4267
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of solitary pulmonary lesions: initial study with gradient-and-spin echo (GRASE)
Siqiang Lv1,2, Zhanguo Sun3, and Xiuzheng Yue4
1Jining Medical University, Jining, China, 2Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, jining, China, 3Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1Jining Medical University, Jining, China, 2Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, jining, China, 3Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Lung, Data Acquisition, SPLs
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM) could obtain parameters of pure water molecule diffusion and microcirculatory perfusion-related diffusion and more accurately reflects the complexity of the microstructure of the tumor tissues. Gradient-and-spin echo (GRASE), incorporating the gradient echo and spin echo techniques, is a fast-imaging sequence with potential for improved IVIM examinations. The aim of the study was to evaluate the feasibility and image quality of the GRASE-IVIM sequence in evaluating solitary pulmonary lesions (SPLs) by comparing with the EPI-IVIM and TSE-IVIM sequences. Our data showed GRASE-IVIM sequence could be a fast and stable alternative technique to evaluate the SPLs.Introduction
IVIM of solitary pulmonary lesions (SPLs) with EPI or TSE has been reported to have its own advantages and disadvantages1. While EPI-IVIM could shorten the scan time, the image quality of which tends to be degenerated by the presence of artifacts, especially in the lung. Although the image quality could be improved by the TSE-IVIM, its acquisition times will be prolonged by using multiple radio frequency (RF) refocusing pulses. Gradient-and-spin echo (GRASE) imaging, incorporating the gradient echo and spin echo techniques2, is another fast-imaging sequence with the potential for improved IVIM examinations. This technique was less prone to magnetic field inhomogeneity compared with the EPI. The scanning time could be shorten compared with TSE. Therefore, we hypothesized that the GRASE-IVIM sequence might provide fewer motion artifacts than EPI-IVIM and a shorter acquisition time than TSE-IVIM in the examination of SPLs. Thus, the present study aimed to evaluate the clinical feasibility and image quality of the GRASE-IVIM sequence in evaluating SPLs by comparing them with TSE-IVIM and EPI-IVIM sequences.Methods
Data acquisitionAll MRI protocols were performed on Philips Ingenia CX 3.0 MRI scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) with a 16-channel body phase array coil. 54 patients (mean age, 58.95 ± 10.38 years) with SPLs were recruited between February 2021 to March 2022, and 54 SPLs were analyzed (38 malignant and 4 benign). The study was approved by the IRB of the Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, and written informed consent was obtained from all the patients. The scan protocol consisted of routine sequences (T1WI, T2WI) and the IVIM-DWI with TSE, GRASE, and EPI techniques, respectively. The sequence parameters for the IVIM-DWI protocol were listed in Table 1.
Data analysis
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and image distortion ratio (DR) of TSE-, GRASE-, and EPI-IVIM were calculated. To calculate the SNR and CNR, a grayscale map with a b-value of 800 s/mm2 was used. Three circular regions of interest (ROIs) were placed in the lesion, the lung, and the erector spinae muscle by two independent radiologists with 5 years of experience, respectively. Regarding the evaluation of distortion, T2WI and IVIM images were semiautomatically fused with a fusion software on the Intellispace portal (Version 10.0, Philips Healthcare) in Figure1. The DR was used to quantitatively compare the image distortions of lesions of three different IVIM sequences.
To calculate the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and IVIM-derived Parameters, ROIs were manually drawn on the maximum cross-sections of lesions across three consecutive slices on the grayscale map with a b-value of 800 s/mm2 by two independent radiologists. It referred to T2WI images, avoiding large blood vessels, cystic changes, and necrotic components. ROIs were automatically duplicated and copied to pseudo-color maps of ADC and IVIM-derived parameters (true diffusion coefficient [D], pseudo-diffusion coefficient [D*], perfusion fraction [f]) by the workstation.
