4409
An 8-Parallel Transmit 32-Receive Array Head Coil for Clinical Use at 7.0 Tesla
Alexander Smerglia1, Labros Petropoulos1, Xiaoyu Yang1, Tsinghua Zheng1, Paul Taylor1, Blaise Whitesell1, Jagjit Sidhu2, Ken Sakaie2, and Mark Lowe2
1Quality Electrodynamics (QED), Mayfield, OH, United States, 2Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States
1Quality Electrodynamics (QED), Mayfield, OH, United States, 2Imaging Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Parallel Transmit & Multiband, Brain
An 8-parallel transmit 32-Rx head coil was built and evaluated for performance in high-field MRI. The coil is comprised of an 8-rung curved degenerate birdcage transmitter and a 32-loop element receive array. The coil housing was designed with an anterior/posterior split and eye windows for patient comfort, and a sizable interior that can fit 99 percent of the general population. A volunteer was imaged to confirm transmit coverage, which includes the entire brain and upper cervical spine. Good B1 uniformity, and improved transmit efficiency over previously built non-curved Tx head coils were also confirmed.Introduction
Ultra-High field imaging of the head in the clinical setting has been hindered by SAR limitations and B1 non-uniformities caused by dielectric inhomogeneities that vary among patients. Parallel transmit (pTx) technology shows promise in resolving these challenges through the increased degrees of freedom provided for optimizing B1 shimming. Still, there are few pTx Head coils on the market. Two of the barriers impeding the development of such pTx head coils are achieving a similar transmit efficiency to existing single transmit (sTx) coils at 7T and providing a comfortable clinical experience. Here we present an 8PTx/32Rx Head coil that produces a uniform B1 field over the entire head region while exhibiting greatly improved transmit efficiency over coils of comparable size. In addition, the coil has been designed mechanically for better a clinical experience with easy workflow and the ability to house nearly all patients comfortably.Method
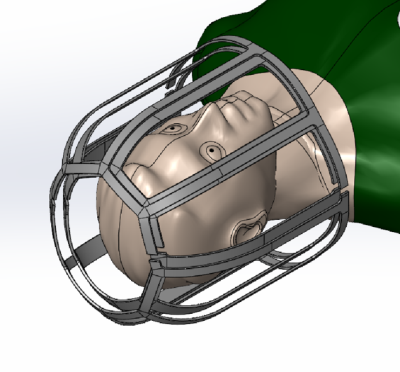
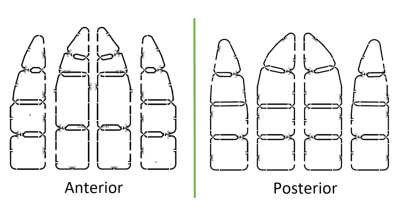
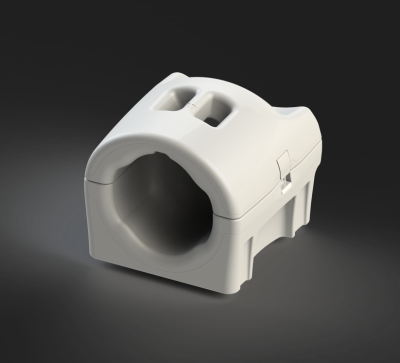
The pTx transmitter (shown in fig. 1) consists of an 8-rung volume degenerate birdcage. A degenerate birdcage design was chosen for its increased efficiency over a set of overlapped loop transmit elements [1]. The birdcage deviates from the traditional cylindrical shape by curving inwards slightly towards the dome of the head. This brings the transmitter closer to the head and increases the transmit efficiency. It also allows the coil’s mechanical design to be more compact and therefore lighter in weight. EM simulations of degenerate birdcages with this shape were performed using Sim4Life (Zurich MedTech, Zurich, Switzerland), and they confirmed the structure produces a uniform B1 field in the head region. Each loop of the birdcage is driven as an independent element by feeding the system transmit signal to a feedpoint on the superior endring. Neighboring transmit elements are isolated by the nature of the shared rung capacitance present on a degenerate birdcage. Non-neighbor elements’ isolations were optimized by careful choice of capacitances on the inferior endring. The transmitter is 27.7cm in diameter and 26.5cm tall in the S-I direction. The partial