4329
Assessment of Cardiac TCA Cycle Activity with Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Acetyl-L-Carnitine1Advanced Imaging Research Center, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, TX, United States, 2Chemistry, California State University, Fullerton, Fullerton, CA, United States, 3Chemistry and Biochemistry, Loyola University Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States, 4Department of Radiology, UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, TX, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Hyperpolarized MR (Non-Gas), Metabolism
Hyperpolarized [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine was developed as a probe to investigate cardiac TCA cycle activity in vivo. [5-13C]Glutamate, which is produced via TCA cycle intermediate a-ketoglutarate, was successfully observed in rat heart under both fasting and fed conditions. Importantly, although pyruvate dehydrogenase activity is decreased in the fasted state, [5-13C]glutamate remained observable at appreciable levels, suggesting that [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine provides complementary information relative to standard assessments of pyruvate oxidation with hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate. In turn, this novel probe may facilitate comprehensive metabolic analyses of acetyl-CoA uptake by the TCA cycle for various cardiac applications.INTRODUCTION
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity regulates glucose oxidation and has been used as a metabolic biomarker for TCA cycle activity in the heart1. Hyperpolarized (HP) [1-13C]pyruvate has been successfully employed in various cardiac applications, because the probe can detect altered glucose oxidation by measuring the PDH-mediated production of HP [13C]bicarbonate. Due to the direct connection to the mitochondrial activity, production of HP [13C]bicarbonate is often considered as a surrogate marker of mitochondrial integrity or viable myocardium. However, PDH activity and TCA cycle metabolism can be decoupled since acetyl-CoA can be formed from other nutrients such as fatty acids and ketones. Indeed, PDH activity is lowered in conditions like fasting2 and diabetes,3 while the TCA cycle activity may or may not be affected in the similar fashion4. [13C]Acetyl-L-carnitine represents a potential hyperpolarized probe that would provide an alternative insight into the TCA cycle metabolism, as acetyl-L-carnitine is essential for fatty acid oxidation and serves as acetyl-CoA buffer in cardiomyocyte5. When needed, acetyl-carnitine also acts as substrate for energy production. During periods of fasting, PDH activity is lowered drastically, while fatty acids are the main energy source for the liver, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle6. Importantly, acetyl-L-carnitine can be converted into acetyl-CoA and subsequently enter the TCA cycle. In this study, we developed [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine as a new hyperpolarization probe that directly assesses in vivo TCA cycle activity through [5-13C]glutamate, a downstream product of the TCA cycle.MATERIALS and METHODS
[1-13C]Acetyl-L-carnitine hydrochloride was prepared in 28% yield by dissolving L-carnitine hydrochloride in [1-13C]acetic acid and then treating the solution with [1-13C]acetyl chloride. For dynamic nuclear polarization, 2.9 M of [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine was prepared in water/glycerol (2/5, w/w) with 15 mM OX063 and polarized using a GE SPINlab. In vivo and in vitro MR spectroscopy experiments were performed at a clinical 3T MR scanner (GE Discovery 750w). The liquid-state polarization levels at the time of dissolution and longitudinal relaxation times (T1) of the hyperpolarized substrates were measured from in vitro experiments (n = 2). Healthy male Wistar rats (286-520g) with fed (n = 6) and overnight fasted (n = 3) conditions were prepared for in vivo experiment. Two of the rats were scanned with both conditions with two days apart between the scans. Anesthetized rats were placed in a 13C/1H dual-tuned birdcage rat coil. 50-mM hyperpolarized [1-13C]acetyl-carnitine was injected intravenously as a bolus (0.625 mmol/kg body weight, up to 4.0 mL, injection rate = 0.25 mL/s), immediately followed by a dynamic 13C pulse-and-acquire scan (10o hard pulse excitation, repetition time = 3 sec, scan time = 4 min). [5-13C]Glutamate and [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine signals are quantified by integrating the time-averaged spectra (0-90s) of the corresponding peaks.RESULTS and DISCUSSION
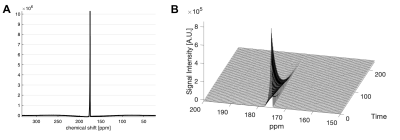
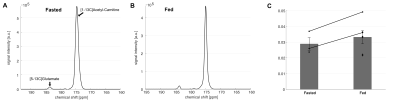
The liquid state polarization level was estimated as 27.4% at the time of dissolution, and the in vitro T1 was 41.4 s (Figure 1). No impurities were observed. In vivo application of HP [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine in rat hearts showed [5-13C]glutamate peak at 183.4 ppm as well as the [1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine peak at 174.6 ppm (Figure 2). The metabolite ratio of [5-13C]glutamate-to-[1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine, measured from the area under the curves, was 0.033 ± 0.010 and 0.029 ± 0.007 for fed and fasted conditions, respectively. Although the nutritional effects viewed by the simple ratio metric were insignificant, the overall trend showed that larger glutamate production was found in the fed group. In particular, the two rats that were scanned under both conditions showed larger [5-13C]glutamate-to-[1-13C]acetyl-L-carnitine ratios. As acetyl-L-carnitine is converted to acetyl-CoA (or vice versa) by reversible carnitine acetyltransferase (CAT), this large and highly flexible metabolite pool buffers the cycling of acetyl-CoA and isotope exchange effect between acetyl-L-carnitine and acetyl-CoA may need to be considered. For instance, myocardial acetyl-L-carnitine levels could reach more than 20-fold higher than acetyl-CoA levels and are doubled with carbohydrate diet as compared to those with high-fat diet5, 7-9.Acknowledgements
National Institute of Health: R01NS107409, R21EB030765, P30DK127984, P41EB015908, SC1GM127213; Department of Defense: W81XWH2210485 The Welch Foundation: I-2009-20190330;References
1. Schroeder, M.A. et al. In vivo assessment of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux in the heart using hyperpolarized carbon-13 magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105, 12051-12056 (2008).
2. Jeoung, N.H. et al. Role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoenzyme 4 (PDHK4) in glucose homoeostasis during starvation. Biochem J 397, 417-425 (2006).
3. Andersen, L.W. et al. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Activity Is Decreased in Emergency Department Patients With Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Acad Emerg Med 23, 685-689 (2016).
4. Satapati, S. et al. Elevated TCA cycle function in the pathology of diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance and fatty liver. J Lipid Res 53, 1080-1092 (2012).
5. Pearson, D.J. & Tubbs, P.K. Carnitine and derivatives in rat tissues. Biochem J 105, 953-963 (1967).
6. Longo, N., Amat di San Filippo, C. & Pasquali, M. Disorders of carnitine transport and the carnitine cycle. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 142c, 77-85 (2006).
7. Renstrom, B., Liedtke, A.J. & Nellis, S.H. Mechanisms of substrate preference for oxidative metabolism during early myocardial reperfusion. Am J Physiol 259, H317-323 (1990).
8. Pellerin, L. & Magistretti, P.J. Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: a mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91, 10625-10629 (1994).
9. Schroeder, M.A. et al. The cycling of acetyl-coenzyme A through acetylcarnitine buffers cardiac substrate supply: a hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 5, 201-209 (2012).
Figures