4499
Hybrid segmentation of ventilation defect regions in low signal-to-noise ratio hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI1State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences - Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan, China, 2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Gas), Lung
Ventilation defect percentage (VDP) generated from hyperpolarized gas (3He or 129Xe) MRI is a sensitive indicator of lung disease. However, the commonly used K-means method for the calculation of VDP is not suitable for low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) images. In this work, we proposed a hybrid segmentation method to segment the ventilation defect regions and calculate VDP values under low SNR conditions. The results show that the proposed method has improved both the accuracy of segmenting VDP map and calculating VDP value.Introduction
Hyperpolarized (HP) gas (3He or 129Xe) MRI is a new imaging technique to map regional lung function. The ratio of ventilated defect volume segmented from 3He or 129Xe ventilation image to total lung volume (TLV) segmented from 1H MRI is a sensitive indicator of lung disease, named as ventilation defect percentage (VDP) 1. Generally, VDP was calculated by using the K-means method 2. Unfortunately, it has been shown K-means method was not suitable for low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) (such as SNR < 6.6 3 or 8 4) ventilation images 3-5. Meanwhile, due to particularity of HP gas technique, it may frequently obtain low SNR ventilation images in clinical 6. Increasing gas dose or re-scanning may mitigate this problem, but increasing physiological burden for patients. To solve this challenge, we proposed a hybrid segmentation method based on K-means method to segment the ventilation defect regions (VDP map) and calculate VDP values under low SNR conditions.Methods
Image acquisitionThe MRI experiments were approved by local institution and were performed with previous parameters 6. The simulated Rician noise was added on the high SNR 129Xe ventilation image (SNR > 12) to mimic low SNR condition. A total of 10 patients were included in this initial study.
De-noising method
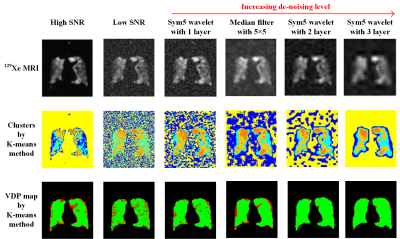
The high degree of de-noising will cause excessive smoothing of ventilation images. The insufficient degree of de-noising will make it difficult to remove all noise. Herein, we studied two commonly used methods: median filter and wavelet de-noising with different parameters, as shown in Figure 1. After comparison, the median filter with radius 5 × 5 was chosen as our de-noising method, although some ventilation defect regions were still lost.
Hybrid segmentation
In K-means method, the bottom cluster of first round (a total of 4 clusters) was further divided into 2 clusters in second round to distinguish the background (ventilation defect regions) and very low ventilation signal. However, under low SNR condition, the noise will largely exist in bottom cluster, hampering discrimination between background and very low signal.
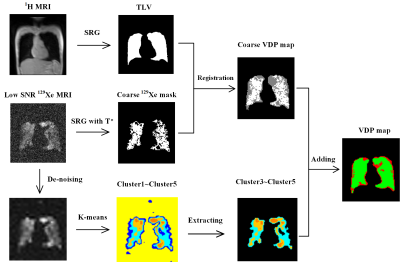
Herein, we solved this problem by discarding the bottom cluster. The top clusters were reserved and combined with a coarse ventilation boundary to generate a fine ventilation boundary. The background will be naturally distinguished from the very low signal after the boundary was generated. We obtained the ventilation boundary through the proposed hybrid segmentation method. The workflow of the hybrid segmentation was shown in Figure 2.
First, we used a special seeded region growing (SRG) to obtain a coarse 129Xe mask. The seed was placed in the main ventilation signal region through manual selection. A special growing threshold T* was calculated based on selected regions to ensure only the main part of ventilation signal was preserved and the noise was reduced as much as possible, although some ventilation signal was removed:
T*=(Max(ventilation)-Min(ventilation))/2-stdev(noise)
Then, a coarse VDP map was generated by combing the coarse 129Xe mask and the lung mask segmented from 1H MRI.