shield (also shown in fig. 1) maintains a roughly 1.5cm separation from the birdcage with a 30.5cm diameter and height of 27.9cm. The receive array consists of 32 loop elements arranged in 8 columns of 4 loops (shown in fig. 2). Elements within the same column were isolated via use of critical overlap. All other element pairs were isolated with ultra-low impedance preamplifiers [2]. The mechanical design (shown in fig. 3) features an anterior/posterior split to help facilitate workflow and patient positioning. Likewise, the unique curvature of the coil former assists in patient positioning and provides patient comfort. The coil also has sizeable eye windows to enhance comfort in the clinical setting. With an S-I height of 25.5 cm, A-P height of 24.9cm, and L-R width of 23.5cm, the inner dimensions of the coil are spacious for a 7.0 Tesla head coil, allowing for over 99 percent of the population to position their head comfortably in the coil, as determined by use of a patient model incorporated in SolidWorks (Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corporation, Waltham, MA).Results
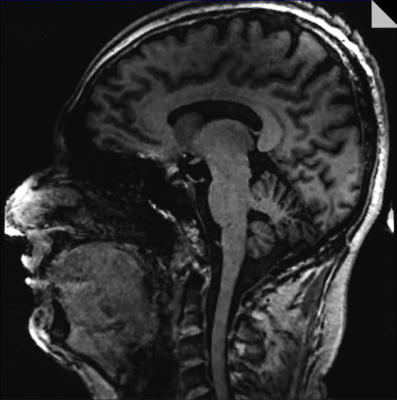
The coil was tested on a Siemens 7T Terra (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen). Imaging was performed on a healthy volunteer under an IRB-approved protocol, and figure 4 was acquired using an MP2RAGE acquisition (sagittal, 288 mm x 272 mm FOV, 240 x 227 matrix, 224 slices 0.83 mm thick, TE/TR=2.9/6000 msec, compressed sensing undersampling factor 10 and 240 Hz/Pixel bandwidth) [3]. The image shows good transmit field coverage and uniformity over the entire patient brain and upper cervical spine area. Additionally, the transmit voltage for this volunteer imaging was 284V for the curved degenerate birdcage, as opposed to a greater than 350V transmit voltage of a previously built non-curved Tx head coil of this size when imaging volunteers [4]. Thus, the transmitter efficiency has improved drastically in this build.Conclusion
A new 8pTx/32Rx Head coil was constructed and tested. The 8-rung degenerate birdcage volume transmitter produced a uniform B1 excitation field covering the entire patient brain and upper cervical spine regions. Furthermore, the transmitter efficiency was greatly improved over previous head coils of similar size at 7 Tesla by use of degenerate decoupling and curved shape of the birdcage. The inner dimensions, overall mechanical curvature, and expanded eye windows provide a comfortable clinical experience for 99 percent of the population.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] R. Stara, et al., “A Degenerate Birdcage with Integrated Tx/Rx Switches and Butler Matrix for the Human Limbs at 7T”, Appl. Magn. Reson. 48:307-326, DOI 10.1007/s00723-017-0864-2 (2017)
[2] H. Fujita, et al., “A 3T Head Transmitter Integrated with 3D Parallel Imaging Capable 16-Channel Receive Array Coil”, in Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 15, 3254 (2007)
[3] J. Marques, et al., “MP2RAGE, a self bias-field corrected sequence for improved segmentation and T1-mapping at high field”, NeuroImage 49 (2010) 1271-1281
[4] T. Zheng, et al., “A Novel clinical Friendly 7T T/R 32-Channel Head Coil Using Skipped-Rung Birdcage as Transmitter” Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 28, 6283 (2020)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4409