4239
Comparing the imaging performance of a three-channel endorectal coil for magnetic resonance imaging at 5T and 3T
Zhiguang Mo1,2, Xiaoping Zhang3, Huageng Liang3, Changjun Tie1,2, Wen Xiao3, Qi Cao3, Chenchen Liu3, Xiaoliang Zhang4, and Ye Li1,2
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, NY, United States., Buffalo, NY, United Stats, Buffalo, NY, United States
1Paul C. Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 2Key Laboratory for Magnetic Resonance and Multimodality Imaging of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen, China, Shenzhen, China, 3Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo, NY, United States., Buffalo, NY, United Stats, Buffalo, NY, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: High-Field MRI, Prostate
We made a three-channel endorectal coil for prostate imaging on the 5T magnetic resonance system and compared the imaging performance of the coils with the same structure on the 5T system and the 3T system. Prostate images at resolution of 0.78 mm × 0.78 mm × 2.5 mm were performed. In vivo prostate study shows that the endorectal coil works on the 5T system shows better image quality compared with the endorectal coil and surface coil array on the 3T system.INTRODUCTION
The endorectal coil (ERC) has been shown to be effective in increasing signal-to-noise (SNR) in the prostate area for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)1,2. Increasing the strength of the magnetic field also works since the signal intensity is proportional to the static magnetic field. In previous work, we have made a three-channel ERC for a 3T magnetic resonance (MR) system3. In this study, we made an ERC essentially with the same structure as the former for prostate on the 5T system. A body coil was employed as the transmitter. We aimed to compare the performance of the ERC on 5T and 3T systems. In vivo studies were performed on a beagle with prostate cancer. As a comparison, the same imaging experiments were performed on the 3T system by a 12-channel surface coil array.METHOD
The coil was formed by three loops wound side by side on a PVC structure (figure 1). The structural part is a cylinder with a diameter of 25 mm and a length of 5 cm, a part of which was cut off and formed a D-shaped section. The loops were decoupled by overlapping, as shown in figure 2. The coupling coefficients and reflection coefficients of the endorectal coils were tuned below -10 dB (figure 2). Of the in vivo studies, condoms were put on the endorectal coils and inserted into the rectum of the beagle. A fast- spin-echo (FSE) sequence with TR = 3154 ms, TE = 132.66 ms, FOV = 200 × 200 mm2, matrix = 256 × 256, slice thickness = 2.5 mm, and NEX =1 was performed on 3T MRI scanner. (uMR 790, Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China). And the parameters were: TR = 3450 ms, TE = 118.4 ms, FOV = 200 × 200 mm2, matrix = 256 × 256, slice thickness = 2.5 mm, and NEX =1, when performed on 5T system (uMR Jupiter, Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China). As a comparison, a 12-channel surface coil array (Body Array Coil, Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China) was covered on the abdomen of the beagle for imaging.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Of the in vivo study, anatomical images were acquired with endorectal coil and surface coil (figure 4). The bladder, prostate and tumor can be identified on all imaging. The image obtained by the ERC on 5T system is clearer and shows richer details than that obtained with surface coil as well as ERC on the 3T system. The coupling coefficients and reflection coefficients of coils are generally considered to be important factors affecting the image quality. The S-parameters of the ERC works on the 3T system (-15 dB) were much better than the ERC works on 5T system (-10 dB). Although the latter shows advantages in this study, we believe there is still room for improvement.CONCLUSION
In this work, we made a three-channel endorectal coil and compared the imaging performance of the coil of this configuration on 5T and 3T systems. A surface coil array was employed as a comparison. Of the in vivo in a beagle, the coil works on the 5T system shows better image quality compared with the endorectal coil and surface coil array on the 3T system.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Key Scientific Instrument Development Project (Grant No. 81927807); National Key Research and Development Program of China, 2021YFE0204400; the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, XDB25000000; National Natural Science Foundation of China, U22A20344; Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS No. Y2021098; Key Laboratory Project of Guangdong Province, 2020B1212060051; Shenzhen city grant, RCYX20200714114735123.References
1.Rata, Mihaela, et al. "Endoluminal MR‐guided ultrasonic applicator embedding cylindrical phased‐array transducers and opposed‐solenoid detection coil." Magnetic resonance in medicine 73.1 (2015): 417-426.
2.Arteaga de Castro, C. S., et al. "Improving SNR and B1 transmit field for an endorectal coil in 7 T MRI and MRS of prostate cancer." Magnetic resonance in medicine 68.1 (2012): 311-318.
3.Mo Z, et al. A novel three-channel endorectal coil for prostate magnetic resonance imaging at 3T. Proc. 31th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, online, 2022.
Figures
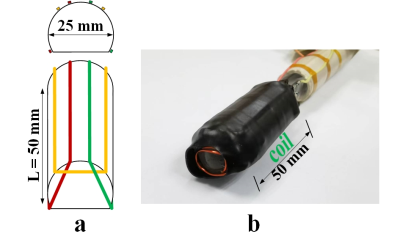
Fig.1.
The
schematic drawing a) and the endorectal coil b) are shown.
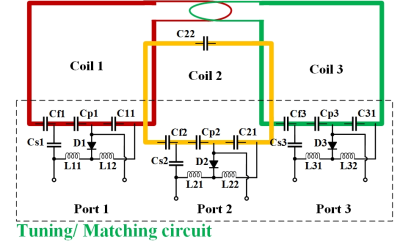
Fig.2. The circuit diagram is shown. All channels
were decoupled by overlapping.
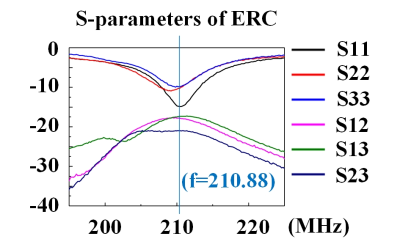
Fig.3. S-parameters
were obtained by placing the ERC-3C and ERC-2C in the rectum of the subject. The coupling coefficients and reflection
coefficients are lower than -10 dB.

Fig.4. Cross-sectional
view of the MRIs of the prostate of a beagle. Anatomical
images obtained at 0.78 mm × 0.78 mm × 2.5 mm were achieved using the endorectal
coil on 3T (a), 5T (b) system and surface coil array on 3T (c) system,
respectively.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4239