4439
MRI-based radiomics nomogram for preoperatively differentiating intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from colorectal liver metastases Abstract
Ying Xu1, Lu Li1, Yi Yang1, Feng Ye1, Sicong Wang2, Lizhi Xie2, Yanan Wang3, and Xinming Zhao1
1Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China, 3Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Cancer Hospital, Zheng Zhou, China
1Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China, 3Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Cancer Hospital, Zheng Zhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Liver, Radiomics, Cholangiocarcinoma; colorectal liver metastases; nomogram; differential diagnosis.
A total of 133 patients in training cohort (64 IMCC and 69 CRLM) and 57 patients in validation cohort (29 IMCC and 28 CRLM) were included. Radiomics features were extracted from the DCE-MR images and selected by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator algorithm to establish the radiomics model.The radiomics nomogram was constructed combining the radiomics model and clinical model.The radiomics nomogram combining radiomics signatures based on DCE-MRI with clinical factors (serum CEA level and tumor diameter) may provide a reliable and noninvasive tool to discriminate IMCC from CRLM, which could help guide treatment strategies and prognosis prediction preoperatively.Objectives
To establish a radiomics nomogram based on dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MR images for preoperatively differentiating intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma (IMCC) from colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM).Methods
A total of 133 patients in training cohort (64 IMCC and 69 CRLM) and 57 patients in validation cohort (29 IMCC and 28 CRLM) were included. Radiomics features were extracted from the DCE-MR images and selected by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator algorithm to establish the radiomics model. Clinical variables and MRI findings were assessed and selected by univariate and multivariate analyses to construct a clinical model. The radiomics nomogram was constructed combining the radiomics model and clinical model. Performance of the radiomics nomogram, radiomics model, and clinical model was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic and decision curve analysis.Results
Six features were selected to construct the radiomics model. The radiomics signature showed better discrimination than the clinical model in the training cohort (AUC [area under the curve], 0.92; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-0.96 vs AUC, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.66-0.83;) and the internal validation cohort (AUC, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.84-0.98 vs AUC, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.60-0.86). The radiomics nomogram incorporated CEA, tumor diameter and radiomics signatures. It showed favorable calibration and best discrimination performance in the training cohort (AUC,0.94; 95% CI, 0.90-0.97) and the internal validation cohort (AUC, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.86–1.00) in the three models. Decision curve analysis demonstrated that the radiomics nomogram outperformed the radiomics model and clinical model.Conclusions
The radiomics nomogram combining radiomics signatures based on DCE-MRI with clinical factors (serum CEA level and tumor diameter) may provide a reliable and noninvasive tool to discriminate IMCC from CRLM, which could help guide treatment strategies and prognosis prediction preoperatively.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