After that, we used the K-means method to generate 5 clusters from the de-noised ventilation image and extract the top 3 clusters of them.
At last, the final VDP map was generated by adding this 3 clusters on the coarse VDP map to compensate the lost ventilation signal.
Results
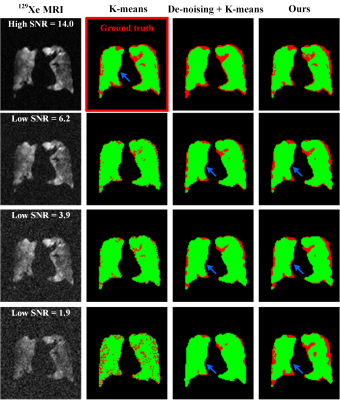
Figure 3 demonstrated the generated VDP maps of a representative chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patient under different SNR conditions by using the K-means method, the combination of de-noising and K-means method, and our hybrid segmentation method. It could be seen that the ventilation defect regions (red color areas) of the low SNR ventilation images segmented by our method were more similar with the ground truth in visual. In addition, our method was still robust when the SNR was continuously decreasing, even when SNR < 2.Quantitative analysis showed the mean Dice score / VDP value (ground truth: 1.00 / 29.4%) of 10 patients under SNR ≈ 4.5 condition by using the K-means method and our method were 0.65 / 14.8% and 0.70 / 26.3%, respectively. The mean Dice score / VDP value under SNR ≈ 3.0 condition by using the K-means method and our method were 0.56 / 12.9% and 0.71 / 26.2%, respectively.
Discussion and Conclusion
In this work, we proposed a hybrid segmentation method to segment ventilation defect regions in low SNR 129Xe MRI. The results showed our method was more robust than the K-means method. The VDP map in our method was generated by combing the coarse 129Xe mask segmented by SRG and the top clusters segmented by K-means. The location and the growing threshold of seed in SRG were manually designed, which should be improved by developing automatic method. Besides, the more patients and quantitative analysis are needed in future.Deep learning de-noising method may also address this task. However, deep learning requires a large number of datasets and expensive computer hardware. In contrast, our method is simple and could be easily accessed in clinical.
In conclusion, we proposed a hybrid segmentation method to segment the ventilation defect regions in low SNR 129Xe MRI, demonstrating both improvement on generating VDP map and calculating VDP value.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFA0704000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (91859206, 82127802, 21921004, 82001915), Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (ZDBS-Y-JSC004), Hubei Provincial Key Technology Foundation of China (2021ACA013). Xin Zhou acknowledges the support from the Tencent Foundation through the XPLORER PRIZE.References
1. Woodhouse N, Wild J M, Paley M N J, et al. Combined helium‐3/proton magnetic resonance imaging measurement of ventilated lung volumes in smokers compared to never‐smokers. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2005; 21(4):365-369.
2. Kirby M, Heydarian M, Svenningsen S, et al. Hyperpolarized 3He magnetic resonance functional imaging semiautomated segmentation. Academic Radiology. 2012; 19(2):141-152.
3. He M, Zha W, Tan F, et al. A comparison of two hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI ventilation quantification pipelines: the effect of signal to noise ratio. Academic Radiology. 2019; 26(7):949-959.
4. Santyr G, Kanhere N, Morgado F, et al. Hyperpolarized gas magnetic resonance imaging of pediatric cystic fibrosis lung disease. Academic Radiology. 2019; 26(3):344-354.
5. Hughes P J C, Horn F C, Collier G J, et al. Spatial fuzzy c‐means thresholding for semiautomated calculation of percentage lung ventilated volume from hyperpolarized gas and 1H MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2018; 47(3):640-646.
6. Xiao S, Deng H, Duan C, et al. Highly and adaptively undersampling pattern for pulmonary hyperpolarized 129Xe dynamic MRI. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2019; 38(5): 1240-1250.
Figures