4291
Computed DWI with 2nd Order motion Compensated DWI for Diagnosis of the Myocardial Infarction without Contrast Agents1Department of Radiology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shenzhen, Ltd., Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Heart, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Computed DWI
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) remains challenge since it’s still difficult to quantify the infarction area, and to assess prognosis. Cardiac DWI could provide essential information for diagnosis of MI without exogenous contrast agents. Higher b-value DWI could improve the detection rate of myocardial infarction, but it is challenging for image acquisition in cardiac DWI due to low SNR and motion. The present study aimed to combine the 2nd order motion compensated diffusion with computed DWI to overcome these challenges. Results of this study indicates the combination is potentially a promising and valuable non-invasive method in detection of MI.Introduction
Diffusion MRI provides unique information on the structure, organization, and integrity of the myocardium without the need for exogenous contrast agents1-2. Higher b-values in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is increasingly used to detect malignancies, it should be useful for improved the accuracy and efficiency of diffusion MRI in the myocardial infarction (MI). However, large b-values can cause severe image signal loss and the use of longer echo times (TE) reduce the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Computed DWI (cDWI) was used to overcome these challenges3-5. Diffusion MRI in the heart, however, has proven technically challenging because of the intrinsic non-rigid deformation during the cardiac cycle, displacement of the myocardium due to respiratory motion, B0 inhomogeneity, and short transverse relaxation times. Motion compensated diffusion was used which makes the diffusion imaging to decreases the sensitivity to cardiac motion and improved the robustness of diffusion MRI in the myocardium 6-7. High b value should be useful to improve the cardiac disease diagnosis. However, even with motion compensated diffusion, motion of cardiac and respiratory makes the high b value is impossible and instable, there is still be challenged to get high b values (b > 600s/mm2) diffusion images for cardiac diffusion. In this study, we investigated to combine the 2nd order motion compensated diffusion with computed DWI to overcome these challenges.Methods
Fig 1 shows the proposed solution in the present study. To decrease the motion impact on cardiac DWI images, the 2nd order motion compensated diffusion (mcDWI) was used for image acquisition. Computed diffusion (cDWI) was implemented to generate higher b-value DWI images. To our knowledge, no published studies have combined mcDWI and cDWI in cardiac imaging. We called the combination of these two techniques as m2cDWI, and obtained the high b-value cardiac DWI images for the first time. To evaluate the feasibility of m2cDWI, we compared the m2cDWI images and origin DWI images with late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) imaging. All scans were acquired on a Philips 3.0T Ingenia CX system (Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherland) with a 32-ch torso and spine coil. Detailed scan parameters were summarized in Table 1.Results
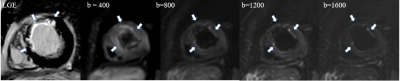
This research has been approved by the local IRB. Three patients with myocardial infarction’s data was collected, retrospectively computed DWI was generated with our proposed solution. In the Fig 2, the subendocardial enhancement seen in LGE might be more clearly shown in the m2cDWI images (b = 800, b=1200, b = 1600) than the origin DWI images (b = 400). It showed that the m2cDWI images seemed to be more sensitive to the myocardial infarction.Discussion
In the present study, a novel scheme m2cDWI was proposed to obtain higher b value cardiac diffusion by combining mcDWI and cDWI, which was more sensitive to myocardial infarction. It could also have the potential improve the detection rate of other microscopic structural remodeling without exogenous contrast agents.Conclusion
The proposed method m2cDWI obtained the high b-value cardiac DWI images for the first time. The pilot study showed that the m2cDWI could obtain higher b-value cardiac DWI images and improve the detection rate of myocardial infarction without exogenous contrast agents.Acknowledgements
NoReferences
1. Timothy GR, Marcel PJ, Himanshu B and David ES, Diffusion MRI in the heart, NBM 2017;30:e3426.
2. Sonia NV, Andrew S, Pedro F, Zohya K, Dudley P, David F, Cardiac Diffusion: Technique and Practical Applications. J. MAGN. RESON. IMAGING 2020;52(2):348-368;
3. Matthew DB, Martin OL, David JC, Dow MK, Computed Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging May Improve Tumor Detection, Radiology 2011;261: 573-581.
4. Toru K, Yuko K, Fuminari K, et. al., Introduction to the Technical Aspects of Computed Diffusion weighted Imaging for Radiologists, Radio Graphics 2018; 38:1131–1144
5. Yoshiko RU, Tsutomu T, Satoru T, et. al., Computed Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer: Basics, Advantages, Cautions, and Future Prospects,KJR, 2018;19(5):832-837.
6. Christian TS, Constantin VD, Martin G, David A and Sebastian K, Second-Order Motion-Compensated Spin Echo Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Human Heart, Magn Reson Med 2016;75:1669–1676.
7. Samo L,Filip S, Erica D, et. al, Motion‐compensated b‐tensor encoding for in vivo cardiac diffusion‐weighted imaging, NBM 2020;33:e4213.
Figures