4395
Manganese-Phenolic Networks Platform Amplifying STING Pathway Activation for MRI Imaging Guided Cancer Chemo- /Immune Therapy1Department of Radiology, Guangzhou First People’s Hospital, GuangZhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Whole Body, Cancer, Immunity therapy
Low immune infiltrates severely hinder cancer immunotherapy. Hence, we developed a manganese-phenolic networks platform (TMPD) The TMPD was based on doxorubicin (DOX) loaded PEG-PLGA nanoparticles and further coated with manganese (Mn)-tannic acid (TA) networks. Mechanistically, DOX could kill cancer cells while Mn2+ could significantly increase the activity of STING pathway related protein to amplify the STING signal and has the function of MRI T1 imaging. The nanoplatform could promote the presentation of tumor antigens and activate a robust innate and adaptive immunity, providing reference for the application of molecular imaging in tumor diagnosis and treatment.Introduction
Immune checkpoint blocking therapy has revolutionized tumor treatment in recent years, but it works in less than one in five patients[1]. One of the important reasons is the existence of Tumor immunogenicity and tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment (TME)[2]. Therefore, improving the immunogenicity of tumor antigens and reversing the tumor immune microenvironment are of great significance for activating the anti-tumor immunity of the body[3]. Recently, cGAS-STING (cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP)- adenosine monophosphate AMP synthase stimulator of type 1 interferon genes) pathway has aroused widespread interest. The activation of STING pathway can promote the expression of type 1 interferon and widely regulate innate immunity and adaptive immunity[4-6]. Manganese ion (Mn2+), as a common nutrient element in vivo, can be used as an agonist to significantly enhance the activation of STING pathway[7-9]. At the same time, Mn2+ has the function of MRI T1 imaging, which can activate the immune system while using MRI to monitor the therapeutic effect, playing an integrated role of diagnosis and treatment[10]. Therefore, we construct a Mn2+-based drug-loaded nanoplatform loaded with doxorubicin, which can kill tumor cells and release tumor antigens while activating STING pathway. The nanoplatform could promote the presentation of tumor antigens and activate a robust innate and adaptive immunity, providing reference for the application of molecular imaging in tumor diagnosis and treatment.Methods and Results
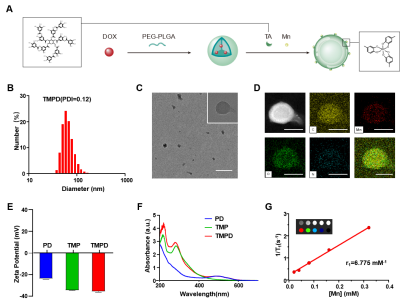
Preparation and Characterization of PD, TMP and TMPDIn this study, DOX, Mn2+, TA and PEG-PLGA were selected to develop a multifunctional nanoplatform with the function of amplifying STING signal. PD nanoparticles were constructed of DOX encapsulated PEG-PLGA nanoparticles by hydrophobic interaction. Then, the PD nanoparticles were coated with manganese (Mn)-tannic acid (TA) networks through coordination to prepare TMPD nanoparticles. In the absence of DOX, the TMPD nanoparticles were redefined as TMP nanoparticles. The size and zeta potential and the zeta potential values of PD, TMP and TMPD demonstrated the success of Mn- TA networks coating. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image and corresponding energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping images indicating the elementary composition of one single TMPD NPs. The absorbance spectrum of TMPD and PD indicating the successful loading of DOX.
Additionally, due to the ability of Mn2+ to be used as an effective T1 contrast agent for MRI, the TMPD was endowed with imaging potential. T1-weighted MR images and T1-map images of TMPD NPs solution were shown. According to the plot of the inverse relaxation time against Mn2+ concentration, the longitudinal relaxivity (r1) of TMPD NPs solution was 6.775 mM-1s-1, which is ~1.91 times higher than that of the clinical contrast agent Gd-DTPA (r1=4.4 mM-1s-1). In conclusion, we have successfully synthesized the TMPD NPs with good capability T1-MR imaging (Figure 1).
