4135
Dark right ventricular blood pool on myocardial T2 mapping in dilated cardiomyopathy: a predictor of cardiac function1Department of Radiology, Xiangya Hospital Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China, 2Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd., Wuhan, Hubei, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy, Cardiovascular
Although the T2 mapping is mainly used to evaluate myocardial water content, it is also sensitive to blood oxygenation levels, we found that in dilated cardiomyopathy the right ventricular dark right ventricular blood pool may affect the accurate quantification of myocardial T2 values. This study investigated the relationship between right ventricular blood pool on myocardial T2 mapping and indicators of cardiac function.Introduction
Differential blood oxygenation between the left and right heart (ΔSaO2) is an established index of cardiac performance. Increased ΔSaO2 has been shown to predict adverse prognosis in patients with heart failure for whom it is commonly used to guide management[1,2]. T2 is sensitive to blood oxygenation and may be able to detect oxygenation differences[3,4]. To investigate the importance of the dark right ventricular blood pool(RVBP) sign on cardiac MRI (CMR) T2 mapping in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM).Method
The clinical and CMR imaging data of 134 consecutive DCM patients from January 1, 2019 to December 30, 2021 were analyzed retrospectively. T2 values of patients and 29 healthy controls(HC) were measured in the septum, left ventricle(LV) and right ventricle(RV) on T2 mapping imaging(T2-prepared balanced steady-state free-precession sequence), and T2RV/T2LV and T2RV/T2septum were calculated. The function and strain of the ventricles were evaluated using cine imaging.Result
The sign of dark-RVBP and relatively bright RVBP on T2 mapping respectively was found in 34.3% (46/134), 35.8% (48/134) of DCM patients. The value of T2septum in patients with dark-RVBP (39.30±3.62 ms) was significantly higher than that in patients with bright-RVBP (38.18±3.10 ms), relatively bright RVBP (37.92±3.26 ms) and in HC (37.17±1.93 ms). The values of T2RV and T2RV/T2septum in patients with dark-RVBP (47.96±8.11 ms and 1.23±0.21) were significantly lower compared to both those in patients with bright-RVBP (73.78±13.23 ms and 1.93±0.24), relatively bright RVBP (58.58±5.58 ms and 1.55±0.15) and HC (82.21±11.46 ms and 2.21±0.31), all P<0.001. LV and RV global longitudinal stains(GLS) and circumferential strain(GCS) showed significant differences between dark-RVBP, relatively bright RVBP and bright-RVBP groups (all P<0.001). The ratio of T2RV/T2LV in patients with dark-RVBP (0.40±0.07) was significantly lower than that in patients with bright-RVBP (0.63±0.07), relatively bright RVBP (0.50±0.06) and in HC (0.75±0.13) , all P<0.001. The ratios of T2RV/T2septum and T2RV/T2LV were both correlated with the severity of the RV dysfunction (both P<0.001).Conclusion
The presence of dark RVBP on the T2 mapping is a marker for RV dysfunction. The ratios of T2RV/T2septum and T2RV/T2LV may be helpful to conveniently detect the severe RV dysfunction.Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ31131) , China.References
[1] Wen Y, Weinsaft JW, Nguyen TD, et al. Free breathing three-dimensional cardiac quantitative susceptibility mapping for differential cardiac chamber blood oxygenation - initial validation in patients with cardiovascular disease inclusive of direct comparison to invasive catheterization. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2019;21(1):70. Published 2019 Nov 18. doi:10.1186/s12968-019-0579-7
[2] Emrich T, Bordonaro V, Schoepf UJ, et al. Right/Left Ventricular Blood Pool T2 Ratio as an Innovative Cardiac MRI Screening Tool for the Identification of Left-to-Right Shunts in Patients With Right Ventricular Disease [published online ahead of print, 2021 Aug 10. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;10.1002/jmri.27881. doi:10.1002/jmri.27881
[3] Portnoy S, Seed M, Sled JG, Macgowan CK. Non-invasive evaluation of blood oxygen saturation and hematocrit from T1 and T2 relaxation times: In-vitro validation in fetal blood. Magn Reson Med. 2017;78(6):2352-2359. doi:10.1002/mrm.26599
[4] Varghese J, Potter LC, LaFountain R, et al. CMR-based blood oximetry via multi-parametric estimation using multiple T2 measurements. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2017;19(1):88. Published 2017 Nov 9. doi:10.1186/s12968-017-0403-1
Figures
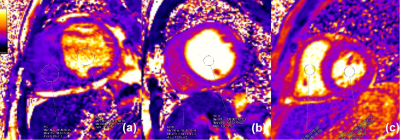
The dark RVBP on T2 maps is mainly caused by the low T2RV correlated with RV disfunction:
(a) A DCM patient with dark RVBP, RVEF: 12%, T2RV: 38.57ms, T2RV/T2septum ratio: 1.06, T2RV/T2LV ratio: 0.40; RVEndoGLS: -8.38%.
(b) A DCM patient with relatively bright RVBP, RVEF: 23%, T2RV: 54.41ms,T2RV/T2septum ratio: 1.32, T2RV/T2LV ratio: 0.51; RVEndoGLS: -24.21%.
(c) A DCM patient with bright RVBP, RVEF: 52%, T2RV: 123.89ms, T2RV/T2septum ratio:3.26, T2RV/T2LV ratio: 0.67. RVEndoGLS: -28.39%.