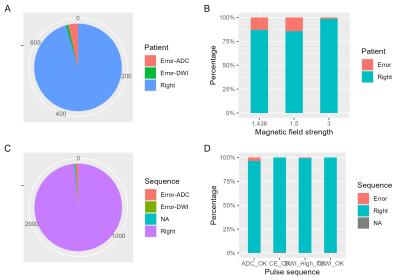
Figure 4 AI
accuracy in classification of the image type at the patient level and the
sequence level.
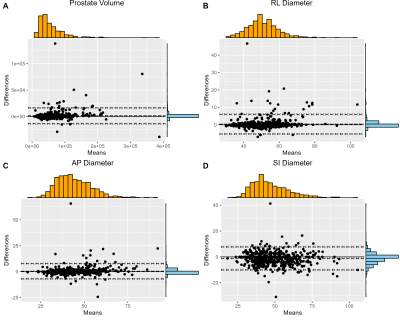
Figure 5 Bland‒Altman analysis of the
prostate volume (A), RL diameter (B), AP diameter (C) and SI diameter (D)
between the model measured values and the expert manually labeled parameters.
and the expert manually labeled parameters. Only 3.1%, 2.7%, 6.6%, and 4.1% of the prostate RL diameter, AP diameter, SI diameter and volume
measurements were outside the 95% LoA,
respectively.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4518