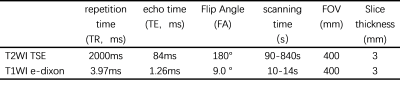4222
Fat Free Muscle Area measurement based on clinical liver MRI workflow to assess sarcopenia1the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Muscle, Fat
Fat free muscle area (FFMA) is an important measurement to evaluate sarcopenia and myosteatosis, and it is associated with poor prognosis in patients with chronic liver and oncologic diseases. FFMA was measured on T2WI-TSE sequence in previous study, which is not in routine MRI workflow, and the scanning time of T2WI-TSE sequence is obviously longer than T1WI edixon sequence, so we develop a method to measure FFMA by T1WI edixon sequence in clinical liver MRI sequence and explore a clinical friendly sarcopenia measurement.Introduction
Sarcopenia and myosteatosis are frequently observed in the elderly population and are associated with poor prognosis in patients with chronic liver and oncologic diseases1-3. The sarcopenia diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of low muscle quantity or quality4. MRI and CT are considered to be gold standards for noninvasive assessment of muscle quantity and mass.5 Due to the drawbacks of CT such as radiation and nephrotoxicity of iodine contrast agent, some studies proposed a method to evaluate sarcopenia based on the measurement of fat free muscle area (FFMA) by magnetic resonance imaging6,7. By determining infiltration of fat into muscle, FFMA accurately assess sarcopenia and show prognostic relevance in patients with proceeded stages of disease. However, FFMA was measured by T2WI TSE without fat saturation in previous studies, which is not a routine clinical sequence. Therefor we developed a method measure FFMA by applying T1WI edixon sequence, which is in the conventional liver MRI workflow, and compared it with previous measurement based on the T2WI TSE sequence.Method
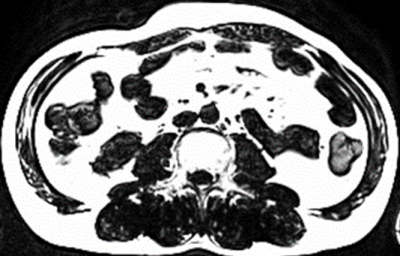
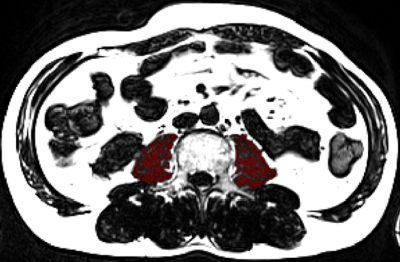
16 patients with fatty liver (F:M=10:6, age 50±1.2) underwent liver MRI examinations on a 3T system (MAGNETOM Vida, Siemens Healthineers). The protocol includes an axial T1WI edixon sequence and T2WI TSE sequence without fat saturation. T2WI TSE and T1WI edixon typical scanning parameters are shown in table1. First, an experienced radiologist carefully delineated the contour of bilateral psoas on the maximum cross-sectional images of lumbar spine three on T2WI TSE and T1WI edixon-fat phase, respectively, and generated the corresponding regions of interest. The total muscle area (TMA) of the psoas muscles was obtained by Itk-snap(www.itksnap.org).Subsequently, both images were converted to binary images based on signal intensity. On T2WI TSE and T1WI edixon-fat phase muscular tissue and adipose tissue are characterized by low and high signal intensity, respectively. Therefore, binarization allowed for separation of lean muscular tissue from intramuscular adipose tissue. Summation of pixels with high signal intensity and multiplication with the corresponding surface area resulted in intramuscular adipose tissue area (ATA), which was subtracted from TMA to obtain FFMA. The algorithm was implemented by scripts in MATLAB software, and the consistency was compared with the previous FFMA measurement results based on T2WI TSE image by Consistency check.Result
The mean value of bilateral psoas FFMA at the maximum cross-sectional area of lumbar spine3 vertebral body measured based on T1WI edixon-fat phase was 217.5mm2 (164.8, 332.5)and that measured based on T2WI TSE sequence was 238.2 mm2 (152.7, 311.3).The intraclass correlation coefficient of the two method was 0.933 (ICC=0.933).Discussion
T1WI edixon sequence is an important sequence for non-invasive screening of fatty liver quantitative detection technology, which can be obtained within one breath hold (about 10-14s). This study developed a new FFMA measurement based on T1WI edixon-fat phase, which enables the measurement of liver fat content and quantitatively evaluate sarcopenia. Since T2WI TSE without fat saturation sequence is not in the conventional liver MRI workflow, and T2WI TSE sequence is affected by respiration and time-consuming (about 90-840s).Therefore, FFMA measurement based on edixon sequence is an efficient method without additional scanning and cost reduction in clinical practice,it makes the quantitative assessment of sarcopenia easier to achieve in routine MRI workflow.Conclusion
FFMA of bilateral psoas muscles based on edixon sequence proposed in this paper are highly consistent with those of previous methods based on T2WI TSE sequence. This method is possible to provide quantitative indicators for evaluating sarcopenia for routine clinical MRI examination.Acknowledgements
noneReferences
1. Hsieh YC, Joo SK, Koo BK, Lin HC, Kim W. Muscle alterations are independently associated with significant fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2021;41(3):494-504.
2. Bhanji RA, Narayanan P, Moynagh MR, et al. Differing Impact of Sarcopenia and Frailty in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Liver Transpl. 2019;25(1):14-24.
3. Ebadi M, Montano-Loza AJ. Clinical relevance of skeletal muscle abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis. 2019;51(11):1493-1499.
4. Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31.
5. Beaudart C, McCloskey E, Bruyere O, et al. Sarcopenia in daily practice: assessment and management. BMC Geriatr. 2016;16(1):170.
6. Praktiknjo M, Book M, Luetkens J, et al. Fat-free muscle mass in magnetic resonance imaging predicts acute-on-chronic liver failure and survival in decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2018;67(3):1014-1026.
7. Faron A, Sprinkart AM, Pieper CC, et al. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Outcome prediction with MRI derived fat-free muscle area. Eur J Radiol. 2020;125:108889.