In vivo MRI performance and Antitumor Efficiency:
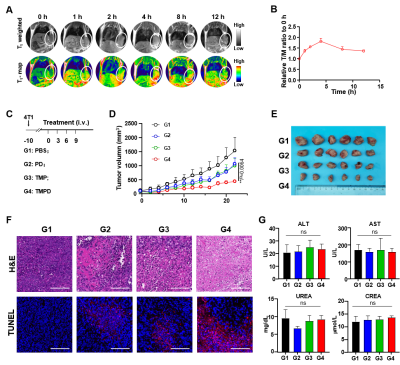
MRI is widely used in clinical and pre-clinical research as a vital imaging tool. Combining imaging capabilities with nanoplatforms could facilitate to early cancer detection and monitoring of treatment effects and post-treatment responses. Since Mn2+ is an effective MRI contrast agent, we used a 3.0T MR scanner to obtain the T1-weight MR image and T1-weighted pseudo color image of TMPD. Mice bearing 4T1 tumors were administrated with TMPD and imaged by 3.0T MR scanner at predetermined time points. T1-weight MR image and T1-weighted pseudo color image revealed a gradual increase in signal intensity, indicating the efficient tumor accumulation of TMPD. Meanwhile, the relative positive enhancement ratio of tumor to muscle reached the maximum of about 1.82 at 4 h post-injection. These data indicate that TMPD presents a good MR imaging performance for T1-weighted MRI.
To evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of TMPD, we inoculated 4T1 cells on the mice mammary fat pad and administrated with various formulations intravenously according to the treatment timeline. PD and TMP groups resulted in only moderate tumor suppression compared to the PBS group; however, TMPD treatment was more effective in controlling tumor growth, possibly due to enhanced activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. TUNEL fluorescence staining and H&E staining o slices showed that TMPD group induced the greatest amount of cell apoptosis and necrosis. Also, the hematology and liver function parameters of each group were within normal limits, indicating that these formulations had negligible system toxicity (Figure 2).
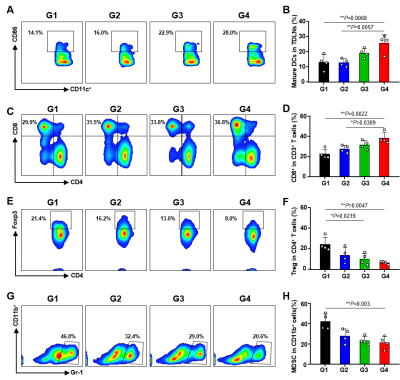
To further demonstrate these treatments could influence the immune responses, we examined the mature DCs (Dendritic cells) and the tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) by flow cytometry. TMPD had the highest frequency of mature DCs (1.9-fold than PBS group) and CD8+ T lymphocytes (1.6-fold than that PBS group). The percentages of immunosuppressive regulatory (Treg) cells in TMPD were showed 0.73-fold compared with PBS group while the percentages of MDSCs were almost 0.5-fold than it. These results demonstrated that the activated cGAS-STING pathway could induce a strong immune response, leading to significant tumor suppression efficacy (Figure 3).
Conclusion
Herein, we designed a nanoplatform TMPD for cancer therapy and MRI imaging. The results revealed that TMPD demonstrate a significant MRI imaging capability and induce robust immunity to kill cancer cells. In conclusion, this strategy provided a promising strategy for cancer theranostic applications.Acknowledgements
1. the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81971574).
2. the GuangDong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515220060).
3. Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Clinical Translational Medicine. the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81971574).
References
[1] Syn N L, Teng M W L, Mok T S K, et al. De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting[J]. The lancet oncology,2017,18(12):e731-e741.
[2] Duan Q, Zhang H, Zheng J, et al. Turning Cold into Hot: Firing up the Tumor Microenvironment[J]. Trends in Cancer,2020,6(7):605-618.
[3] Dolladille C, Ederhy S, Sassier M, et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Rechallenge After Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients With Cancer[J]. JAMA Oncol,2020,6(6):865-871.
[4] Diamond M S, Kinder M, Matsushita H, et al. Type I interferon is selectively required by dendritic cells for immune rejection of tumors[J]. J Exp Med,2011,208(10):1989-2003.
[5] Jiang M, Chen P, Wang L, et al. cGAS-STING, an important pathway in cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol,2020,13(1):81.
[6] Burdette D L, Monroe K M, Sotelo-Troha K, et al. STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP[J]. Nature,2011,478(7370):515-518.
[7] Lv M, Chen M, Zhang R, et al. Manganese is critical for antitumor immune responses via cGAS-STING and improves the efficacy of clinical immunotherapy[J]. Cell Research,2020,30(11):966-979.
[8] Hou L, Tian C, Yan Y, et al. Manganese-Based Nanoactivator Optimizes Cancer Immunotherapy via Enhancing Innate Immunity[J]. ACS Nano,2020,14(4):3927-3940.
[9] Wang C, Guan Y, Lv M, et al. Manganese Increases the Sensitivity of the cGAS-STING Pathway for Double-Stranded DNA and Is Required for the Host Defense against DNA Viruses[J]. Immunity,2018,48(4):675-687.
[10] Ni K, Lan G, Chan C, et al. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks enhance radiotherapy to potentiate checkpoint blockade immunotherapy[J]. Nat Commun,2018,9(1):2351.