4142
A clinical study using T1-mapping and ECV and late gadolinium enhancement to detect early myocardium involoved in rheumatologic diseases
Ying Liu1, Ping Tian1, Jianmin Zheng1, and Minwen Zheng1
1Xijing Hospital, Xi'an, China
1Xijing Hospital, Xi'an, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Myocardium, Quantitative Imaging
Myocardial involvement is frequently observed in rheumatologic diseases but typically remains subclinical. This study aimed to detect early subclinical cardiac involvement and to investigate characteristics of myocardial involvement by cardiac MR (CMR) imaging. In 75 of 83 patients with rheumatologic diseases, elevated global native T1 and ECV values were observed. Furthermore, 51 patients showed positive segment distribution of late gadolinium enhancement, including subendocardial contrast, intramural contrast and transmural contrast. Thus, T1-mapping, ECV and late gadolinium enhancement could detect early myocardial involvement in rheumatologic diseases patients without overt LV dysfunction.Objective: Rheumatologic diseases are autoimmune
inflammatory disorders including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus
erythematosus (SLE), antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APAS), systemic
sclerosis (SS), ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and others. Rheumatologic
diseases can affect the myocardium, cardiac valves, pericardium, conduction
system and arterial vasculature. Myocardial involvement is frequently
observed in rheumatologic diseases but typically remains subclinical. These
disorders may be due to a variety of mechanisms, including immune
abnormalities, inflammation, small-vessel disease, accelerated atherosclerosis,
and increased coagulability. Cardiac involvement may be clinically
silent or explosively cause considerable morbidity and mortality. This study
aimed to detect early subclinical cardiac involvement and to investigate
characteristics of myocardial involvement by cardiac MR (CMR) imaging.
Methods: From April 2014 to October
2022, a total of 83 patients with rheumatologic diseases performed CMR (Siemens
1.5T Aera) were enrolled in this retrospective study. CMR parameters, including
left ventricular (LV) morphologic and functional parameters, and CMR tissue
characterization imaging parameters, such as native T1, T2, extracellular
volume (ECV) and late gadolinium enhancement, were analyzed.
Results: In
all 83 patients, there were 34cases with rheumatoid arthritis, 22 cases with systemic lupus
erhythematosus, 11 cases with Systemic sclerosis, 7 cases with ankylosing
spondylitis, 6 cases with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and 4 cases with polymyositis. In 75 of
83 patients with Rheumatologic
diseases, elevated global native T1 and ECV values
were observed. Global ECV values were higher in the 75 patients group when
compared with the left 8 patients group (35.62 ± 2.43% vs 24.29 ± 3.90%; P <0.01).
Furthermore, 51 patients showed positive segment distribution of late
gadolinium enhancement, including subendocardial contrast, intramural contrast and transmural contrast. Most of myocardial LGE
(53 of 78 segments)were intramural, patchy or linear, and distributed in the
middle or basal segment of the left ventricle.
Conclusion: T1-mapping,
extracellular volume quantification and late gadolinium enhancement could detect early myocardial
involvement in rheumatologic diseases patients without overt LV dysfunction,
therefore, CMR was a valuable tool for the diagnosis
of cardiac involvement in patients with rheumatologic
diseases.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Multimodality Cardiac Imaging in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Khayata M, Wang TKM, Chan N, Alkharabsheh S, Verma BR, Oliveira GH, Klein AL, Littlejohn E, Xu B.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021 Nov 12:101048. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.101048. 2.Echocardiography in the Assessment of Patients with Rheumatologic Diseases. Al-Mohaissen MA, Chan KL.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2016 Aug;18(8):72. doi: 10.1007/s11886-016-0757-2. 3.Imaging for screening cardiovascular involvement in patients with systemic rheumatologic diseases: more questions than answers. Sade LE, Akdogan A.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Sep 1;20(9):967-978. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jez171.Figures
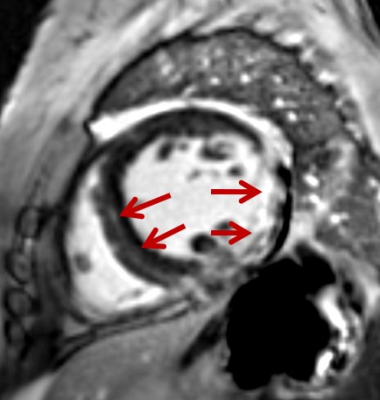
A
47-year-old woman with polymyositis. Late gadolinium enhancement image showed intramural contrast in ventricular septum and transmural
contrast in lateral wall of the left ventricle.
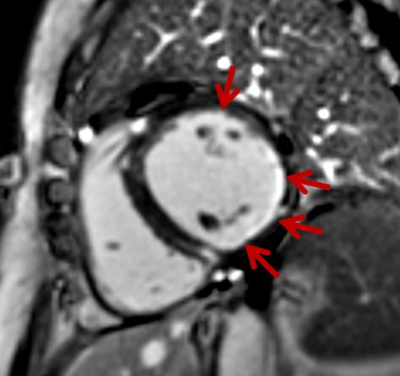
A 56-year-old
woman with systemic lupus
erhythematosus. Late gadolinium enhancement image showed endocardial
contrast in in lateral wall and posterior wall of the left
ventricle.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4142