4137
Relation of N-Terminal Pro–B-Type Natriuretic Peptide to Native T1 at Cardiac MRI1THE FIRST AFFILIATED OF XI'AN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY, XI'AN, China, 2THE FIRST AFFILIATED OF XI'AN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY, XI'an, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Xi'an, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Heart, Body
The purpose of this study was to explore the relationship and closeness between N-Terminal pro–B-Type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and native T1, so as to predict the occurrence of heart failure(HF). This retrospective study included 43 participants. Native T1 value were measured on T1 mapping images. The result reflects native T1 values correlated positively with NT-proBNP, and had high sensitivity and specificity. Native T1 has high predictive performance for HF.Introduction
The neurohormone B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is secreted primarily from the ventricular myocardium in response to increased wall stress in increased left ventricular (LV) filling pressures (e.g., in ventricular volume expansion or pressure overload). Elevated levels of the serum biomarkers BNP and NT-proBNP have been consistently shown to predict mortality and hospitalization in patients with heart failure and coronary or other cardiovascular disease[1]. T1 mapping is a cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging technique used to calculate the T1 time of a certain tissue, previous study showed that Native T1 value is useful in characterization of myocardial tissue[2]. The main purpose of this study is to explore the relationship between NT-proBNP and native T1 value.Methods
This retrospective study from February 2022 to October 2022 included 43 participants (overall mean age 6 standard deviation, 52.0 years±16.6 [range, 16–82 years]; mean age of women, 53.07 years±19.91[range, 16–82 years]; mean age of men, 51.55 years±14.76 [range, 21–74 years]). All participants both underwent NT-proBNP measurements and cardiac MRI at 3.0T system (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare), in which native T1 was measured in the septum of the left ventricle on T1 mapping images(Fig.1). Among these patients, the NT-proBNP level > 450 pg/mL predicts a diagnosis of acute HF[3], 4 patients with the extreme elevation of NT pro-BNP levels (≥3000 pg/ml) were excluded because it is mainly determined by impaired renal function Pearson's correlation coefficient and linear regression were used to calculate the correlation the between NT-proBNP and the Native T1 value. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed to determine the sensitivity and specificity of Native T1 value to detect HF.Results
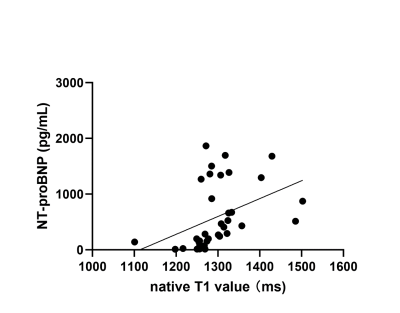
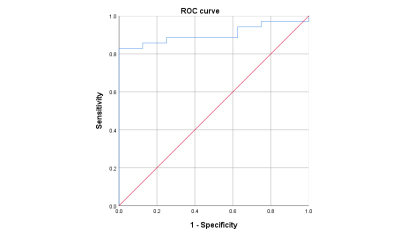
Fig2 shows that the Native T1 values correlated positively with NT-proBNP (r = 0.404; P<0.05). The most accurate cut-off point of native T1 value to predict HF was 1270.275ms (Fig.3), with area under the curve(AUC) of 0.904(95%CI 0.814-0.993), a sensitivity of 82.9%, specificity of 100.0%. Univariable logistic regression results are significant(odds ratio,1.024; 95%CI: 1.001,1.047; P=0.041<0.05).Discussion
NT‐proBNP is an established diagnostic biomarker for the presence of heart failure(HF) reflected in diagnostic algorithms of current HF guidelines[5]. Over the past decades, a large number of publications investigated the prognostic properties of NT‐proBNP for mortality and various cardiovascular events in patients with HF and other cardiovascular (CV) diseases as well as in general elderly populations.Our findings demonstrated a good correlation between NT-proBNP and native T1[6], thus establishing MRI myocardial T1 mapping as a noninvasive tool in the study of prediction of NT‐proBNP. Because of NT-proBNP is closely related to HF and CV diseases. Native T1 is thus regarded as a promising method for the detection of HF and CV diseases without the necessity of administration of gadolinium contrast agent.
Conclusion
Native T1 is closely related to NT-proBNP and has high predictive performance for HF.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Bergler-Klein J. NT-proBNP as a Cornerstone for Prognosis in Valve Disease: All We Need Is Blood. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 14;75(14):1673-1675.
2. Karur GR,et al. Use of Myocardial T1 Mapping at 3.0 T to Differentiate Anderson-Fabry Disease from Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Radiology. 2018 Aug;288(2):398-406.
3. Selby V. Age-stratified NT-proBNP Thresholds Identify Acute Heart Failure[J]. Clinical Cardiology Alert, 2018, 37(4). MLA
4. Cui H, Huo G, Liu L, et al. Association of cardiac and renal function with extreme N-terminal fragment pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels in elderly patients[J]. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2012, 12(1): 1-7.
5. Schmitt W, Rühs H,et al. NT-proBNP Qualifies as a Surrogate for Clinical End Points in Heart Failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Aug;110(2):498-507.
6. Gaspar AS,et al. Myocardial T1 mapping with magnetic resonance imaging - a useful tool to understand the diseased heart. Rev Port Cardiol. 2022 Jan;41(1):61-69.