4234
A wireless unilateral Rx-only RF coil for dedicated MRI of a human breast at 1.5 T
Aleksander Fedotov1, Pavel Tikhonov1, Georgiy Solomakha1, Victor Puchnin1, Alena Shchelokova1, and Anna Hurshkainen1
1Department of Physics, ITMO University, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation
1Department of Physics, ITMO University, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation
Synopsis
Keywords: High-Field MRI, RF Arrays & Systems
Wireless dedicated radiofrequency coils have recently proven to be a good alternative to conventional cable-connected coils due to compatibility with the scanners of different vendors. Due to significant increase of B1+ with respect to body coil manual calibration procedure needed often for operation of wireless coils.The goal of this work is to develop the first Rx-only wireless coil for dedicated breast MRI to overcome the aforementioned drawback. For that the passive detuning structure inserted to wireless Helmholtz resonator was designed and studied.Introduction
Wireless radiofrequency (RF) coils have recently proven to be a good alternative to conventional cable-connected coils in clinical applications [1,2,3]. The operational principle of such coils is based on inductive electromagnetic coupling of transmit birdcage coil body coil of MRI scanner. The main advantage of such operation is ability of using wireless coils with MRI scanners of different vendors. Inductively coupled wireless coils are usually considered as transceiver coils since their resonant operation is ensured both during transmission and reception. Due to significant increase of B1+ with respect to birdcage (BC) the reference voltage required for the same flip angle achievement is drastically lower. Therefore manual reference voltage calibration procedure accompanies often operation of wireless coils. The goal of this work is to develop the first Rx-only wireless coil for breast MRI to overcome the aforementioned drawback. For that, the wireless unilateral breast coil based on Helmholtz resonator equipped with the passive detuning circuit was developed and evaluated numerically.Methods
Helmholtz resonator consisting of two coils each having one turn was chosen as a volume wireless coil for the human breast. The main view of the coil is depicted in Figure 1. The overall dimensions of the resonator are 157x152x50 mm. Sizewere chosen according to the averaged dimensions of the targeted ROI – woman breast. To achieve a main goal of creating a Rx-only coil, the passive detuning circuit, inserted in the gap of the resonator conductor, was considered. Circuit diagram (?) of the detuning circuit is depicted in Figure 2. Detuned citcuit consists of an inducatance and capacitance that forms anresonant circuit with frequencyclose to the frequency of the Helmholtz coil tuning and a pair of anti-parallel pin-diodes inserted in series with the inductance of LC-circuit. To simulate the coil operation both at transmit and receive mode two different equivalent circuits of anti-parallel pin-diodes were considered. In receive, or low current mode it has a high reactive resistance and can be described as a 1 pF capacitor with … resistor in parallel. In transmit, or high current mode it can be considered as a 1 ohm resistor. To simulate the coil CST Studio 2021 software (Dassault Systèmes) was used. A birdcage coil driven in quadrature mode by two discrete ports was considered in simulations as a transmit body coil. A homogeneous phantom with averaged properties of human body (epsilon = 40, conductivity = 0.35 S/m) was used in simulations. To tune the Helmholtz coil to the Larmor frequency of 63.8 MHz the 3.3 pF capacitor was inserted in series to the conductor of the coil. A set of four different simulations was performed. In order to study operation of the wireless coil in transmit mode a simulation of a BC with inductively coupled resonator assembled with detuning circuit in high-current mode was performed. As a reference, a BC without resonator also was simulated. To study the coil in receive mode a simulation of a BC with inductively coupled resonator assembled with detuning circuit in low-current mode was performed. As a reference, a BC with resonator without detuning circuit was simulated.Results
In Figures 3 and 4 show magnetic numerically simulated magnetic field distributions at central transverse plane of the wireless coil both in transmit and receive mode respectively are depicted. These maps illustrate the effective detuning capabilities of the considered circuit. At both transmit and receive modes magnetic field values in the targeted ROI are no more than 10% differ with respect to reference cases.Discussion
The simulation results shown that the designed wireless coil in transmit mode provides the maximum (or its mean value?) of B1+ no more than 8% higher than BC coil alone. Additionally, in receive mode the considered wireless coil provides B1- comparable (no more than 10% lower) with the reference case of the wireless coil without detuning circuit. The acquired results shown that considered passive detuning circuit could be effectively used for Rx-only wireless coil development.Сonclusion
Wireless RF coils are actively developed nowadays towards different dedicated medical applications. Due to the possibility of using these coils with MRI scanners of different manufacturers it could be a good alternative to wire-connected coils. By this study we develop the direction of applicability of such coils for clinical studies by simplification of calibration procedure which is usually challenging while using wireless inductively coupled coils.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by state assignment No. FSER-2022-0010 within the framework of the national project "Science and Universities".References
1. Shchelokova, Alena V., et al. "Volumetric wireless coil based on periodically coupled split‐loop resonators for clinical wrist imaging." Magnetic resonance in medicine 80.4 (2018): 1726-1737.
2. Shchelokova, Alena, et al. "Ceramic resonators for targeted clinical magnetic resonance imaging of the breast." Nature communications 11.1 (2020): 1-7.
3. Puchnin, Viktor, et al. "Quadrature transceive wireless coil: Design concept and application for bilateral breast MRI at 1.5 T." Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (2022)
Figures
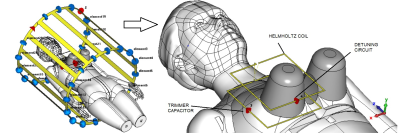
Wireless detunable RF coil for human breast: main view
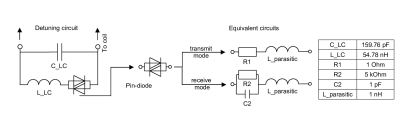
Detuning cirсuit description
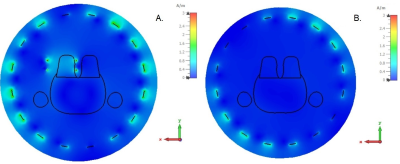
H-field distribution in central transverse plane of the coil: transmit mode (A) and reference (B) (birdcage coil)
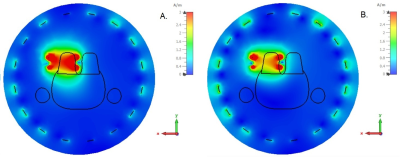
H-field distribution in central transverse plane of the coil: receive mode (A) and reference (B) (birdcage coil + resonator without detuning cirсuit)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4234