4389
Design of a well decoupled 4-channel catheter Radio Frequency coil array for endovascular MR imaging at 3T1Department of Biomedical Engineering, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Interventional Devices, Blood vessels
Catheter-based radio frequency (RF) coils for interventional MRI are proposed as a means of obtaining high resolution images with significant advantages over conventional external signal detecting RF coils. A 4-channel catheter array coil was designed to improve the power transmission and SNR using parallel imaging and ultra-sensitive imaging with maximum proximity inside a blood vessel phantom. This design can be scaled to smaller/larger form to fit in tiny/wide vascular structure to provide the required B1 fields and sufficient decoupling among the resonant elements. Numerical simulation was employed to validate the performance and the feasibility of the proposed design.
Introduction
Due to the constraint size of the catheter, its limited space, and challenges to address strong electromagnetic coupling among coil elements, the conventional catheter RF coils usually have only one channel and cannot be used for parallel imaging 1-3. In this work, we propose a unique miniaturized 4-channel radio-frequency coil array to acquire high resolution endovascular images or accelerated imaging with parallel imaging. The electromagnetic decoupling issue among the 4 coil elements is addressed by using a unique geometric layout which does not require any decoupling circuits, providing a practical method for the miniature catheter coil array design. The 4-channel catheter coil array design possesses sufficient decoupling performance among all 4 resonant elements and shows the endovascular imaging potential in accelerated imaging and improved detection sensitivity as a result of its proximity to the imaging target. The design was validated through numerical simulation at 3T.Methods
The proposed catheter-based RF coil designed on a 3-dimensional plane is shown in Fig.1. The design is a quadruple of four intrinsically decoupled rectangular shaped coils with two of the quadruple having an 8-shaped coil with a jumper at the junction. The coil design was made very much precise as the choice of usage is intuitive and it should be designed to fit in specific vascular tubes. The proposed coils are designed to fit a blood vessel with 2 cm outer diameter and 1.6 cm inner diameter. The coils are made of very thin copper tape of 0.2 mm width. The electric parameters and the physical dimension of the design are depicted in the caption of Fig.1. The rectangular-shaped coil and the 8-shaped coil are stacked together with 2 mm gap from each edge as shown in Fig 1. All the 4 coils are designed without any intersection between them. Numerical simulations and analysis of the integrated coil system were conducted using full wave electromagnetic analysis. Tuning capacitors (Cf) and matching capacitors (Cm) are used the 4 coils element are operating at 127 MHZ (the Larmor frequency of 3T for proton 1H). Each coil is matched to 50 ohm and excited with 1 W input power. Simulated scattering parameters among all the coils is shown in Fig. 2. The surface current distribution along the RF coils were also observed in Fig. 3 to further indicated how well the 4 coils are decoupled. The transmit B1 field distribution normalized to the accepted input power in the XY (transversal) plane through the center of the RF coils (see Fig. 4) is also illustrated for each channel and also for all 4 channels simultaneously.Results
The catheter was implemented at 3T frequency and characterized using simulated results. The simulated scattering parameters versus frequency in Fig. 2, shows excellent matching at the input of each coil and strong decoupling among all of them. The matching value at the input port of all the 4 coils range from -38 dB to -35 dB while very low coupling value are obtained between all 4 coils ranging from -80 dB to -20 dB at 127 MHz. The simulated current density distribution of the catheter RF coils at the Larmor frequency are illustrated in Fig. 3. The distribution obtained, where only one coil is exited at a time is characteristic of strong decoupling performance within the 4-channel RF coils. The residual current in the passive coils is very negligible. The simulated transmit B1 field map obtained from individual element in Fig. 4, shows selective image coverage within the vessels which is suitable for interventional vascular applications. The combined transmit B1 field show strong constructive interference of the electromagnetic field covering larger field of view.Conclusion
A catheter-based 4-channel RF coil array system with intrinsic decoupling for endovascular MR imaging and spectroscopy was designed and investigated for 3T. The proposed design does not require extra decoupling circuit and therefore making miniature multichannel catheter RF coil design practical. The scattering parameters and B1 field distributions were analyzed by the simulation, which explains the importance in interventional vascular applications. The design and the structure of the 4-channel catheter-based RF coil can be further optimized for high resolution imaging and can support additional channel such as dipole aligned in the z-direction to further increase the field efficiency and parallel imaging performance.Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the NIH under a BRP grant U01 EB023829 and by the State University of New York (SUNY) under SUNY Empire Innovation Professorship Award.
References
1. Zhang X, Martin A, Jordan C, Lillaney P, Losey A, Pang Y, Hu J, Wilson M, Cooke D, Hetts SW. Design of catheter radio frequency coils using coaxial transmission line resonators for interventional neurovascular MR imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Apr;7(2):187-194. doi: 10.21037/qims.2016.12.05. PMID: 28516044; PMCID: PMC5418149.
2. Martin AJ, McLoughlin RF, Chu KC, Barberi EA, Rutt BK. An expandable intravenous RF coil for arterial wall imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998 Jan-Feb;8(1):226-34. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880080138. PMID: 9500285.
3. Settecase F, Hetts SW, Martin AJ, Roberts TP, Bernhardt AF, Evans L, Malba V, Saeed M, Arenson RL, Kucharzyk W, Wilson MW. RF Heating of MRI-Assisted Catheter Steering Coils for Interventional MRI. Acad Radiol. 2011 Mar;18(3):277-85. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2010.09.012. Epub 2010 Nov 13. PMID: 21075019; PMCID: PMC3034801.
Figures
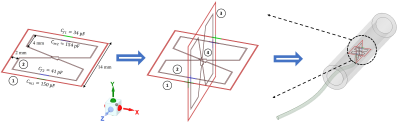
Fig. 1. The design of 3-dimensional catheter coil inside a vessel within a vascular phantom.
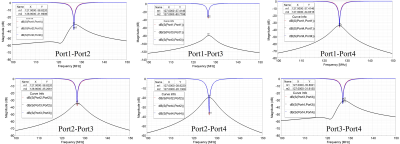
Fig. 2. Simulated scattering parameters of the catheter RF coils showing excellent input impedance matching and good isolation among all 4 channels
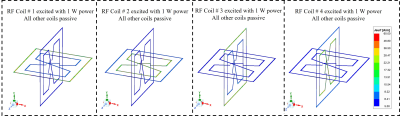
Fig. 3. Simulated surface current distribution obtained along the catheter RF coils at 127 MHz (3T) with one coil excited at a time.
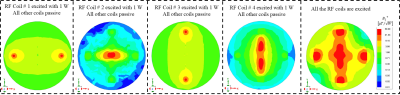
Fig. 4. Simulated transmit B1 field distribution normalized to the accepted input power in the XY (transversal) plane through the center of the catheter RF coils at 127 MHz (3T).