The intra- and interobserver agreements were assessed with the interclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Friedman test was used to compare the SNR, CNR, and DR of all sequences. Test-retest reproducibility of ADC and IVIM-derived parameters were evaluated by using the coefficient of variation (CV). The 95% Bland-Altman limits of agreements (LoAs) were used to assess the repeatability of ADC and IVIM parameters derived from all sequences. The p values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. SPSS 25.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, USA) and MedCalc 15.0 (Ostende, Belgium) software were conducted for statistical analysis.
Results
Compared with TSE- and GRASE-IVIM, EPI-IVIM had higher SNR, lower CNR, and higher DR (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in SNR, CNR, and DR between TSE-IVIM and GRASE-IVIM (P>0.05) in Table2 and 3. Bland-Altman analysis showed wide limits of agreement of ADC and IVIM-derived parameters of the three sequences. The reproducibility of TSE-IVIM and GRASE-IVIM parameters of SPLs were excellent for ADC and D, and it was good for ADC and D value in EPI-IVIM in Table4.Discussion and conclusion
GRASE-IVIM could reduce the image distortion and improve the test-retest reproducibility of ADC and D value compared with EPI-IVIM. Although the image quality of GRASE-IVIM was similar to TSE-IVIM, the acquisition time was obviously shorter than that of TSE-IVIM in SPLs imaging. Our data showed GRASE-IVIM sequence could be another fast and stable alternative technique to evaluate the SPLs. Although further analysis should be conducted to consider the value of GRASE-IVIM in a large SPLs cohort.Acknowledgements
This paper is funded by Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Program (202009011151)References
1. Wan Q, Lei Q, Wang P, et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Lung Cancer: Comparison Between Turbo Spin-Echo and Echo-Planar Imaging. Journal of computer assisted tomography 2020;44(3): 334-340.
2. Yoshida M, Nakaura T, Inoue T, et al. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with GRASE sequence at 3.0T: does it improve image quality and acquisition time as compared with 3D TSE? European radiology 2018;28(6): 2436-2443.
Figures
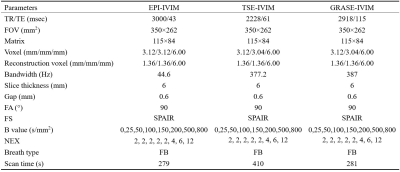
Table1 the
details of parameters and scan time for IVIM-DWI protocols
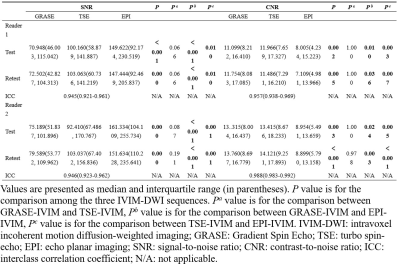
Table2 the results of the Friedman test for SNR and
CNR
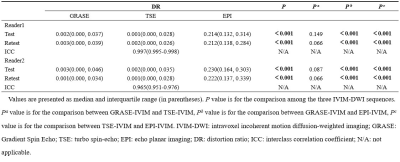
Table3
the results of the Friedman test for DR
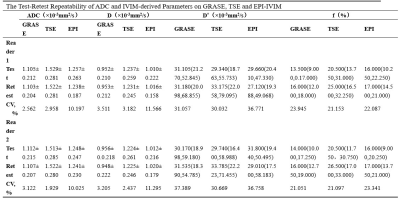
Table4
test-retest repeatability of ADC and IVIM-derived parameters on GRASE-, TSE-,
and EPI-IVIM
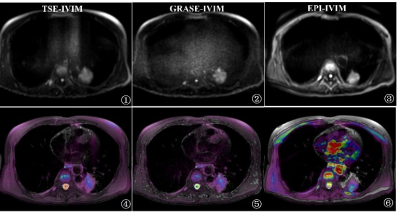
Figure1
the fusion image of T2WI and IVIM-DWI
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4267