4446
High resolution diffusion weighted imaging on pancreas through reduced FOV and compressed SENSE: a feasibility study1MR Clinical Science, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare (China), Shenzhen, China, 3MR Application, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 4Philips Healthcare (China), Beijing, China, 5MR R&D, Philips Health Technology, Suzhou, China, 6Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Pancreas, Data Acquisition
Pancreas imaging remains challenging because of its small size and motion, and conventional diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) suffers from poor image quality due to low signal-to-noise (SNR) and image blurring. This study performs several schemes to achieve high resolution high image quality pancreas DWI with reduced FOV using Compressed SENSE.
Introduction
MRI has played a critical role in the evaluation of pancreatic pathologies including detection of pancreatic cysts and lesions, and the screening of patients at high risk for pancreatic cancer1,2. The pancreas remains a challenging organ to image because of its small size and the body motion, and conventional diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) of pancreas suffers from poor image quality due to low signal-to-noise (SNR) and image blurring. Compressed SENSE (CS)3 has been reported to effectively improve image quality through its iterative reconstruction procedure, including wavelet-based de-noising process, on EPI-based DWI4,5. In addition, the reduced FOV imaging by iZoom (an improved Zoom method)6 has recently been proposed to image small regions with potentially high resolutions due to its nature of insensitive to B1 non-linearity. In this work, we propose to combine the iZoom with CS for pancreas diffusion weighted imaging and investigate the performance with different imaging acceleration schemes and imaging resolutions.Method
Pancreas imaging was performed on a 3.0 T Ingenia Elition system (Philips Healthcare) using a combination of 16-ch dStream Torso coil and the integrated FlexCoverage Posterior coil. Three healthy volunteers participated in this study under informed consent. T2w image was acquired as anatomical landmark, with scanning parameters FOV = 400 x 400 mm2, voxel size = 1.35 x 1.35 x 5 mm3, TE/TR = 78/2725 ms. The conventional single shot EPI was acquired with FOV = 370 x 303 mm2, voxel size = 2.8 x 2.8 x 6 mm3, TE/TR = 86/1789 ms, b-value = 0, 500 s/mm2, and SENSE factor of 2.4. The reduced FOV DWI was acquired using iZoom with different protocol settings, while the same FOV, b-values and voxel size were applied. SENSE parallel imaging and Compressed SENSE (CS) acceleration schemes were separately combined with iZoom to compare their imaging performances. Detailed protocol settings including TE/TR, acceleration schemes, b-value and spatial resolution are listed in Table 1. A respiratory triggering was used during the image acquisition.Results
Pancreas imaging of T2w, conventional DWI, and reduced FOV imaging through iZoom with SENSE or Compressed Sense (CS) were shown for 2 axial planes (S1, S2) in Figure 1. Compared to conventional DWI, reduced FOV imaging provided better tissue contrast, and iZoom combined with CS (iZoom-CS2) clearly improved the image quality with regard to denoising (regions with red arrows). iZoom with parallel imaging (iZoom-S2) had banding noise (as circled in Figure 1) and was not practically useful. Figure 2 shows the high resolution (1.5 x 1.5 mm2) pancreas imaging compared with iZoom-CS of baseline resolution (2 x 2 mm2). iZoom with CS = 2 high resolution imaging (iZoom-CS2-HR) provided an optimal high resolution pancreas DWI image, preserving fine structures (see magnified regions). iZoom with CS 3 images suffered from banding noise artifact.Discussion and Conclusion
One of the limitations of pancreas diffusion weighted imaging is the image quality, and it is well noted that the single shot EPI results in low in-plane resolution. In this work, we show that the pancreas DWI can be improved by applying the reduced FOV (iZoom) to increase spatial resolution to 1.5 x 1.5 mm2 against the conventional DWI (2.8 x 2.8 mm2), which is almost two-fold increase. The image quality can be further improved by combining compressed SENSE to the reduced FOV imaging. The high resolution DWI of pancreas has the potential to reveal details of pancreatic tumors more clearly, adding diagnostic value and further data quantification information.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Figures
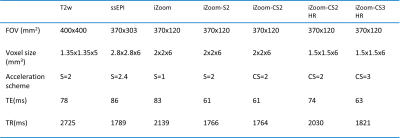
Table 1 scanning parameters of T2w, conventional DWI and iZoom imaging with different acceleration schemes and resolutions.
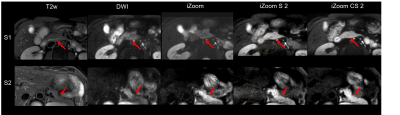
Figure 1. Pancreas imaging of T2w, conventional DWI, and reduced FOV imaging through iZoom with Sense or Compressed Sense (CS) were shown for 2 axial planes (S1, S2). iZoom-CS2 clearly improved the image quality through denoising (regions with red arrows). iZoom-S2 has the noise breakthrough as circled.
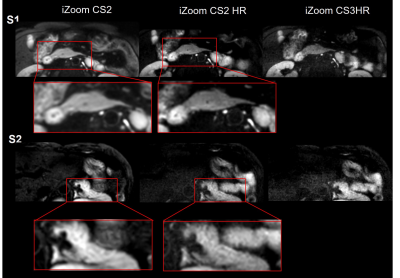
Figure 2. High resolution (1.5mm x 1.5mm) pancreas images are shown and compared with iZoom-CS of baseline resolution (2mm*2mm). iZoom with CS = 2 high resolution imaging (iZoom-CS2-HR) provides an optimal high resolution pancreas DWI images, preserving fine structures (see magnified regions).