4280
Diagnostic performance of the vesical imaging-reporting and data system for detecting muscle-invasive bladder cancer based on tumor locations.1Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, Shenzhen, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Tumor
The VI-RADS criterion was reported to have limitations, particularly for tumors location. So we evaluated the diagnostic performance of Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) scoring and diagnostic accuracies based on tumor locations. VI-RADS had superior diagnostic performance for detecting MI, especially in tumors located at the bladder lateral, posterior walls and ureteric orifices.Introduction
The VI-RADS criterion was reported to have limitations, particularly for tumors location. So we evaluated the diagnostic performance of Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) scoring and diagnostic accuracies based on tumor locations.Methods
This retrospective study included 375 consecutive patients who underwent mp-MRI before transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) from August 2015 through August 2021. Two blinded radiologists reviewed and scored all MRI examinations according to VI-RADS based on tumor locations. Cut-off values ≥3 indicated muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). The interobserver agreement was assessed by kappa (κ) statistics. ROC analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance for MIBC.Results
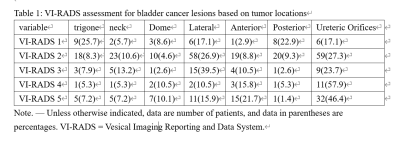
252 with non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer and 123 with MIBC. At consensus reading, 35 (9.3%) case was scored as VI-RADS 1, 216 cases (57.6%) were scored as VI-RADS 2, 38 (10.1%) were scored as VI-RADS 3, 19 (5.1%) were scored as VI-RADS 4, and 69 (18.4%) were scored as VI-RADS 5. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of VI-RADS in the detection of MIBCa was 0.86. The diagnostic accuracy/sensitivity/specificity of VI-RADS scores were 86.1/75.0/89.3%, 81.8/100/0%, 69.2/94.7/84.4%, 84.0/89.6/88.0%, 81.8/80.0/80.0%, 100/100/100%, 84.9/889.1/87.2% located on the bladder trigone, neck, dome, lateral, anterior, posterior walls and ureteric orifices. Therefore, the diagnostic accuracy of VI-RADS was significantly higher for tumors located on the bladder lateral, posterior walls and ureteric orifices.Conclusion
VI-RADS had superior diagnostic performance for detecting MI, especially in tumors located at the bladder lateral, posterior walls and ureteric orifices. Keywords: VI-RADS; Muscle-invasive bladder cancer; Tumor locationsAcknowledgements
noReferences
1.Wang H, Luo C, Zhang F, et al. Multiparametric MRI for Bladder Cancer: Validation of VI-RADS for the Detection of Detrusor Muscle Invasion. Radiology 2019;291(3):668–674.
2. Del Giudice F, Barchetti G, De Berardinis E, et al. Prospective Assessment of Vesical Imaging Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) and Its Clinical Impact on the Management of High-risk Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Patients Candidate for Repeated Transurethral Resection. Eur Urol 2020;77(1):101–109.
3. Ueno Y, Tamada T, Takeuchi M, et al. VI-RADS: Multiinstitutional Multireader Diagnostic Accuracy and Interobserver Agreement Study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2021;216(5):1257–1266.
4. Metwally MI, Zeed NA, Hamed EM, et al. Te validity, reliability, and reviewer acceptance of VI-RADS in assessing muscle invasion by bladder cancer: a multicenter prospective study. Eur Radiol 2021;31(9):6949–6961.