1 Ren L, Zhu D, Benson AB, 3rd et al (2020) Shanghai international consensus on diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of colorectal liver metastases (version 2019). Eur J Surg Oncol 46:955-966 2 Brindley PJ, Bachini M, Ilyas SI et al (2021) Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7:65 3 Tsilimigras DI, Brodt P, Clavien PA et al (2021) Liver metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7:27 4 Seo N, Kim DY, Choi JY (2017) Cross-Sectional Imaging of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Development, Growth, Spread, and Prognosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 209:W64-W75 5 You MW, Yun SJ (2019) Differentiating between hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using contrast-enhanced MRI features: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Radiol 74:406 e409-406 e418 6 Saleh M, Virarkar M, Bura V et al (2020) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: pathogenesis, current staging, and radiological findings. Abdom Radiol (NY) 45:3662-3680 7 Granata V, Grassi R, Fusco R et al (2021) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its differential diagnosis at MRI: how radiologist should assess MR features. Radiol Med 126:1584-1600 8 Chiu CT, Chiang JM, Yeh TS et al (2008) Clinicopathological analysis of colorectal cancer liver metastasis and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: are they just apples and oranges? Dig Liver Dis 40:749-754 9 Rastogi A, Wani S (2017) Colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 85:59-66 10 Shaukat A, Kahi CJ, Burke CA, Rabeneck L, Sauer BG, Rex DK (2021) ACG Clinical Guidelines: Colorectal Cancer Screening 2021. Am J Gastroenterol 116:458-479 11 Kanth P, Inadomi JM (2021) Screening and prevention of colorectal cancer. BMJ 374:n1855 12 Okano K, Yamamoto J, Moriya Y et al (1999) Macroscopic intrabiliary growth of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Surgery 126:829-834 13 Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK, Gores GJ (2018) Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:95-111 14 Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 278:563-577 15 Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R et al (2012) Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer 48:441-446 16 Zhou Y, Zhou G, Zhang J, Xu C, Zhu F, Xu P (2022) DCE-MRI based radiomics nomogram for preoperatively differentiating combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma from mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eur Radiol. 10.1007/s00330-022-08548-2 17 Wang T, Wang W, Zhang J, Yang X, Shen S, Wang W (2020) Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Differentiating Combined Hepatocellular Cholangiocarcinoma From Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Front Oncol 10:598433 18 Hong JH, Jung JY, Jo A et al (2021) Development and Validation of a Radiomics Model for Differentiating Bone Islands and Osteoblastic Bone Metastases at Abdominal CT. Radiology 299:626-632 19 Nie P, Yang G, Wang Z et al (2020) A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of renal angiomyolipoma without visible fat from homogeneous clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 30:1274-1284 20 Renzulli M, Brocchi S, Cucchetti A et al (2016) Can Current Preoperative Imaging Be Used to Detect Microvascular Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Radiology 279:432-442 21 Jan YY, Chen MF, Wang CS, Jeng LB, Hwang TL, Chen SC (1996) Surgical treatment of hepatolithiasis: long-term results. Surgery 120:509-514 22 Yap FY, Varghese BA, Cen SY et al (2021) Shape and texture-based radiomics signature on CT effectively discriminates benign from malignant renal masses. Eur Radiol 31:1011-1021 23 Jing R, Wang J, Li J et al (2021) A wavelet features derived radiomics nomogram for prediction of malignant and benign early-stage lung nodules. Sci Rep 11:22330Figures
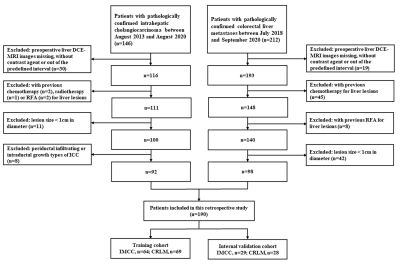
Figure
1. Flowchart of patient selection.
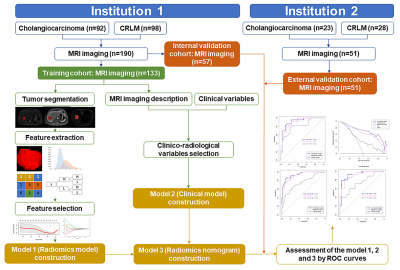
Figure
2. Workflow of the key steps to conduct radiomics
analysis and the three models.
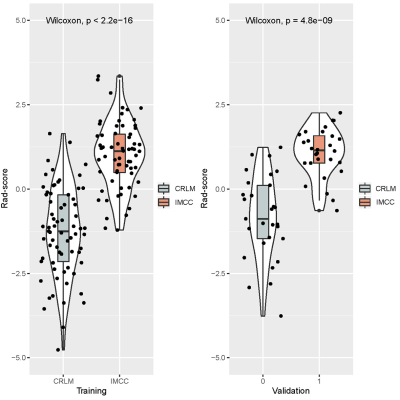
Figure
3. Violin plots comparing the Rad-score of the
IMCC and CRLM in the training cohort and internal validation cohort.
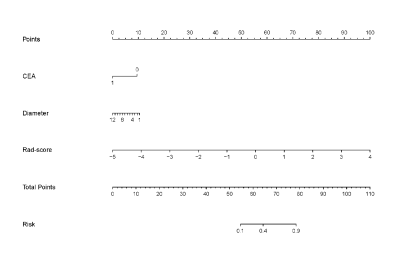
Figure
4. The radiomics nomogram incorporating the CEA
level, tumor diameter, and radiomics signature (Rad-score).
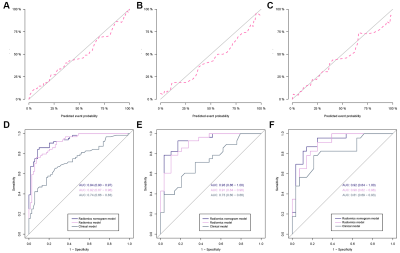
Figure
5. Calibrations of the nomogram in the training
cohort (A), internal validation cohort (B) and external validation cohort (C).
Diagnostic performance of the radiomics model, clinical model and radiomics
nomogram was compared through ROC curves in the training cohort (D), internal
validation cohort (E) and external validation cohort (F).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4439