4351
A deep learning-based liver tumor segmentation algorithm in enhanced multi–phase MRI images
Meng Dou1,2, Ying Zhao 3, Tao Lin3, Yu Yao1,2, and Ailian Liu3
1Chengdu institute of computer application, Chinese academy of sciences, Chengdu, China, 2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 3Department of Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
1Chengdu institute of computer application, Chinese academy of sciences, Chengdu, China, 2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 3Department of Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence
In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based liver tumor segmentation algorithm in enhanced multi-phase MRI images. The experimental results show that the proposed method can segment liver and tumor in enhanced multi-phase MRI images with a smaller resource occupation, and outperforms the comparison method.Synopsis
Enhanced multi-phase MRI images have great value for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) and liver tumor segmentation is also significant as it can be used as the basis for related medical applications. In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based liver tumor segmentation algorithm in enhanced multi-phase MRI images. The experimental results show that the proposed method can segment liver and tumor in enhanced multi-phase MRI images with a smaller resource occupation, and outperforms the comparison method.Introduction
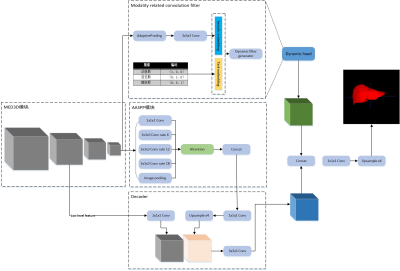
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has great reference value for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver tumor segmentation from enhanced multi-phase MRI images is also significant as it can be used as the basis for related medical applications. We propose a deep learning-based liver tumor segmentation algorithm in enhanced multi-MRI images. In the encoding stage, the 3D ResNet is used as the encoder and initialized with pre-trained parameters. In the decoding stage, the Attention Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling module (AASPP)module is used to extract multi-scale information. Finally, we propose a novel module named modality-related convolution module (MRC) to model the modality information. The experimental results show that the proposed method can segment the liver and tumor in enhanced multi-phase MRI images and outperforms the comparison method.Materials and Methods
The experimental data were all retrospectively collected from the Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, using GE magnetic resonance equipment. First, a junior radiologist (3 years of experience in abdominal MRI diagnosis) manually annotates the liver and tumor, and then a senior radiologist (10 years of experience in abdominal MRI diagnosis) performed verification and correction. The dataset contains three phases of MRI images of 40 patients with HCC: Arterial phase, Venous phase, Delay phase. During training, 40 samples are divided into training cohort (30 cases), Validation cohort (4 cases), and test cohort (6 cases). All training data is resampled to [1mm,1mm,1mm]. At the same time, in order to reduce the over-fitting phenomenon, the training set is augmented by Random affine, random rotation, and random elastic deformation.In this paper, we proposed a deep learning-based liver tumor segmentation algorithm for enhanced multi-phase MRI images. This model followed the encoder-decoder structure. In the encoding stage, the 3D ResNet was used to extract features and initiated with parameters. In the decoding stage, we proposed the 3D Attention Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling module (AASPP) to extract the image context information of different scale objects using 3D dilated convolution and the attention mechanism. Finally, the phase image information is encoded, concated with the semantic coding extracted by the 3D ResNet network, and then used as a convolution kernel parameter. This 3D convolution layer was used to calculate the feature map output by 3D ResNet to obtain the image[1]encoding information, which is then concated with the decoder output for final liver segmentation. The network structure is shown in Figure 1.
Results
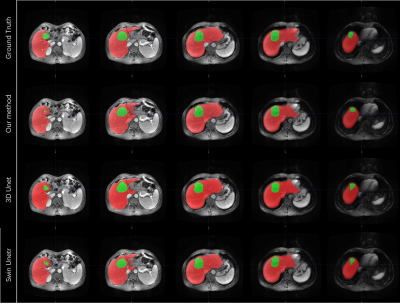
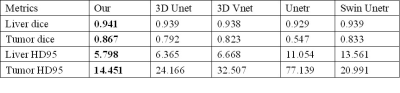
In this part, we compare our proposed method with other methods. The average surface distance and volumetric dice were introduced to measure the segmentation performance. It can be observed in Table 1 that our method has achieved the best results on the two evaluation indexes of volume DSC and average surface distance, reaching 0.941, 5.798mm and 0.867, 14.451 for liver and tumor. The results in Figure 2 also verify the advantages of our method.Conclusion
Enhanced multi-phase MRI images has great reference value for the diagnosis and prognosis of HCC. Liver segmentation from multi-phase enhanced MRI images can be used as the basis for other medical applications, such as liver cancer diagnosis, treatment planning, and image-guided surgery. In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based liver tumor segmentation algorithm in enhanced multi-phase MRI images. Experimental results show that the proposed method can better segment the liver and tumor in multi-phase MRI images.Acknowledgements
I would like to extend my deep gratitude to all those who have offered me practical, cordial, and selfless support in writingthis abstract. Firstly, I am extremely grateful to my supervisor, Prof. Yaoyu, and Prof. Liu Ailian. They guide me, influence me, and helpme in the process of writing this abstract.Secondly, I am much obliged to all my colleagues and their selfless help.References
1. Chen, S., Ma, K. & Zheng, Y. Med3D: Transfer Learning for 3D Medical Image Analysis. arXiv:1904.00625 [cs] (2019).
2. Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F. & Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. in Computer Vision – ECCV 2018 (eds. Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C. & Weiss, Y.) vol. 11211 833–851 (Springer International Publishing, 2018)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4351